Abstract
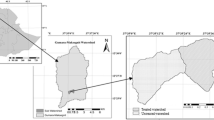
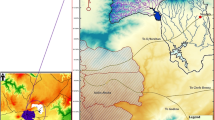
In central-northern Tunisia, a combination of dryness, erratic rainfalls, and the undulating terrain create an erosion-prone environment. Soil and water conservation (SWC) measures have been widely applied to reduce the losses of water and top-soil from agricultural fields and thereby increase crop-production and the rural communities’ livelihoods. However, the impacts of various SWC interventions are interrelated and difficult to predict. The objective of this study is to evaluate the impacts of Bench Terraces (BTs), in combination with small scale reservoirs (Hill Lakes (HLs)), on runoff and erosion using the Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) across semi-arid environments of Tunisia. Development and testing of the BT parameter set was performed using monthly surface runoff and multiple bathymetric sediment measurements obtained from the HLs of small BT-treated catchments (< 20 km2). The established Bench Terraces (BTs) parameter set was applied to the Rmel watershed (675 km2) to eventually test the parameters’ performance at the integrated landscape level. SWAT simulation using the defined BT parameter set and ‘pond’ approaches for the scattered HLs across Rmel produced a ‘good’ modelling performance indicated by NSE values of 0.89 and 0.91 during calibration and validation. A combination of BTs and HLs overall reduced runoff and sediment yield by 33% and 17% respectively. The Rmel case study demonstrates the robustness of the BT parameter-set obtained from small and quasi-homogeneous training catchments. The enhanced knowledge about SWC impacts, and its consideration in modelling (across scales), will eventually support planning and management in Tunisia’s dry and degradation-prone landscapes.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbaspour KC, Yang J, Maximov I, Siber R, Bogner K, Mieleitner J, Zobrist J, Srinivasan R (2007) Modelling hydrology and water quality in the pre-alpine/alpine Thur watershed using SWAT. J Hydrol 333:413–430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2006.09.014
Abbaspour KC, Rouholahnejad E, Vaghefi S, Srinivasan R, Yang H, Kløve B (2015) A continental-scale hydrology and water quality model for Europe: calibration and uncertainty of a high-resolution large-scale SWAT model. J Hydrol 524:733–752
Al Ali Y, Touma J, Zante P, Nasri S, Albergel J (2008) Water and sediment balances of a contour bench terracing system in a semi-arid cultivated zone (El-Gouazine, central Tunisia). Hydrol Sci J 53(4):883–892. https://doi.org/10.1623/hysj.53.4.883
Aouissi J, Benabdallah S, Lili Chabaâne Z, Cudennec C (2018) Valuing scarce observation of rainfall variability with flexible semi-distributed hydrological modelling – mountainous Mediterranean context. Sci Total Environ 643:346–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.06.086
Arnold JG, Srinivasan R, Muttiah RS, Williams JR (1998) Large-area hydrologic modeling and assessment: part I. Model development. J Am Water Resour Assoc 34:73–89
Arnold JG, Moriasi DN, Gassman PW, Abbaspour KC, White MJ, Srinivasan R, Santhi C, Harmel RD, Griensven A, Van-Liew MW, Van Kannan N, Jha MK (2012) SWAT: model use, calibration, and validation. Am Soc Agric Biol Eng 55(4):1491–1508
Attia R, Agrebaoui S, Dridi B, Al Ali Y, Andrieux P, Pepin Y, Touma J, Zante P (2004) Les états de surface et leur caractérisation hydrodynamique par simulation de pluie dans le bassin versant d’El Gouazine. Publication interne-mission IRD de Tunis 57p
Ben Ayed A (1966) Etude pédologique de 1’URD de Zaghouan
Ben Khelifa W, Hermassi T, Strohmeier S, Zucca C, Ziadat F, Boufaroua M, Habaieb H (2017) Parameterization of the effect of bench terraces on runoff and sediment yield by SWAT modeling in a small semi-arid watershed in northern Tunisia. Land Degrad Dev 28:1568–1578. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.2685
Ben Khelifa W, Strohmeier S, Benabdallah S, Habaieb H (2021) Evaluation of bench terracing model parameters transferability for runoff and sediment yield on catchment modelling. J Afr Earth Sci 178:104177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2021.104177
Boufaroua M, Slimani M, Oweis T (2013) Albergel J (2013) Hill Lakes: innovative approach for sustainable rural management in the semi-arid areas in Tunisia. Global NEST J 15(3):366–373
Cherif B, Mizouri M, Khaldi R (1995) Guide de conservation des eaux et du sol, Project PNUD/FAO, TUN/86/020, Tunis, 274p
Collinet J, Zante P (2002) Le ravinement sur marnes gypseuses en Tunisie semi-aride. In: Roose E, Sabir M, De Noni G (eds) Techniques traditionnelles de GCES en milieu méditerranéen. Bulletin - Réseau Erosion, (21), 301–319. La Gestion Traditionnelle de l'Eau, de la Biomasse et de la Fertilité des Sols, Base d'une Nouvelle Approche de la Lutte Antiérosive dans les Montagnes Marocaines : Journées Scientifiques, Salé (MAR), 2002/02/08-09
de la Paix MJ, Lanhai L, ** C, Ahmed S, Varenyam A (2013) Soil degradation and altered flood risk as a consequence of deforestation. Land Degrad Dev 24:478–485. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.1147
Hooke JM (2006) Human impacts on fluvial systems in the Mediterranean re-gion. Geomorphology 79:311–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2006.06.036
Malagò A, Pagliero L, Bouraoui F, Franchini M (2015) Comparing calibrated parameter sets of the SWAT model for the Scandinavian and Iberian peninsulas. Hydrol Sci J 60(5):949–967. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2014.978332
Ministry of Agriculture (2014) Revue sectorielle de l’eau en Tunisie. Bureau de planification et des équilibres hydrauliques. 72p
Mirzabaev, A., J. Wu, J. Evans, F. García-Oliva, I.A.G. Hussein, M.H. Iqbal, J. Kimutai, T. Knowles, F. Meza, D. Nedjraoui, F. Tena, M. Türkeş, R.J. Vázquez, M. Weltz (2019) Desertification. In: Climate Change and Land: an IPCC special report on climate change, desertification, land degradation, sustainable land management, food security, and greenhouse gas fluxes in terrestrial ecosystems [P.R. Shukla, J. Skea, E. CalvoBuendia, V. Masson-Delmotte, H.-O. Pörtner, D.C. Roberts, P. Zhai, R. Slade, S. Connors, R. van Diemen, M. Ferrat, E. Haughey, S. Luz, S. Neogi, M. Pathak, J. Petzold, J. Portugal Pereira, P. Vyas, E. Huntley, K. Kissick, M. Belkacemi, J. Malley, (eds.)]
Moriasi DN, Gitau MW, Pai N, Daggupati P (2015) Hydrologic and water quality models: Performance measures and evaluation criteria. Trans ASABE 58(6):1763–1785. https://doi.org/10.13031/trans.58.10715
Mosbahi M, Benabdallah S (2020) Assessment of land management practices on soil erosion using SWAT model in a Tunisian semi-arid catchment. J Soils Sediments 20:1129–1139. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-019-02443-y
Nash J, Sutcliffe JV (1970) River flow forecasting through conceptual models part I—A discussion of principles. J Hydrol 10(3):282–290
Nasri S (2007) Characteristics and hydrological impacts of a cascade of bench terraces on a semi-arid hillslope in central Tunisia. Hydrol Sci J 52(6):1134–1145. https://doi.org/10.1623/hysj.52.6.1134
National Centers for Environmental Prediction’s (NCEP’s). 2014. Climate forecast system reanalysis (CFSR). SWAT model website
ONAGRI (Observatoire National de l'Agriculture). 2019. Répartition géographique des lacs collinaires. http://www.agridata.tn/dataset/repartition-geographyque-des-lacs-collinaires-en-tunisie/resource/522edfc6-c65d-4159-a879-9ca0f4ea2288
Oweis TY (2017) Rainwater harvesting for restoring degraded dry agro-pastoral ecosystems; a conceptual review of opportunities and constraints in a changing climate. Environ Rev 25:135–149. https://doi.org/10.1139/er-2016-0069
Roose E (2002) Analyse du système des banquettes mécaniques Propositions d'améliorations, de valorisation et d'évolution pour les gouvernorats de Kairouan, Siliana et Zaghouan. Projet GCP/TUN/028/1TA- FAO
Strohmeier S, Haddad M, De Vries J, Nouwakpo S, Al-Hamdan O, Weltz M (2017) Restoring Degraded Rangelands in Jordan: Optimizing Mechanized Micro Water Harvesting using Rangeland Hydrology and Erosion Model (RHEM). Simo &Poch (Eds). Book of Abstracts of the 1st World Conference on Soil and Water Conservation under Global Change-CONSOWA Lleida. June 12–16, 2017.Departament de Medi Ambient iCienciesdel Sol (Udl), Lleida, Spain. ISBN: 978–84–697–2908–3
Talineau JC, Selmi S, Alaya K (1994) Les lacs collinaires en Tunisie semi-aride. Sécheresse 506 n°4 vol. 5: (251- 256).
USDA-SCS (1972) National engineering handbook, Section 4, Hydrology. USDA-Soil Conservation Service, Washington, DC
Verner D, Treguer D, Redwood J, Christensen J, McDonnell R, Elbert C, Konishi Y (2018) Climate variability, drought, and drought management in Tunisia’s agricultural sector. World Bank Group, Washington, DC.
Williams J (1969) Flood routing with variable travel time or variable storage coefficients. Trans ASAE 12(1):100–103
Williams JR, Berndt HD (1977) Sediment yield prediction based on watershed hydrology. Trans ASAE 20:1100–1104
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully thank the General Director of Water Resources (DGRE), General Directorate of Dams and Large Hydraulic Works (DGBTH) and the Regional Commissariat for Agricultural Development of Zaghouan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Fethi Lachaal
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Water Quality, Global Changes and Groundwater Responses
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khelifa, W.B., Strohmeier, S., Benabdallah, S. et al. Modelling the impact of soil and water conservation structures at various scales in Tunisian semi-arid region. Arab J Geosci 14, 2804 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-09086-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-09086-9