Abstract
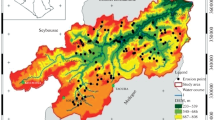
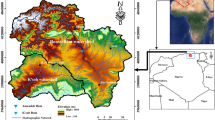
Water erosion is one of the most severe environmental problems, especially in arid and semi-arid regions. It is responsible for soil loss and degradation of ecosystems. This study is interested in map** water erosion hazard (WEH) in the Chaffar Watershed (Southeastern Tunisia), using analytical hierarchy process (AHP) and fuzzy logic modeling. The importance of major factors affecting erosion (field slope, soil lithology, vegetation index, land use, and rainfall) was inspired from a review of the literature, field investigations, and experts’ knowledge. Water erosion conditioning factors and their spatial distributions were evaluated in a geographic information system (GIS). Water erosion hazard maps, simulated by AHP and fuzzy logic, were validated by field observations and Sentinel-2 satellite images. The resulting erosion hazard maps were found to be compatible with the results derived from the Sentinel-2 images. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve validation result shows that, compared to the AHP model (AUC=84.7%), the fuzzy logic model (AUC =90.5%) predicted slightly better water erosion in the Chaffar Watershed. Generally, a moderate hazard of water erosion was found throughout the study watershed. The area characterized by a high to very high risk of water erosion was estimated to be 25% and 32% using fuzzy logic and AHP methods respectively. Highly eroded areas, which are quite limited, require immediate action.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abaoui J, El Ghmari A, El Harti A, Bachaoui EM, Bannari A, El Bouadili A (2005) Cartographie de l’erosion hydrique en zone montagneuse : cas du bassin versant des ait bou goumez,haut atlas, maroc. Estud Geol 61:33–39
Abdellaali T, Elmouden A, Aboulouafa M (2019) Soil erosion risk map** using the analytical hierarchy process (AHP) and geographic information system in the Tifnout-Askaoun Watershed, Southern Morocco. Eur Sci J 15(30):1857–7881. https://doi.org/10.19044/esj.2019.v15n30p338
Ahmad B (2015) Landslide susceptibility map** using multi-criteria evaluation techniques in Chittagong Metropolitan Area. Bangladesh Landslides 12:1077–1095. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-014-0521-x
Akgùn A, Tùrk N (2011) Map** erosion susceptibility by a multivariate statistical method: a case study from the Ayvalık region, NW Turkey. Comput Geosci 37:1515–1524
Albalawneh A, Chang TK, Huang CW, Mazahreh S (2015) Using landscape metrics analysis and analytic hierarchy process to assess water harvesting potential sites in Jordan. Environment 2:415–434
Alvarez Grima M (2000) Neuro-fuzzy modeling in engineering geology: applications to mechanical rock excavation, rock strength estimation, and geological map**. Balkema, Rotterdam
Amouri M (1998) Gestion des ressources en eau de la nappe profonde de Sfax. Tunis : Rapport interne de la Direction Générale de Ressource en Eau
Arabameri A, Rezaei K, Pourghasemi HR, Lee S, Yamani M (2018) GIS-based gully erosion susceptibility map**: a comparison among three data-driven models and AHP knowledge-based technique. Environ Earth Sci 77:628. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7808-5
Arabameri A, Cerda A, Pradhan B, Tiefenbacher JP, Lombardo L, Tien Bui D (2020) A methodological comparison of head-cut based gully erosion susceptibility models: combined use of statistical and artificial intelligence. Geomorphology 359:107136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2020.107136
Arar A, Chenchouni H (2012) How could geomatics promote our knowledge for environmental management in Eastern Algeria. J Environ Sci Technol 5:291–305
Arar A, Chenchouni H (2014) A “simple” geomatics-based approach for assessing water erosion hazard at montane areas. Arab J Geosci 7:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-012-0782-4
Bailly JS, Arnaud M, Puech C (2007) Boosting: a classification method for remote sensing. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 7:232–247
Bayramin I, Dengiz O, Baskan O, Parlak M (2003) Soil erosion risk assessment with ICONA model, case of study: Beypazari Area. Turk J Agric For 27:105–116
Ben Othmen D, Ayadi I, Abida H, Laignel B (2016) Spatial and inter-annual variability of specific sediment yield: case of hillside reservoirs in Central Tunisia. Bull Eng Geol Environ 77:141–152. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-016-0976-1
Bou Kheir R, Girard MC, Shaban A, Khawlie M, Faour G, Darwich T (2001a) Apport de la télédétection pour la modélisation de l’érosion hydrique des sols dans la région côtière du Liban. Télédétection, Vol. 2, n° 2, p. 79-90
Bou Kheir R, Girardlzy M-Cl., Khawlielry M Abadallahlly C (2001b) Erosion hydrique des sols dans les milieux méditerranéens : une revue bibliographique. Etude et Gestion des Sols
Bou Kheir R, Abdallah C, Khawlie M (2008) Assessing soil erosion in Mediterranean karst landscapes of Lebanon using remote sensing and GIS. Eng Geol 99:239–254
Bouamrane A, Derdous O, Dahri N, Tachi S, Boutebba K, Bouziane MT (2020) A comparison of the analytical hierarchy process and the fuzzy logic approach for flood susceptibility map** in a semi-arid ungauged basin (Biskra basin: Algeria). Int J River Basin Manag:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1080/15715124.2020.1830786
Bouaziz R (2010) Les cours d'eau exoréiques de la côte de Sfax : Leur évolution depuis le Pléistocène supérieur. PhD thesis, University of Sfax. P25
Bouaziz M, Wijaya A, Gloaguen R (2009) Gully erosion map** using aster data and drainage network analysis in the main Ethiopian rift. In: Proceeding of the International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IRARSS), Cape Town, South Africa. pp. I13eI16
Bouaziz M, Wijaya A, Gloaguen R (2011) Remote gully erosion map** using ASTER data and geomorphologic analysis in the main ethiopian rift. Geo Spat Inf Sci 14(4):246–254
Boufaroua M, Albergel J (2001) Bilan de l'érosion sur les petits bassins versants des lacs collinaires de la dorsale tunisienne. Soil structure, water and solute Paris: IRD, 88-96 multigr International Symposium in Memory of Michel Rieu, Bondy (FRA)
Boufeldja S, Baba Hamed K, Bouanani A, Belkendil A (2020) Identifcation of zones at risk of erosion by the combination of a digital model and the method of multi-criteria analysis in the arid regions: case of the Bechar Wadi watershed. Appl Water Sci 10:121. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-020-01191-6
Braiki H (2018) Construction d’une démarche participative pouraméliorer la gestion de l’eau et du sol, Une application aux politiques des aménagements de conservation des eaux et des solsen Tunisie Centrale. Thèse de doctorat. Sciences de l’environnement. Montpellier : AgroParisTech, Institut National Agronomique de Tunisie
Chafai A, Brahim N, Slim Shimi N (2020) Map** of water erosion by GIS/RUSLE approach: watershed Aydariver Tunisia study. Arab J Geosci 13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-05774-0
Chaffi S (2013) Impact des aménagements de conservation des eaux et des sols dans le bassin versant chaal-tarfaoui. Mémoire de fin des études effectué à l’école nationale des ingénieurs de Sfax (ENIS)
Chang CL, LO SL, YU SL (2005) The parameter optimization in the inverse distance method by genetic algorithm for estimating precipitation. Environ Monit Assess 117:145–155. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-006-8498-0
CNEA (2008) Étude stratégique sur le développement durable et l’agriculture dans les gouvernorats de Gabes, Sidi Bouzid, Nabeul, le Kef et Bizerte. Tunis: ministère de l’Agriculture, Centre nationales études agricoles
Conforti M, Aucelli PC, Robustelli G, Scarciglia F (2011) Geomorphology and GIS analysis for map** gully erosion susceptibility in the Turbolo stream catchment (Northern Calabria, Italy). Nat Hazards 56:881–898. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-010-9598-2
Conoscenti C, Di Maggio C, Rotigliano E (2008) Soil erosion susceptibility assessment and validation using a geostatistical multivariate approach: a test in Southern Sicily. Nat Hazard 46:287–305
CRDA (2015) Rapport final novembre 2015 Commissariat régional de développement agricole (CRDA), Arrondissement des eaux, 2015
Dahri N, Abida H (2017) Monte Carlo simulation-aided analytical hierarchy process (AHP) for flood susceptibility map** in Gabes Basin (southeastern Tunisia). Environ Earth Sci 76. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6619-4
Das B, Bordoloi R, Thungon LT, Paul A, Pandey PK, Mishra M, Tripathi OP (2020) An integrated approach of GIS, RUSLE and AHP to model soil erosion in West Kameng watershed, Arunachal Pradesh. J Earth Syst Sci 129. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-020-1356-6
Eastman JR (1997) IDRISI for Windows version 2.0. Tutorial exercises. Worcester-MA, Graduate School of Geography, Clark University. p 192
Eckelmann W, Baritz R, Bialousz S, Bielek P, Carre F, Houšková B, Jones RJA, Zupan M (2006) Common criteria for risk area identification according to soil threats. European Soil Bureau Research ReportNo.20, EUR 22185 EN, 94pp
Fan JR, Zhang JH, Zhong XH, Liu SZ, Tao HP (2004) Monitoring of soil erosion and assessment for contribution of sediments to rivers in atypical watershed of the upper Yangtze river basin. Land Degrad Dev 15:411–442
Fehri N (2003) Anthropic action and soil erosion in the Chaâl-Tarfaoui (Sfax plain, Tunisia). Méditerranée 100:87–90. https://doi.org/10.3406/medit.2003.3291
Felfoul M, Snane MH, Mlaouhi A, Megdiche MF (1999) Relationships between the lithology and the gully growth rate of the Oued Maiez watershed in Central Tunisia. Bull Eng Geol Environ 57:285–293
Fernandez C, Wu JQ, DK MC, Stöckle CO (2003) Estimating water erosion and sediment yield with GIS, RUSLE, and SEDD. J Soil Water Conserv 58(3):128–136
Fourati M, Bouaziz R, El Amri A, Majdoub R (2015) Identification des anomalies de fonctionnement des ouvrages de conservation des eaux et du sol du bassin versant Sidi Salah. Identification of the operating anomalies of soil and water conservation works at the watershed Sidi Salah. International Journal of Innovation and Applied Studies. ISSN 2028-9324 Vol. 10
Gao J, Wang H (2018) Temporal analysis on quantitative attribution ofkarst soil erosion: a case study of a peakcluster depression basin in Southwest China. Catena 172:369–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2018.08.035
Gayen A, Saha S (2017) Application of weights-of-evidence (WoE) and evidential belief function (EBF) models for the delineation of soil erosion vulnerable zones: a study on Pathro river basin, Jharkhand, India. Model Earth Syst Environ 3(3):1123–1139
Gumbel EJ (1958) Statistics of extremes. Columbia University Press, New York
Güntner A (2002) Large-scale hydrological modelling in the semi-arid north-east of Brazil. PhD thesis, Faculty of Mathematics and Sciences 31 at the University of Potsdam
Hajjem A (1985) Étude hydrogéologique préliminaire de la nappe de The Chaffar (Sahel Sud de Sfax). Sfax : Commissariat régional de développement agricole (CRDA), Arrondissement des eaux, 1985
Jebari S, Berndtsson R, Bahri A, Boufaroua M (2008) Exceptional rainfall characteristics related to erosion risk in Semiarid Tunisia. The Open Hydrology Journal (1):25–33
Jemai S (2019) Etude de la variabilité pluviométrique et simulation des crues éclair dans le bassin versant de Gabès (Sud-Est Tunisien). PhD thesis, University of Sfax p 155
Kachouri S, Achour H, Abida H, Bouaziz S (2014) Soil erosion hazard map** using analytic hierarchy process and logistic regression: a case study of Haffouz watershed. Central Tunisia. Arab J Geosci 8:4257–4268. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1464-1
Kefi M, Yoshino K, Setiawan Y, Zayani K, Boufaroua M (2011) Assessment of the effects of vegetation on soil erosion risk by water: a case of study of the Batta watershed in Tunisia. Environ Earth Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-010-0891-x
Khemiri K, Jebari S (2021) Évaluation de l’érosion hydrique dans des bassins versants de lazone semi-aride tunisienne avec les modèles RUSLE et MUSLE couplés à un Système d’information géographique. Cahiers Agricultures 30(2):7. https://doi.org/10.1051/cagri/2020048
Kia BMB, Pirasteh S, Pradhan B, Mahmud AR, Sulaiman WNA, Moradi A (2012) An artificial neural network model for flood simulation using GIS: Johor River Basin, Malaysia. Environ Earth Sci 67:251–264
Knight EJ, Kvaran G (2004) Landsat 8 operational land imager design, characterization and performance. Remote Sens 6:10286–10305
Kornejady A, Heidari K, Nakhavali M (2015) Assessment of landslide susceptibility, semi-quantitative risk and management in the Ilam dam basin, Ilam, Iran. Environ Resour Res 3(1). https://doi.org/10.22069/ijerr.2015.2563
Ligonja PJ, Shrestha RP (2015) Soil erosion assessment in kondoa eroded area in Tanzania using universal soil loss equation, geographic information systems and socioeconomic approach. Land Degrad Dev 26(4):367–379
Majdoub R, Fourati M, Sahtout N, Ben Ammar A, Bouaziz R (2016) Contribution d’un Système d’Information Géographique à l’évaluation de la dégradation du sol et des aménagements anti-érosifs au niveau du bassin versant de Oued Agareb (Contribution of Geographic Information Systems to the evaluation land degradation and anti-erosion management in the watershed of Oued Agareb). Journal of Materials and Environmental Science. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/308900220
Malczewski J (1999) GIS and multicriteria decision analysis. Wiley, Brisbane
Manadhar R, Odeh IO, Ancev T (2009) Improving the accuracy of land use and land cover classification of Landsat data using post-classification Enhancement [J]. Remote Sens 1:330–344
Manavalan R (2017) SAR image analysis techniques for flood area map** -literature survey. Earth Sci Inf 10:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-016-0274-2
Mihi A, Benarfa N, Arar A (2019) Assessing and map** water erosion-prone areas in northeastern Algeria using analytic hierarchy process, USLE/RUSLE equation, GIS, and remote sensing. Applied Geomatics. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12518.019.00289.0
MuratSaç M, İçhedef M (2015) Application of 137Cs technique for evaluation of erosion and deposition rates within cultivated fields of Salihli region, Western Turkey. J Radiat Res Appl Sc 8:477–482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrras.2015.04.001
Neji N (2016) Étude comparative de l’envasement des retenues collinaires ElGonna et Bouladhieb (Sfax). Mastère de recherche au sein de la faculté des sciences de Sfax
Pourghasemi HR, Pradhan B, Gokceoglu C, Mohammadi M, Moradi HR (2012) Application of weights-of evidence and certainty factor models and their comparison in landslide susceptibility map** at Haraz watershed, Iran. Arab J Geosci 6:2351–2365. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-012-0532-7
Pradhan B (2010a) Remote sensing and GIS-based landslide hazard analysis and cross-validation using multivariate logistic regression model onthree test areas in Malaysia. Adv Space Res 45(10):1244–1256
Pradhan B (2010b) Landslide Susceptibility map** of a catchment area usingfrequency ratio, fuzzy logic and multivariate logistic regression approaches. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 38(2):301–320. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-010-0020-z
Pradhan B, Lee S (2009) Landslide risk analysis using artificial neural network model focusing on different training sites. Int J Phys Sci 3(11):1–15
Pradhan B, Lee S (2010) Delineation of landslide hazard areas on Penang Island, Malaysia, by using frequency ratio, logistic regression, and artificial neural network models. Environ Earth Sci 60:1037–1054
Rahmati O, Nazari Samani A, Mahdavi M, Pourghasemi HR, Zeinivand H (2014) Groundwater potential map** at Kurdistan region of Iran using analytic hierarchy process and GIS. Arab J Geosci 8:7059–7071. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1668-4
Rahmati O, Haghizadeh A, Pourghasemi HR, Noormohamadi F (2016) Gully erosion susceptibility map**: the role of GIS-based bivariate statistical models and their comparison. Nat Hazards 82:1231–1258. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-016-2239-7
Rahmati O, Kornejady A, Samadi M, Deo RC, Conoscenti C, Lombardo L, Dayal K, Taghizadeh-Mehrjardi R, Pourghasemi HR, Kumar S (2019) PMT: New analytical framework for automated evaluation of geo-environmental modelling approaches. Sci Total Environ 664:296–311
Razavi-Termeha SV, Sadeghi-Niarakia A, Choib S-M (2020) Gully erosion susceptibility map** using artificial intelligence and statistical models. Geomatics Nat Hazards Risk 11:821–844. https://doi.org/10.1080/19475705.2020.1753824
Renard KG, Foster GR, Weesies GA, McCool DK, Yoder DC (1997) Predicting soil erosion by water: a guide to conservation planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation. Agricultural Handbook No. 703. US Department of Agriculture: 404 pp
Roose E (1984) Erosion et conservation des sols : place de la recherche française en régions tempérées et tropicales. In: Livre jubilaire du cinquantenaire AFES 1934-1984. AFES, Paris, pp 321–333
Roy J, Saha S (2019) GIS-based gully erosion susceptibility evaluation using frequency ratio, cosine amplitude, and logistic regression ensembled with fuzzy logic in Hinglo River Basin, India. Remote Sensing Applications: Society and Environment 15:100247
Saaty T (1977) A scaling method for priorities in hierarchical structures. J Math Psychol 15:234–281
Saaty T (1980) The analytic hierarchy process. McGraw-Hill, New York
Saaty T (2000) Decision making for leaders: the analytical hierarchy process for decisions in a complex world. RWS Publications, Pittsburgh
Saha S, Gayen A, Pourghasemi HR, Tiefenbacher JP (2019) Identification of soil erosion-susceptible areas using Fuzzy logic and analytical hierarchy process modeling in an agricultural watershed of Burdwan district, India. Environ Earth Sci 78:649. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8658-5
Shahabi H, Khezri S, Bin Ahmad B, Hashim M (2014) Landslide susceptibility map** at central Zab basin, Iran: a comparison between analytical hierarchy process, frequency ratio, and logistic regression models. Catena 115:55–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2013.11.014
Simonneaux V, Cheggour A, Deschamps C, Mouillot F, Cerdan O, Le Bissonnais Y (2015) Land use and climate change effects on soil erosion in a semi-arid mountainous watershed (High Atlas, Morocco). Journal of Arid Environments, Elsevier
Smith SJ, Williams JR, Menzel RG, Coleman GA (1984) Prediction of sediment yield from Southern Plains grasslands with the Modified Universal Soil Loss Equation. J Range Manag 37(4):295–297
Tafreshi GM, Nakhaei M, Lak R (2019) Land subsidence risk assessment using GIS Fuzzy logic spatial modeling in Varamin aquifer, Iran. GeoJournal 86:1203–1223. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10708-019-10129-8
Tairi A, Elmouden A, Aboulouafa M (2019) Soil erosion risk map** using the analytical hierarchy process (AHP) and geographic information system in the Tifnout-Askaoun Watershed, Southern Morocco. European Scientific Journal October 2019 edition Vol.15, No.30 ISSN: 1857 – 7881 (Print) e - ISSN 1857- 7431
Vrieling A (2006) Satellite remote sensing for water erosion assessment: a review. Catena 65:2–1
Vrieling A, and Rodrigues SC. (2004) Erosion assessment in the Brazilian Cerrados using multi-temporal SAR imagery, Proceedings of the 2004 Envisat & ERS Symposium. SP-572. ESA, Salzburg, Austria
Vrieling A, Sterk G, Beaulieu N (2002) Erosion risk map**: a methodological case study in the Colombian Eastern Plains. J Soil Water Conserv 57(3):158–163
Wang J, Rich PM, Price KP, Kettle WD (2004) Relations between NDVI and tree productivity in the central great plains. Int J Remote Sens 25:3127–3138
White CS (1986) Volatile and water-soluble inhibitors of nitrogen mineralization and nitrification in a ponderosa pine ecosystem. Biol Fertil Soils 2:97–104
Wischmeier WH, Smith DD (1958) Rainfall energy and its relationship to soil loss. EOS Trans Am Geophys Union 39:285. https://doi.org/10.1029/TR039i002p00285
Wu Q, Wang M (2007) A framework for risk assessment on soil erosion by water using an integrated and systematic approach. J Hydrol 337:11–21
Yang X, **e X, Liu DL, Ji F, Wang L (2015) Spatial interpolation of daily rainfall data for local climate impact assessment over Greater Sydney Region. Adv Meteorol 2015:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/563629
Zadeh LA (1988) Fuzzy logic. Computer 21:83–93
Zhang X, Drake N, Wainwright J (2002) Scaling land surface parameters for global-scale soil erosion estimation. Water Resour Res 38(9):19(1)–19(9)
Ziadat FM, Taimeh AY (2013) Effect of rainfall intensity, slope, land use and antecedent soil moisture on soil erosion in an arid environment. Land Degrad Dev 24:582–590
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the Regional Office of the Ministry of Agriculture (CRDA) of Sfax for their contribution to the fieldwork.
Funding
This work was funded by the Tunisian Ministry of High Education and Scientific Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Amjad Kallel
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Neji, N., Ayed, R.B. & Abida, H. Water erosion hazard map** using analytic hierarchy process (AHP) and fuzzy logic modeling: a case study of the Chaffar Watershed (Southeastern Tunisia). Arab J Geosci 14, 1208 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-07602-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-07602-5