Abstract
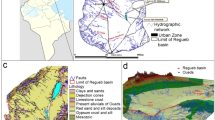
Siwa Oasis is a tectonically induced depression located in the northern part of the Western Desert. It is intensively characterized by salt mineralization and salt pans. This paper aims to investigate the evaluation of salts from the near-surface underground water in Siwa Oasis to assess the quality of salt for several uses. The study results show that the precipitated minerals identified by XRD are halite, sylvite, gypsum, carnallite, magnesium sulfate hydrate, sodium chlorate, and bischofite. More than 90% of NaCl present in the solution precipitate alone in the first stages. Analysis of heavy metals and trace elements indicated that all the salt samples were found at very low concentrations below the allowable limits. The study indicates that the type of Siwa salt is a very good quality salt, which needs a very simple refining process to meet and exceed the international standards of edible (food) salt.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdallah A (2007) Assessment of salt weathering in Siwa Oasis (The Western Desert of Egypt). Bull De la Soc De Geog De Egypt 80:66–83
Abdel-Motelib A, Taher A, El Manawi AH (2015) Composition and diagenesis of ancient Shali city buildings of evaporite stones (kerchief), Siwa Oasis, Egypt. Quat Int 369:78–85
Abdel Rahman MA, Metwaly MM, Shalaby A (2019) Quantitative assessment of soil saline degradation using remote sensing indices in Siwa Oasis. Remote Sens Appl Soc Environ 13:53–60
Baumé A (1768) Contribution a létude des origins de la drouerie pharmaceutique et de lindustrie du sel ammoniac en France Par René Davy PP1955-150
Elnaggar A, El-Hamidi K, Mousa M, Albakry M (2017) Map** soil salinity and evaluation of water quality in Siwa Oasis using GIS. J Soil Sci Agric Eng 8(1):9–19
Elsaied HE, El-Karim MSA, Wassel MA (2017) Biodiversity of uncultured bacteria in hypersaline lakes, Siwa Oasis, Egypt, as determined by polymerase chain reaction and denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (PCR-DGGE) of 16S rRNA gene phylotypes. Int J Genet Mol Biol 9(2):8–15
Gad A, Abd El Bakey SM and Sakr S (2020) Concentrations of heavy metals and associated human health risk in unrefined salts of inland hypersaline lakes, Egypt. Int J Environ Anal Chem, pp.1-14.
Gindy AR, El-Askary (1969) Stratigraphy, structure, and origin of Siwa depression, Western Desert of Egypt. AAPG Bull 53(3):603–625
Madani AA (2005) Soil salinity detection and monitoring using Landsat data: a case study from Siwa Oasis, Egypt. GISci Remote Sens 42(2):171–181
Masoud A, Koike K (2006a) Tectonic architecture through Landsat-7 ETM+/SRTM DEM-derived lineaments and relationship to the hydrogeologic setting in Siwa region, NW Egypt. J Afr Earth Sci 45(4-5):467–477
Masoud AA, Koike K (2006b) Arid land salinization detected by remotely-sensed landcover changes: a case study in the Siwa region, NW Egypt. J Arid Environ 66(1):151–167
Mueller D, Pliett H, Kuhlmann KP, Wenzel F (2002) Structural preservation of the Temple of the Oracle in Siwa Oasis, Egypt. Conserv Manag Archaeol Sites 5(4):215–230
Rovero L, Tonietti U, Fratini F, Rescic S (2009) The salt architecture in Siwa Oasis–Egypt (XII–XX centuries). Constr Build Mater 23(7):2492–2503
Safaa H, Esam I (2018) Detection and evaluation of groundwater in Siwa Oasis, Egypt using hydrogeochemical and remote sensing data analysis: Safaa and Esam. Water Environ Res 90(5):465–478
Soetan KO, Olaiya CO, Oyewole OE (2010) The importance of mineral elements for humans, domestic animals and plants: a review. Afr J Food Sci 4(5):200–222
Soylak M, Peker DSK, Turkoglu O (2008) Heavy metal contents of refined and unrefined table salts from Turkey, Egypt and Greece. Environ Monit Assess 143(1):267–272
Taher MH, Yossif H (2017) Change detection of land cover and salt affected soils at Siwa Oasis, Egypt. Alexandaria Science Exchange Journal 38(3):446–462
Weather Spark (2016) https://weatherspark.com/y/91744/Average-Weather-in-Siwa-Oasis-Egypt-Year-Round#Section-Clouds .
Zaher EM (2010) Geological and environmental studies on wadi el natrun solar salinas. Damietta University, M.SC. thesis
Zaher MA, Saibi H, Mansour K, Khalil A, Soliman M (2018) Geothermal exploration using airborne gravity and magnetic data at Siwa Oasis, Western Desert, Egypt. Renew Sust Energ Rev 82:3824–3832
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Zakaria Hamimi
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Current Advances in Geological Research of Egypt
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khalil, M., Elharairey, M., Atta, E. et al. Evaluation of salts in salt pans, Siwa Oasis, Egypt. Arab J Geosci 14, 770 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-07060-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-07060-z