Abstract
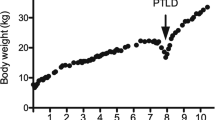
Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder (PTLD) is a rare complication of solid organ transplantation as the result of immunosuppressant medications. Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) has been implicated in most of these cases, specifically with B-cell predominant lymphoma. This case report describes a 24-year-old female who presented with recurrent GI bleed within 6 months post-orthostatic heart transplant. Endoscopic evaluations including video capsule study, push enteroscopy, and colonoscopy revealed multiple ulcerated lesions in duodenum, jejunum, and colon secondary to Epstein–Barr Virus-associated monomorphic PTLD. Despite continuation of rituximab after discharge, she returned to the hospital for recurrent GI bleed requiring additional endoscopic intervention. PTLD is a devastating disease of the post-transplant population. Due to a high risk of recurrent GI bleeding, patients with PTLD may benefit from careful monitoring by gastroenterology as an outpatient with a low threshold for repeat endoscopic evaluation despite being on immunotherapy or chemotherapy.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Mansour Z, Nelson BP, Evens AM. Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease (PTLD): risk factors, diagnosis, and current treatment strategies. Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2013;8:173–83.
Green M, Michaels MG. Epstein-Barr virus infection and posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder. Am J Transplant. 2013;13(Suppl 3):41–54 (quiz).
Patek B, Strahotin C. Early onset post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder presenting with diarrhea post-orthotopic liver transplant treated successfully with single rituximab agent. Cureus. 2019;11: e6200.
Inayat F, Hassan GU, Tayyab GUN, et al. Post-transplantation lymphoproliferative disorder with gastrointestinal involvement. Ann Gastroenterol. 2018;31:248–51.
Younes BS, Ament ME, McDiarmid SV, et al. The involvement of the gastrointestinal tract in posttransplant lymphoproliferative disease in pediatric liver transplantation. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1999;28:380–5.
Mukhtar MS, Wolman SL. Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder as a cause of oesophageal ulceration and stricture: case report and literature review. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2021;8:e000602.
Brahmbhatt AN, Baah NYO. Embolization for acute gastrointestinal hemorrhage secondary to post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder. Radiol Case Rep. 2020;15:396–9.
Siegel A, Boike J, Trivedi I, et al. Posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder of the small bowel as an unexpected cause of iron deficiency anemia decades after heart transplantation. ACG Case Rep J. 2017;4: e86.
Gandhi S, Behling E, Behrens D, et al. Late-onset posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorders after solid organ transplantation in adults: a case series and review of the literature. Case Rep Transplant. 2020;2020:8247308.
Chia SC, Chau YP, Tan YM. Late-onset post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease presenting as massive occult gastrointestinal haemorrhage. Singap Med J. 2008;49:e117–20.
San-Juan R, Comoli P, Caillard S, et al. Epstein-Barr virus-related post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder in solid organ transplant recipients. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2014;20(Suppl 7):109–18.
Walti LN, Mugglin C, Sidler D, et al. Association of antiviral prophylaxis and rituximab use with posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorders (PTLDs): a nationwide cohort study. Am J Transplant. 2021;21:2532–42.
Van Besien K, Bachier-Rodriguez L, Satlin M, et al. Prophylactic rituximab prevents EBV PTLD in haplo-cord transplant recipients at high risk. Leuk Lymphoma. 2019;60:1693–6.
Shahid S, Prockop SE. Epstein-Barr virus-associated post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorders: beyond chemotherapy treatment. Cancer Drug Resist. 2021;4:646–64.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mitsuhashi, S., Chalikonda, D., Nazir, B. et al. Recurrent bleeding duodenal and colonic ulcers due to post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder. Clin J Gastroenterol 16, 39–42 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12328-022-01718-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12328-022-01718-1