Abstract
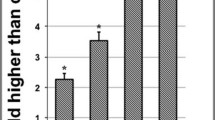
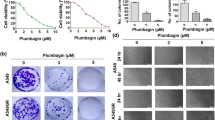
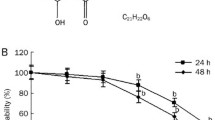
Plumbagin is a naturally-derived phytochemical which exhibits promising medicinal properties, including anticancer activities. In the present study, the anticancer potential of plumbagin has been demonstrated in lung cancer cells by targeting reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the intrinsic mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Plumbagin showed impressive cytotoxic, anti-proliferative, and anti-migratory activities with IC50 3.10 ± 0.5 μM and 4.10 ± 0.5 μM in A549 and NCI-H522 cells, respectively. Plumbagin treatment significantly reduced the size of A549 tumor spheroids in a concentration-dependent manner. Plumbagin enhanced ROS production and arrested lung cancer cells in S and G2/M phase. Expression of antioxidant genes such as glutathione S-transferase P1 and superoxide dismutase-2 were found to be upregulated with plumbagin treatment in A549 cells. Plumbagin induced dissipation in mitochondrial membrane potential and affected the expression of intrinsic apoptotic pathway proteins. Increased expression of cytochrome c promotes the activation of pro-apoptotic protein Bax with decreased expression of anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2. Further, plumbagin activated the mitochondrial downstream pathway protein caspase-9 and caspase-3 leading to apoptosis of A549 cells. Collectively, plumbagin could be a promising future phytotherapeutic candidate for lung cancer treatment via targeting intrinsic mitochondrial apoptotic pathway and ROS.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afsar T, Trembley JH, Salomon CE, Razak S, Khan MR, Ahmed K (2016) Growth inhibition and apoptosis in cancer cells induced by polyphenolic compounds of Acacia hydaspica: involvement of multiple signal transduction pathways. Sci Rep 6(1):23077. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep23077
Asadi-Samani M, Farkhad NK, Mahmoudian-Sani MR, Shirzad H (2019) Antioxidants as a double-edged sword in the treatment of cancer antioxidants. IntechOpen. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.85468
Benien P, Swami A (2014) 3D tumor models: history, advances and future perspectives. Future Oncol 10(7):1311–1327. https://doi.org/10.2217/fon.13.274
Cao YY, Yu J, Liu TT, Yang KX, Yang LY, Chen Q, Shi F, Hao JJ, Cai Y, Wang MR (2018) Plumbagin inhibits the proliferation and survival of esophageal cancer cells by blocking STAT3-PLK1-AKT signaling. Cell Death Dis 9(2):17. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-017-0068-6
Czabotar PE, Lessene G, Strasser A, Adams JM (2014) Control of apoptosis by the BCL-2 protein family: implications for physiology and therapy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 15(1):49. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3722
Edmondson R, Broglie JJ, Adcock AF, Yang L (2014) Three-dimensional cell culture systems and their applications in drug discovery and cell-based biosensors. Assay Drug Dev Technol 12(4):207–218. https://doi.org/10.1089/adt.2014.573
Eldhose B, Gunawan M, Rahman M, Latha MS, Notario V (2014) Plumbagin reduces human colon cancer cell survival by inducing cell cycle arrest and mitochondria-mediated apoptosis. Int J Oncol 45(5):1913–1920. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2014.2592
Heavey S, Godwin P, Baird AM, Barr MP, Umezawa K, Cuffe S, Finn SP, O’Byrne KJ, Gately K (2014) Strategic targeting of the PI3K–NFκB axis in cisplatin-resistant NSCLC. Cancer Biol Ther 15(10):1367–1377. https://doi.org/10.4161/cbt.29841
Hua P, Sun M, Zhang G, Zhang Y, Tian X, Li X, Cui R, Zhang X (2015) Cepharanthine induces apoptosis through reactive oxygen species and mitochondrial dysfunction in human non-small-cell lung cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 460(2):136–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.02.131
Huang TC, Chiu PR, Chang WT, Hsieh BS, Huang YC, Cheng HL, Huang LW, Hu YC, Chang KL (2018) Epirubicin induces apoptosis in osteoblasts through death-receptor and mitochondrial pathways. Apoptosis 23(3–4):226–236. https://doi.org/10.1007/s1049
Inbaraj JJ, Chignell CF (2004) Cytotoxic action of juglone and plumbagin: a mechanistic study using HaCaT keratinocytes. Chem Res Toxicol 17(1):55–62. https://doi.org/10.1021/tx034132s
Jamal MS, Parveen S, Beg MA, Suhail M, Chaudhary AG, Damanhouri GA, Abuzenadah AM, Rehan M (2014) Anticancer compound plumbagin and its molecular targets: a structural insight into the inhibitory mechanisms using computational approaches. PLoS ONE 9(2):e87309. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0087309
** Y, Fan JT, Gu XL, Zhang LY, Han J, Du SH, Zhang AX (2017) Neuroprotective activity of cerebrosides from Typhonium giganteum by regulating caspase-3 and Bax/Bcl-2 signaling pathways in PC12 cells. J Nat Prod 80(6):1734–1741. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.6b00954
Kalainayakan SP, FitzGerald KE, Konduri PC, Vidal C, Zhang L (2018) Essential roles of mitochondrial and heme function in lung cancer bioenergetics and tumorigenesis. Cell Biosci 8(1):56. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13578-018-0257-8
Katt ME, Placone AL, Wong AD, Xu ZS, Searson PC (2016) In vitro tumor models: advantages, disadvantages, variables, and selecting the right platform. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 4:12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2016.00012
Kim B, Srivastava SK, Kim SH (2015) Caspase-9 as a therapeutic target for treating cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets 19(1):113–127. https://doi.org/10.1517/14728222.2014.961425
Lee JH, Won YS, Park KH, Lee MK, Tachibana H, Yamada K, Seo KI (2012) Celastrol inhibits growth and induces apoptotic cell death in melanoma cells via the activation ROS-dependent mitochondrial pathway and the suppression of PI3K/AKT signaling. Apoptosis 17(12):1275–1286. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-012-0767-5
Letai A (2017) Apoptosis and cancer. Annu Rev Cancer Biol 1:275–294. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-cancerbio-050216-121933
Maheswari U, Ghosh K, Sadras SR (2018) Licarin A induces cell death by activation of autophagy and apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Apoptosis 23(3–4):210–225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-018-1449-8
Miller KD, Siegel RL, Lin CC, Mariotto AB, Kramer JL, Rowland JH, Stein KD, Alteri R, Jemal A (2016) Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2016. CA A Cancer J Clini 66(4):271–289. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21349
Pajaniradje S, Mohankumar K, Pamidimukkala R, Subramanian S, Rajagopalan R (2014) Antiproliferative and apoptotic effects of Sesbania grandiflora leaves in human cancer cells. BioMed Res Int 2014:474953. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/474953
Qiu JX, Zhou ZW, He ZX, Zhao RJ, Zhang X, Yang L, Zhou SF, Mao ZF (2015) Plumbagin elicits differential proteomic responses mainly involving cell cycle, apoptosis, autophagy, and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition pathways in human prostate cancer PC-3 and DU145 cells. Drug Des Dev Ther 2015(9):349–417. https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S71677
Tilak JC, Adhikari S, Devasagayam TP (2004) Antioxidant properties of Plumbago zeylanica, an Indian medicinal plant and its active ingredient, plumbagin. Redox Rep 9(4):219–227. https://doi.org/10.1179/135100004225005976
Tripathi SK, Biswal BK (2018) Pterospermum acerifolium (L.) wild bark extract induces anticarcinogenic effect in human cancer cells through mitochondrial-mediated ROS generation. Mol Biol Rep 45(6):2283–2294. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-018-4390-6
Tripathi SK, Panda M, Biswal BK (2019) Emerging role of plumbagin: cytotoxic potential and pharmaceutical relevance towards cancer therapy. Food Chem Toxicol 125:566–582. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2019.01.018
Wang F, Wang Q, Zhou ZW, Yu SN, Pan ST, He ZX, Zhang X, Wang D, Yang YX, Yang T (2015) Plumbagin induces cell cycle arrest and autophagy and suppresses epithelial to mesenchymal transition involving PI3K/Akt/mTOR-mediated pathway in human pancreatic cancer cells. Drug Des Dev Ther 2015(9):537–560. https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S73689
Wang JP, Hsieh CH, Liu CY, Lin KH, Wu PT, Chen KM, Fang K (2017) Reactive oxygen species-driven mitochondrial injury induces apoptosis by teroxirone in human non-small cell lung cancer cells. Oncol Lett 14(3):3503–3509. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2017.6586
Xu KH, Lu DP (2010) Plumbagin induces ROS-mediated apoptosis in human promyelocytic leukemia cells in vivo. Leukemia Res 34(5):658–665. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.leukres.2009.08.017
Xu TP, Shen H, Liu LX, Shu YQ (2013) Plumbagin from Plumbago Zeylanica L induces apoptosis in human non-small cell lung cancer cell lines through NF-κB inactivation. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 14(4):2325–2331. https://doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2013.14.4.2325
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tripathi, S.K., Rengasamy, K.R.R. & Biswal, B.K. Plumbagin engenders apoptosis in lung cancer cells via caspase-9 activation and targeting mitochondrial-mediated ROS induction. Arch. Pharm. Res. 43, 242–256 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-020-01221-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-020-01221-6