Abstract
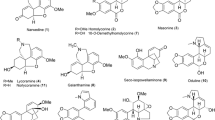
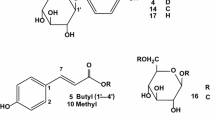
Edible insects have been reported to produce metabolites showing various pharmacological activities, recently emerging as rich sources of health functional food. In particular, the larvae of Protaetia brevitarsis seulensis (Kolbe) have been used as traditional Korean medicines for treating diverse diseases, such as breast cancer, inflammatory disease, hepatic cancer, liver cirrhosis, and hepatitis. However, only few chemical investigations were reported on the insect larvae. Therefore, the aim of this study was to discover and identify biologically active chemical components of the larvae of P. brevitarsis seulensis. As a result, a quinoxaline-derived alkaloid (1) was isolated, which was not reported previously from natural sources. In addition, other related compounds (2, 4–10, 15, 16) were also encountered for the first time from the larvae. The structures of all the isolated compounds were established mainly by analysis of HRESIMS, NMR, and electronic circular dichroism data. Compound 5 exhibited inhibition of tyrosinase with IC50 value of 44.8 µM.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alves AV, San**ez-Argandoña EJ, Linzmeier AM, Cardoso CA, Macedo ML (2016) Food value of mealworm grown on Acrocomia aculeata pulp flour. PLoS ONE 11:e0151275
Chang TS (2009) An updated review of tyrosinase inhibitors. Int J Mol Sci 10:2440–2475
Chu JP, Choi WH (2014) Antibacterial composition comprising Hermetia illucens larval extracts or fractions thereof. Patent 1,014,281,570,000
Crumeyrolle-Arias M, Tournaire MC, Cane A, Launay JM, Barritault D, Medvedev A (2004) Inhibition of brain mitochondrial monoamine oxidases by the endogenous compound 5-hydroxyoxindole. Biochem Pharmacol 67:977–979
Engel MS, Grimaldi DA (2004) New light shed on the oldest insect. Nature 427:627–630
Feng Y, Chen XM, Zhao M, He Z, Sun L, Wang CY, Ding WF (2017) Edible insects in China: utilization and prospects. Insect Sci. doi:10.1111/1744-7917.12449
Gao Y, Yu L, Peng C, Li Z, Guo Y (2010) Diketopiperazines from two strains of South China Sea sponge-associated microorganisms. Biochem Syst Ecol 38:931–934
He R, Wang B, Wakimoto T, Wang M, Zhub L, Abe I (2013) Cyclodipepitides from metagenomic library of a Japanese marine sponge. J Braz Chem Sac 24:1926–1932
Huang R, Zhou X, Xu T, Yang X, Liu Y (2010) Diketopiperazines from marine organisms. Chem Biodivers 7:2809–2829
Kim DH, Kim HH, Kim HJ, Jung HG, Yu JM, Lee ES, Cho YH, Kim DI, An BJ (2014) CopA3 peptide prevents ultraviolet-induced inhibition of type-I procollagen and induction of matrix metalloproteinase-1 in human skin fibroblasts. Molecules 19:6407–6414
Kim JH, Yoon JY, Yang SY, Choi SK, Kwon SJ, Cho IS, Jeong MH, Ho Kim Y, Choi GS (2016) Tyrosinase inhibitory components from Aloe vera and their antiviral activity. J Enzym Inhib Med Chem 25:1–6
Lai ZQ, Liu WH, Ip SP, Liao HJ, Yi YY, Qin Z, Lai XP, Su ZR, Lin ZX (2014) Seven alkaloids from Picrasma quassioides and their cytotoxic activities. Chem Nat Compd 50:884–888
Lee SH, Son HU (2013) An extract from Lycorma delicatula for anti-allergic inflammation or treatment to allergic inflammation-related diseases and a cosmetical or pharmaceutical composition comprising the same. Patent 1,015,126,310,000
Lee JH, Kim IW, Shin YP, Park HJ, Lee YS, Lee IH, Kim MA, Yun EY, Nam SH, Ahn MY, Kang D, Hwang JS (2015) Scolopendrasin I: a novel antimicrobial peptide isolated from the centipede Scolopendra subspinipes mutilans. J Ind Entomol 31:14–19
Lee W, Lee J, Kulkarni R, Kim MA, Hwang JS, Na M, Bae JS (2016) Antithrombotic and antiplatelet activities of small-molecule alkaloids from Scolopendra subspinipes mutilans. Sci Rep 6:21956
Lee J, Lee W, Kim MA, Hwang JS, Na M, Bae JS (2017) Inhibition of platelet aggregation and thrombosis by indole alkaloids isolated from the edible insect Protaetia brevitarsis seulensis (Kolbe). J Cell Mol Med 21:1217–1227
Li G, Yu K, Li F, Xu K, Li J, He S, Cao S, Tan G (2014) Anticancer potential of Hericium erinaceus extracts against human gastrointestinal cancers. J Ethnopharmacol 153:521–530
Mehnaz S, Saleem RS, Yameen B, Pianet I, Schnakenburg G, Pietraszkiewicz H, Valeriote F, Josten M, Sahl HG, Franzblau SG, Gross H (2013) Lahorenoic acids A-C, ortho-dialkyl-substituted aromatic acids from the biocontrol strain Pseudomonas aurantiaca PB-St2. J Nat Prod 76:135–141
MFDS (2016) Expand recognition of raw materials for edible insect food. IOP. http://www.mfds.go.kr/index.do?mid=675&seq=33818&sitecode=1&cmd=v. Accessed 11 Oct 2016
Noda N, Kubota S, Miyata Y, Miyahara K (2000) Optically active N-acetyldopamine dimer of the crude drug “Zentai”, the cast-off shell of the Cicada, Cryptotympana sp. Chem Pharm Bull 48:1749–1752
Pan X, Matsumoto M, Nishimoto Y, Ogihara E, Zhang J, Ukiya M, Tokuda H, Koike K, Akihisa M, Akihisa T (2014) Cytotoxic and nitric oxide production-inhibitory activities of limonoids and other compounds from the leaves and bark of Melia azedarach. Chem Biodivers 11:1121–1139
Shi YN, Tu ZC, Wang XL, Yan YM, Fang P, Zuo ZL, Hou B, Yang TH, Cheng YX (2014) Bioactive compounds from the insect Aspongopus chinensis. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 24:5164–51649
Suh HJ, Kang SC (2012) Antioxidant activity of aqueous methanol extracts of Protaetia brevitarsis Lewis (Coleoptera: Scarabaedia) at different growth stages. Nat Prod Res 39:150–517
Takaya Y, Furukawa T, Miura S, Akutagawa T, Hotta Y, Ishikawa N, Niwa M (2007) Antioxidant constituents in distillation residue of Awamori spirits. J Agric Food Chem 55:75–79
Tang JJ, Luo Q, Di L, Zhang L, Lu Q, Hou B, Zuo ZL, **a HL, Ma XJ, Cheng YX (2015) Compounds from the Chinese black ant (Polyrhachis dives) and NMR behavior of the isomers with formamide group. J Asian Nat Prod Res 17:20–26
Xu MZ, Lee WS, Han JM, Oh HW, Park DS, Tian GR, Jeong TS, Park HY (2006) Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of N-acetyldopamine dimers from Periostracum Cicadae. Bioorg Med Chem 14:7826–7834
Yan YM, Ai J, Shi YN, Zuo ZL, Hou B, Luo J, Cheng YX (2014) (±)-Aspongamide A, an N-acetyldopamine trimer isolated from the insect Aspongopus chinensis, is an inhibitor of p-Smad3. Org Lett 16:532–535
Yan YM, Li LJ, Qin XC, Lu Q, Tu ZC, Cheng YX (2015) Compounds from the insect Blaps japanensis with COX-1 and COX-2 inhibitory activities. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 25:2469–2472
Yeo H, Kim Youn, Kim M, Yun EY, Hwang JS, Jeong WS, Jun M (2013) Fatty acid composition and volatile constituents of Protaetia brevitarsis Larvae. Prev Nutr Food Sci 18:150–156
Yoo YC, Shin BH, Hong JH, Lee J, Chee HY, Song KS, Lee KB (2007) Isolation of fatty acids with anticancer activity from Protaetia brevitarsis larvae. Arch Pharm Res 30:361–365
Yun EY, Hwang JS, Goo TW, Kim MA, Choi YC, Jun M, Kim JY, Yeo HL (2014) Composition for preventing or treating dementia comprising Tenebrio molitor extract. Patent 1,014,045,660,000
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a grant (PJ010840) from the Agenda program, Rural Development Administration.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
12272_2017_942_MOESM1_ESM.doc
Supplementary Material 1 HR-ESI-MS, 1H NMR, 13C NMR, HSQC, and HMBC spectra for compounds 1 – 16 can be found in the online version (DOC 3560 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, J., Hwang, I.H., Kim, J.H. et al. Quinoxaline-, dopamine-, and amino acid-derived metabolites from the edible insect Protaetia brevitarsis seulensis . Arch. Pharm. Res. 40, 1064–1070 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-017-0942-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-017-0942-x