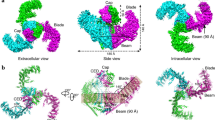
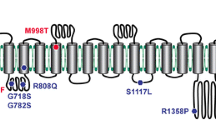
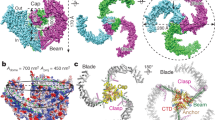
Abstract
Mechanosensitive channels mediate touch, hearing, proprioception, and blood pressure regulation. Piezo proteins, including Piezo1 and Piezo2, represent a new class of mechanosensitive channels that have been reported to play key roles in most, if not all, of these modalities. The structural architecture and molecular mechanisms by which Piezos act as mechanosensitive channels, however, remain mysterious. Two new studies have now provided critical insights into the atomic structure and molecular basis of the ion permeation and mechano-gating properties of the Piezo1 channel.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ranade SS, Syeda R, Patapoutian A. Mechanically Activated Ion Channels. Neuron 2015, 87: 1162–1179.
Coste B, Mathur J, Schmidt M, Earley TJ, Ranade S, Petrus MJ, et al. Piezo1 and Piezo2 are essential components of distinct mechanically activated cation channels. Science 2010, 330: 55–60.
**ao R, Xu XZ. Mechanosensitive channels: in touch with Piezo. Curr Biol 2010, 20: R936–938.
Coste B, Murthy SE, Mathur J, Schmidt M, Mechioukhi Y, Delmas P, et al. Piezo1 ion channel pore properties are dictated by C-terminal region. Nat Commun 2015, 6: 7223.
Coste B, **ao B, Santos JS, Syeda R, Grandl J, Spencer KS, et al. Piezo proteins are pore-forming subunits of mechanically activated channels. Nature 2012, 483: 176–181.
Ge J, Li W, Zhao Q, Li N, Chen M, Zhi P, et al. Architecture of the mammalian mechanosensitive Piezo1 channel. Nature 2015, 527: 64–69.
Zhao Q, Wu K, Geng J, Chi S, Wang Y, Zhi P, et al. Ion Permeation and Mechanotransduction Mechanisms of Mechanosensitive Piezo Channels. Neuron 2016, 89: 1248–1263.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, X.Z.S. Demystifying Mechanosensitive Piezo Ion Channels. Neurosci. Bull. 32, 307–309 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-016-0033-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-016-0033-x