Abstract
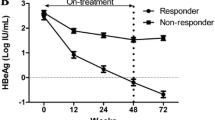
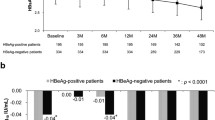
Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) loss is an ideal treatment endpoint for patients with chronic hepatitis B (CHB). We investigated the predictive value of on-treatment HBsAg levels for HBsAg loss in hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg)-negative CHB patients who received 120-week PEG-IFNα-2a treatment. Serum HBV DNA, HBsAg, and anti-HBs levels were assayed at baseline and every 3 months during the treatment. Of 81 patients, 12 achieved HBsAg loss, 20 achieved HBsAg < 100 IU/mL, and 49 maintained HBsAg ≥ 100 IU/mL. HBsAg loss rate was only 3.7% at 48 weeks, while it reached to 11.1% and 14.8% after treatment of 96 weeks and 120 weeks. The cutoff HBsAg levels at 12 weeks predicting HBsAg loss at 96 weeks and 120 weeks of treatment were 400 IU/mL and 750 IU/mL, with AUC 0.725 and 0.722, positive predictive value (PPV) 29.41% and 30.56%, and negative predictive value (NPV) 93.75% and 97.78%, respectively. The cutoff HBsAg levels at 24 weeks predicting HBsAg loss at 96 weeks and 120 weeks of treatment were 174 IU/mL and 236 IU/mL respectively, with AUC 0.925 and 0.922, PPV 40.0% and 46.15%, and both NPV 100%. The predictive ability of the cutoff HBsAg levels at 24 weeks was better than that at 12 weeks for HBsAg loss at either 96 or 120 weeks (χ2 = 3.880, P = 0.049 and χ2 = 4.412, P = 0.036). These results indicate that extended therapy is critical to HBsAg loss in HBeAg-negative CHB patients during PEG-IFN treatment, and the HBsAg level at 24 weeks can be used to predict HBsAg loss during tailoring PEG-IFN therapy.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brunetto MR, Oliveri F, Colombatto P, Moriconi F, Ciccorossi P, Coco B, Romagnoli V, Cherubini B, Moscato G, Maina AM, Cavallone D, Bonino F (2010) Hepatitis B surface antigen serum levels help to distinguish active from inactive hepatitis B virus genotype D carriers. Gastroenterology 139:483–490
Chan HL, Wong VW, Tse AM, Tse CH, Chim AM, Chan H, Wong GL, Sung JJ (2007) Serum hepatitis B surface antigen quantitation can reflect hepatitis B virus in the liver and predict treatment response. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 5:1462–1468
Chan HL, Wong VW, Wong GL, Tse CH, Chan HY, Sung JJ (2010) A longitudinal study on the natural history of serum hepatitis B surface antigen changes in chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 52:1232–1241
Chan HL, Wong GL, Chim AM, Chan HY, Chu SH, Wong VW (2011a) Prediction of off-treatment response to lamivudine by serum hepatitis B surface antigen quantification in hepatitis B e antigen-negative patients. Antivir Ther 16:1249–1257
Chan HL, Wong GL, Tse CH, Chan HY, Wong VW (2011b) Viral determinants of hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance in hepatitis B e antigen-negative chronic hepatitis B patients. J Infect Dis 204:408–414
Chen YC, Sheen IS, Chu CM, Liaw YF (2002) Prognosis following spontaneous HBsAg seroclearance in chronic hepatitis B patients with or without concurrent infection. Gastroenterology 123:1084–1089
Chen CJ, Yang HI, Su J, Jun S, Jen CL, You SL, Lu SN, Huang GT, Iloeje UH, REVEAL-HBV Study Group (2006) Risk of hepatocellular carcinoma across a biological gradient of serum hepatitis B virus DNA level. JAMA 295:65–73
Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association (2019) The Guidelines of Prevention and Treatment for Chronic Hepatitis B (2019 Version). Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 27:938–961
Chu CM, Liaw YF (2007) Spontaneous relapse of hepatitis in inactive HBsAg carriers. Hep Intl 1:311–315
Chu CJ, Hussain M, Lok AS (2002) Quantitative serum HBV DNA levels during different stages of chronic hepatitis B infection. Hepatology 36:1408–1415
Cornberg M, Wong WS, Locarnini S, Brunetto M, Janssen HLA, Chan HL (2017) The role of quantitative hepatitis B surface antigen revisited. J Hepatol 66:398–411
European Association for the Study of the Liver. European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL 2017 (2017) Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol 67:370–398
Giersch K, Lena A, Tassilo V, Maura D, Marc L (2017) Serum HBV pgRNA as a clinical marker for cccDNA activity. J Hepatol 66:460–462
Gill U, Micco L, Li L, Peppa D, Ushiro-Lumb I, Foster G, Maini M, Kennedy P (2011) Pegylated interferon alpha modulates innate immunity in eag positive chronic hepatitis B and determines changes in HBSag quantification. J Hepatol 54:S32
Hadziyannis SJ, Papatheodoridis GV (2006) Hepatitis B e antigen-negative chronic hepatitis B: natural history and treatment. Semin Liver Dis 26:130–141
Hsu YS, Chien RN, Yeh CT, Sheen IS, Chiou HY, Chu CM, Liaw YF (2002) Long-term outcome after spontaneous HBeAg seroconversion in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 35:1522–1527
Hu P, Shang J, Zhang W, Gong G, Li Y, Chen X, Jiang J, **e Q, Dou X, Sun Y, Li Y, Liu Y, Liu G, Mao D, Chi X, Tang H, Li X, **e Y, Chen X, Jiang J, Zhao P, Hou J, Gao Z, Fan H, Ding J, Zhang D, Ren H (2018) HBsAg Loss with peg-interferon alfa-2a in hepatitis B patients with partial response to nucleos(t)ide analog: new Switch Study. J Clin Transl Hepatol Mar 28:25–34
Hui CK, Lau GK (2006) Current issues and future directions in treatment. Semin Liver Dis 26:192–197
Koffas A, Dolman GE, Kennedy PT (2018) Hepatitis B virus reactivation in patients treated with immunosuppressive drugs: a practical guide for clinicians. Clin Med (Lond) 18:212–218
Lampertico P, Viganò M, Di Costanzo GG, Sagnelli E, Fasano M, Di Marco V, Boninsegna S, Farci P, Fargion S, Giuberti T, Iannacone C, Regep L, Massetto B, Facchetti F, Colombo M, PegBe Liver Study Group (2013) Randomised study comparing 48 and 96 weeks peginterferon α-2a therapy in genotype D HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B. Gut 62:290–298
Lau GK, Piratvisuth T, Luo KX, Marcellin P, Thongsawat S, Cooksley G, Gane E, Fried MW, Chow WC, Paik SW, Chang WY, Berg T, Flisiak R, McCloud P, Pluck N, Peginterferon Alfa-2a HBeAg-Positive Chronic Hepatitis B Study Group (2005) Peginterferon Alfa-2a, lamivudine, and the combination for HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B. N Engl J Med 352:2682–2695
Li GJ, Yu YQ, Chen SL, Fan P, Shao LY, Chen JZ, Li CS, Yi B, Chen WC, **e SY, Mao XN, Zou HH, Zhang WH (2015) Sequential combination therapy with pegylated interferon leads to loss of hepatitis B surface antigen and hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg) seroconversion in HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B patients receiving long-term entecavir treatment. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 7:4121–4128
Li MH, Zhang L, Qu XJ, Lu Y, Shen G, Wu SL, Chang M, Liu RY, Hu LP, Li ZZ, Hua WH, Song SJ, **e Y (2017) Kinetics of hepatitis B surface antigen level in chronic hepatitis b patients who achieved hepatitis B surface antigen loss during pegylated interferon alpha-2a treatment. Chin Med J (Engl) 130:559–565
Li MH, Yi W, Zhang L, Lu Y, Lu HH, Shen G, Wu SL, Hao HX, Gao YJ, Chang M, Liu YR, Hu LP, Cao WH, Chen QQ, Li JN, Wan G, **e Y (2019) Predictors of sustained functional cure in HBeAg-negative patients achieving HBsAg seroclearance with interferon-alfa-based therapy. J Viral Hepat 26(Suppl. 1):32–41
Liu J, Yang HI, Lee MH, Jen CL, Batrla-Utermann R, Lu SN, Wang LY, You SL, Chen CJ (2016) Serum Levels of Hepatitis B Surface Antigen and DNA Can Predict Inactive Carriers With Low Risk of Disease Progression. Hepatology 64:381–389
Mak LY, Seto WK, Fung J, Yuen MF (2019) Novel developments of hepatitis B: treatment goals, agents and monitoring tools. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol 12:109–120
Manesis EK, Papatheodoridis GV, Hadziyannis E (2010) significance of serum HBsAg levels for the definition of the inactive hepatitis B carrier state. Hepatology 52(SUPPL):560A
Ning Q, Han M, Sun Y, Jiang J, Tan D, Hou J, Tang H, Sheng J, Zhao M (2014) Switching from entecavir to PegIFN alfa-2a in patients with HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B: a randomised open-label trial (OSST trial). J Hepatol 61:777–784
Papatheodoridis GV (2011) Treatment of HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B patients with nucleos(t)ide analogues. Liver Int 31:95–103
Marcellin P, Lau GK, Bonino F, Farci P, Hadziyannis S, ** R, Lu ZM, Piratvisuth T, Germanidis G, Yurdaydin C, Diago M, Gurel S, Lai MY, Button P, Pluck N, Peginterferon Alfa-2a HBeAg-Negative Chronic Hepatitis B Study Group (2004) Peginterferon alfa-2a alone, lamivudine alone, and the two in combination in patients with HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B. N Engl J Med 351:1206–1217
Marcellin P, Bonino F, Lau GK, Farci P, Yurdaydin C, Piratvisuth T, ** R, Gurel S, Lu ZM, Wu J, Popescu M, Hadziyannis S, Peginterferon alfa-2a in HBeAgnegative Chronic Hepatitis B Study Group (2009) Sustained response of hepatitis B e antigen-negative patients 3 years after treatment with peginterferon alpha-2a. Gastroenterology 136:2169–2179
Patrick M, Lau George KK, Ferruccio B, Patrizia F, Stephanos H, ** Rui L, Zhi-Meng PT, Georgios G, Cihan Y, Moises D, Selim G, Ming-Yang L, Peter B, Nigel P (2004) Peginterferon Alfa-2a HBeAg-Negative Chronic Hepatitis B Study Group. Peginterferon alfa-2a alone, lamivudine alone, and the two in combination in patients with HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B. N Engl J Med 351:1206–1217
Patrick M, Ferruccio B, Lau George KK, Patrizia F, Cihan Y, Teerha P, Rui J, Gurel Selim L, Jian Z-MW, Matei P, Stephanos H, Peginterferon alfa-2a in HBeAg-negative Chronic Hepatitis B Study Group (2009) Sustained response of hepatitis B e antigen-negative patients 3 years after treatment with peginterferon alpha-2a. Gastroenterology 136:2169–2179
Rijckborst V, ter Borg MJ, Cakaloglu Y, Ferenci P, Tabak F, Akdogan M, Simon K, Raptopoulou-Gigi M, Ormeci N, Zondervan PE, Verhey E, van Vuuren AJ, Hansen BE, Janssen HL, PARC Study Group (2010) A randomized trial of peginterferon alpha-2a with or without ribavirin for HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B. Am J Gastroenterol 105:1762–1769
Seto WK, Lo YR, Pawlotsky JM, Yuen MF (2018) Chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Lancet 392:2313–2324
Simonetti J, Bulkow L, McMahon BJ, Homan C, Snowball M, Negus S, Williams J et al (2010) Clearance of hepatitis B surface antigen and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in a cohort chronically infected with hepatitis B virus. Hepatology 51:1531–1537
Sonneveld MJ, Hansen BE, Piratvisuth T, Jia JD, Zeuzem S, Gane E, Liaw YF, **e Q, Heathcote EJ, Chan HL, Janssen HL (2013) Response-guided peginterferon therapy in hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B using serum hepatitis B surface antigen levels. Hepatology 58:872e80
Terrault NA, Lok ASF, McMahon BJ, Chang KM, Hwang JP, Jonas MM, Brown RS Jr, Bzowej NH, Wong JB (2018) Update on prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of chronic hepatitis B: AASLD 2018 hepatitis B guidance. Hepatology 67:1560–1599
WHO. Global hepatitis report 2017. Geneva. https://www.who.int/hepatitis/publications/global-hepatitisreport2017/en/. Accessed 4 April 2019
**e Y, Yi W, Zhang L, Lu Y, Hao HX, Gao YJ, Ran CP, Lu HH, Chen QQ, Shen G, Wu SL, Chang M, Hu LP, Liu RY, Sun L, Wan G, Li MH (2019) Evaluation of a logistic regression model for predicting liver necroinflammation in hepatitis B e antigen-negative chronic hepatitis B patients with normal and minimally increased alanine aminotransferase levels. J Viral Hepat 26(Suppl. 1):42–49
Yim HJ, Lok AS (2006) Natural history of chronic hepatitis B virus infection: what we knew in 1981 and what we know in 2005. Hepatology 43:S173–S181
Acknowledgements
This study was funded in part by the Bei**g Hospitals Authority of Hospitals Clinical Medicine Development of Special Funding Support (XMLX 201706), the National Science and Technology Major Project of China (2017ZX10203202-003, 2017ZX10201201-001-006, and 2017ZX10201201-002-006), Bei**g Science and Technology Commission (D161100002716002), and the Digestive Medical Coordinated Development Center of Bei**g Hospitals Authority (XXZ0302 and XXT28).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YX designed the study. ML, LZ, YL, QC, HL, FS and ZZ performed the data collection and patient followup. YX and GW conducted data analysis. ML and LZ drafted the manuscript. LZ and YX revised and finalized the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Animal and Human Rights Statement
The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Bei**g Ditan Hospital (Approval number: JDL2013-031-07). Written informed consent was obtained from all patients, and the study was registered at clinicaltrials.gov (Clinical Trials. gov ID: NCT02387684).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, M., Zhang, L., Lu, Y. et al. Early Serum HBsAg Kinetics as Predictor of HBsAg Loss in Patients with HBeAg-Negative Chronic Hepatitis B after Treatment with Pegylated Interferonα-2a. Virol. Sin. 36, 311–320 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12250-020-00290-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12250-020-00290-7