Abstract
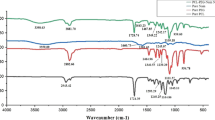
In this study, we developed optimal multifunctional electrospun wound dressings possessing an antibacterial activity and rich in iron, a vital trace element for cell growth. Therefore, synthetic ferric oxide nanoparticles (α-Fe2O3 NPs) were ultrasonically dispersed into preheated gelatin-glycerol solution. A variety of techniques (X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared (FTIR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), differential thermal analysis (DTA), in-vitro swelling-degradation studies and antibacterial tests) were used to characterize the electrospun mats. The results highlight that α-Fe2O3 NPs could be successfully dispersed into the electrospun gelatin nanofibers. The electrospun ferric oxide-gelatin-glycerol nanofibrous mats revealed free beads nanofibers with appropriated swelling-degradation behavior. It was observed that addition of α-Fe2O3 NPs enhanced the antibacterial activity of electrospun mats against positive and negative bacteria.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. J. Meinel, O. Germershaus, T. Luhmann, H. P. Merkle, and L. Meinel, Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm., 81, 1 (2012).
D. Kai, S. S. Liow, and X. J. Loh, Mater. Sci. Eng. CMater. Biol. Appl., 45, 659 (2014).
J. Boateng and O. Catanzano, J. Pharm. Sci., 104, 3653 (2015).
L. I. F. Moura, A. M. A. Dias, E. Carvalho, and H. C. de Sousa, Acta Biomater., 9, 7093 (2013).
M. Tummalapalli, M. Berthet, B. Verrier, B. L. Deopura, M. S. Alam, and B. Gupta, Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 82, 104 (2016).
K. Jalaja, P. R. A. Kumar, T. Dey, S. C. Kundu, and N. R. James, Carbohydr. Polym., 114, 467 (2014).
Y. Z. Zhang, J. Venugopal, Z.-M. Huang, C. T. Lim, and S. Ramakrishnam, Polymer, 47, 2911 (2006).
H. Li, J. Hu, H. Yang, L. Tao, and L. Zhu, J. Controlled Release, 213, e40 (2015).
G. Speit, S. Neuss, P. Schütz, M. Fröhler-Keller, and O. Schmid, Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen., 649, 146 (2008).
N. Latorre, J. F. Silvestre, and A. F. Monteagudo, Actas Dermo-Sifiliogr., 102, 86 (2011).
J. Biscarat, B. Galea, J. Sanchez, and C. Pochat-Bohatier, Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 74, 5 (2015).
V. Švachová, L. Vojtová, D. Pavlinák, L. Vojtek, V. Sedláková, P. Hyršl, M. Alberti, J. Jaroš, A. Hampl, and J. Jancár, Mater. Sci. Eng. C-Mater. Biol. Appl., 67, 493 (2016).
J. Liang, Q. **a, S. Wang, J. Li, Q. Huang, and R. D. Ludescher, Food Hydrocoll., 44, 94 (2015).
N. Riquelme, P. Díaz-Calderón, J. Enrione, and S. Matiacevich, Food Chem., 175, 478 (2015).
D. F. Pisani, C. D. K. Bottema, C. Butori, C. Dani, and C. A. Dechesne, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 396, 767 (2010).
E. De Giglio, M. A. Bonifacio, S. Cometa, D. Vona, M. Mattioli-Belmonte, M. Dicarlo, E. Ceci, V. Fino, S. R. Cicco, and G. M. Farinola, Colloids Surf. B-Biointerfaces, 136, 600 (2015).
F. D. Halstead, M. Rauf, A. Bamford, C. M. Wearn, J. R. B. Bishop, R. Burt, A. P. Fraise, N. S. Moiemen, B. A. Oppenheim, and M. A. Webber, Burns, 41, 1683 (2015).
M. M. Soltan Dallal, R. Safdari, H. Emadi Koochak, S. Sharifi-Yazdi, M. R. Akhoondinasab, M. R. Pourmand, A. Hadayatpour, and M. K. Sharifi-Yazdi, Burns, 42, 578 (2016).
T. Lam, P. Pouliot, P. K. Avti, F. Lesage, and A. K. Kakkar, Adv. Colloid Interface Sci., 199-200, 95 (2013).
M. Mahmoudi, S. Sant, B. Wang, S. Laurent, and T. Sen, Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev., 63, 24 (2011).
D. J. R. Lane, A. M. Merlot, M. L. Huang, D. Bae, P. J. Jansson, S. Sahni, D. S. Kalinowski, and D. R. Richardson, BBA-Mol. Cell Res., 1853, 1130 (2015).
B. Silva and P. Faustino, BBA-Mol. Basis Dis., 1852, 1347 (2015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morsy, R., Hosny, M., Reicha, F. et al. Development and characterization of multifunctional electrospun ferric oxide-gelatin-glycerol nanofibrous mat for wound dressing applications. Fibers Polym 17, 2014–2019 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-016-6915-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-016-6915-8