Abstract
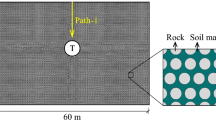
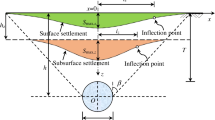
Complex ground conditions or support failures during tunnel construction can lead to high ground loss, which may cause damage to surrounding structures. In this paper, a series model tests are carried out in order to clarify tunnelling-induced ground deformation at high ground loss conditions. The model tunnel in this test is shallowly buried in loose sand and the tunnel volume loss (Vl,t) is set from 4% to 10%. The Vl,t is controlled by a water-filling-drainage system and the ground deformation is monitored by digital image correlation (DIC) system. The results show that the Peck-Gaussian function can be used to fit the settlement data well, and the increase of Vl,t has no significant effect on the width of the settlement trough, while the horizontal displacement can be described by modified empirical method. The width of influence aera caused by tunnelling decreases linearly with depth, and the width near the tunnel crown is about 78% of that on the surface. For loose sand ground, it is the shear band rather than the soil arch that dominates the ground deformation. Furthermore, excavation leads to a volume contraction of the ground, which suggests predictions based on tunnel over-excavation trend to underestimate the ground deformation, and that should be taken seriously in consideration of the safety of the engineering project. This study can provide a better understanding of ground deformation induced by tunnelling.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A :
-
Fitting parameter of horizontal displacement
- B cs :
-
Boundary coefficient determined by ground slope
- C :
-
Cover depth of the tunnel crown
- c :
-
Cohesion
- C u :
-
Coefficient of uniformity
- C c :
-
Coefficient of curvature
- D :
-
Diameter of the tunnel
- D r :
-
Relative density of the sand
- i :
-
Distance to the inflection point of the settlement trough
- K :
-
Through width parameter
- K s :
-
Through width parameter on surface
- n :
-
Length ration of model to prototype
- R 2 :
-
Coefficient of determination
- S max :
-
Maximum settlement
- S hmax :
-
Maximum horizontal displacement
- S(x):
-
Fitting equation of settlement
- S h(x):
-
Fitting equation of horizontal displacement
- V l,t :
-
Tunnel volume loss
- V l,s :
-
Soil volume loss
- x :
-
Horizontal offset distance from tunnel centreline
- Z :
-
Depth measured from ground surface
- Z t :
-
Depth of tunnel axis
- α :
-
Modification parameter of model to prototype
- γ :
-
Shear strain
- ε xx :
-
Horizontal strain
- ε yy :
-
Vertical strain
- ε v :
-
Volumetric strain
- φ :
-
Friction angle of the sand
- ∂i/∂z :
-
Slope of parameter i against depth
References
Ahmed M, Iskander M (2011) Analysis of tunneling-induced ground movements using transparent soil models. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering 137(5):525–535, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000456
Ahmed M, Iskander M (2012) Evaluation of tunnel face stability by transparent soil models. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology 27(1):101–110, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2011.08.001
Boldini D, Losacco N, Franza A, DeJong MJ, Xu J, Marshall A (2021) Tunneling-induced deformation of bare frame structures on sand: Numerical study of building deformations. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering 147(11):04021116, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0002627
Celestino TB, Gomes RAMP, Bortolucci AA (2000) Errors in ground distortions due to settlement trough adjustment. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology 15(1):97–100, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0886-7798(99)00054-1
Cording EJ (1991) Control of ground movements around tunnels in soil. Proceedings of 9th Pan-American conference on soil mechanics and foundation engineering, Valparaiso, Chile, 2195–2244
Dyer MR, Hutchinson MT, Evans N (1996) Sudden valley sewer: A case history. Proceedings of the international symposium on geotechnical aspects of underground construction in soft ground, London, UK, 671–676
Franza A, Marshall AM, Zhou B (2019) Greenfield tunnelling in sands: The effects of soil density and relative depth. Géotechnique 69:297–307, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1680/jgeot.17.p.091
Farrell R, Mair R, Sciotti A, Pigorini A (2014) Building response to tunnelling. Soils and Foundations 54(3):269–279, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sandf.2014.04.003
Fuglsang LD, Ovesen NK (1988) The application of the theory of modelling to centrifuge studies. In: Craig WH, James RG, Schofield AN Centrifuges in Soil Mechanics. CRC Press, London, UK, 116–136, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1201/9781003079378-13
Idinger G, Aklik P, Wu W, Borja RI (2011) Centrifuge model test on the face stability of shallow tunnel. Acta Geotechnica 6(2):105–117, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-011-0139-2
Khatami H, Deng A, Jaksa M (2021) Map** soil arching-induced shear and volumetric strains in dense sands. Transportation Geotechnics 2021:100547, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trgeo.2021.100547
Li Y, Yang S, Tang X, Ding Y, Zhang Q (2020) Experimental investigation of the deformation and failure behavior of a tunnel excavated in mixed strata using transparent soft rock. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering 24(1):1–13, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-020-0072-8
Lu DC, Lin QT, Tian Y, Du XL, Gong QM (2020) Formula for predicting ground settlement induced by tunnelling based on gaussian function. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology 103:103443, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2020.103443
Lu H, Shi JW, Wang Y, Wang R (2019) Centrifuge modeling of tunneling-induced ground surface settlement in sand. Underground Space 4(4):302–309, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.undsp.2019.03.007
Mair RJ, Taylor RN (1997) Bored tunnelling in the urban environment. International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering, Hamburg 4:2353–2385
Mair RJ, Taylor RN, Bracegirdle A (1993) Subsurface settlement profiles above tunnels in clays. Geótechnique 43:315–320, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.1993.43.2.315
Marshall AM, Farrell R, Klar A, Mair R (2012) Tunnels in sands: The effect of size, depth and volume loss on greenfield displacements. Géotechnique 62(5):385–399, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.10.P.047
Marshall AM, Klar A, Mair RJ (2010) Tunneling beneath buried pipes: View of soil strain and its effect on pipeline behavior. Journal of Geotechnical & Geoenvironmental Engineering 136(12):1664–1672, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000390
Moussaei N, Khosravi MH, Hossaini MF (2019) Physical modeling of tunnel induced displacement in sandy grounds. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology 90:19–27, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2019.04.022
O’Reilly MP, New BM (1982) Settlements above tunnels in the United Kingdom: Their magnitude and prediction. Tunnelling 82, Proceedings of the 3rd international symposium, Brighton, UK, 173–181
Peck RB (1969) Deep excavations and tunnelling in soft ground. Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Mexico City, 225–290
Rankin WJ (1988) Ground movements resulting from urban tunnelling: Predictions and effects. Geological Society 5:79–92, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1144/GSL.ENG.1988.005.01.06
Ritter S, Giardina G, Dejong MJ, Mair RJ (2017) Influence of building characteristics on tunnelling-induced ground movements. Géotechnique 67:926–937, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1680/jgeot.SIP17.P.138
Sohaei H, Hajihassani M, Namazi E, Marto A (2020) Experimental study of surface failure induced by tunnel construction in sand. Engineering Failure Analysis 118:104897, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2020.104897
Son M, Cording EJ (2005) Estimation of building damage due to excavation-induced ground movements. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering 131:162–177, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2005)131:2(162)
Standing JR, Selemetas D (2013) Greenfield ground response to EPBM tunnelling in London Clay. Géotechnique 63:989–1007, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.12.P.154
Sugiyama T, Hagiwar T, Nomoto T, Nomotom M, Ano Y, Mair RJ, Bolton MD, Soga K (1999) Observations of ground movements during tunnel construction by slurry shield method at the docklands light railway Lewisham extension-east London. Soils and Foundations 39(3):99–112, DOI: https://doi.org/10.3208/sandf.39.3_99
Sun JZ, Liu JY (2014) Visualization of tunnelling-induced ground movement in transparent sand. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology 40236–240, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2013.10.009
Vorster TEB, Klar A, Soga K, Mair RJ (2005) Estimating the effects of tunneling on existing pipelines. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering 131(11):1399–1410, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2005)131:11(1399)
Wong RCK, Kaiser PK (1991) Performance Assessment of Tunnels in Cohesionless Soils. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering 117(12): 1880–1901, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9410(1991)117:12(1880)
Wood DM (2004) Geotechnical modelling. CRC Press, Boca Raton, USA, 246–252, DOI: https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203477977
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support for this study provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41831290), and the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (Grant No. LGJ22D020001 & No. LQ20E080006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, T., Wang, R., Xue, F. et al. Experimental Investigation on the Effect of Volume Loss on Ground Movements Induced by Tunnelling in Sand. KSCE J Civ Eng 27, 122–134 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-022-0342-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-022-0342-8