Abstract
Objectives
To prospectively assess the performance of pediatric appendicitis score (PAS) in diagnosing acute appendicitis in the children with lower abdominal pain and correlated with ultrasound findings; and to assess the impact of the PAS on clinical outcome and its efficacy in differentiating between complicated and uncomplicated appendicitis.
Methods
A prospective study was done which included cases of lower abdominal pain. Appendectomy was done for PAS ≥ 6, and diagnosis was confirmed on histopathology. A receiver operator characteristic (ROC) curve was created to assess the PAS performance. The sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of ultrasonography in diagnosing appendicitis were assessed, and analysis of agreement between ultrasonography and PAS score was done by kappa statistics.
Results
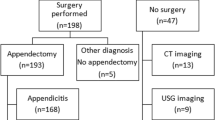
Of 260 cases with lower abdominal pain, 205 were suspected of having appendicitis. One hundred fifty-nine had PAS ≥ 6. There were 2/159 (1.26%) cases of negative appendectomies and 2/46 (4.34%) cases of missed appendicitis. The mean PAS was significantly higher in patients with appendicitis than in those without appendicitis. The area under the ROC curve was 0.9925. Sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative predictive value of PAS were 98.74%, 95.65%, 95.7% and 95.65%, respectively. Complicated appendicitis had significantly more PAS, fever, and cough tenderness than uncomplicated appendicitis. The sensitivity and specificity of ultrasonography were 86.79% and 17.39%, respectively. Agreement between ultrasonography-proven appendicitis and PAS-dependent appendicitis was weak.
Conclusion
PAS has high efficacy in diagnosing acute appendicitis. Clinical outcome was more favorable with the use of PAS. Ultrasonography should be used judiciously and in combination with clinical judgment.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Keohane D, O’Leary P, Nagle M, Cichelli K, McCormack T. A correlation of blood panel results and histologically confirmed appendicitis. Cureus. 2020;12:e10641.
Eng KA, Abadeh A, Ligocki C, et al. Acute appendicitis: a meta-analysis of the diagnostic accuracy of US, ct, and mri as second-line imaging tests after an initial US. Radiology. 2018;288:717–27.
Lee KH, Lee S, Park JH, et al. Risk of hematologic malignant neoplasms from abdominopelvic computed tomographic radiation in patients who underwent appendectomy. JAMA Surg. 2021;156:343–51.
Samuel M. Pediatric appendicitis score. J Pediatr Surg. 2002;37:877–81.
Bhatt M, Joseph L, Ducharme FM, Dougherty G, McGillivray D. Prospective validation of the pediatric appendicitis score in a Canadian pediatric emergency department. Acad Emerg Med. 2009;16:591–6.
Escribá A, Gamell AM, Fernández Y, Quintillá JM, Cubells CL. Prospective validation of two systems of classification for the diagnosis of acute appendicitis. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2011;27:165–9.
Schneider C, Kharbanda A, Bachur R. Evaluating appendicitis scoring systems using a prospective pediatric cohort. Ann Emerg Med. 2007;49:778–84.
Mandeville K, Pottker T, Bulloch B, Liu J. Using appendicitis scores in the pediatric ED. Am J Emerg Med. 2011;29:972–7.
Zúñiga RV, Arribas JL, Montes SP, et al. Application of pediatric appendicitis score on the emergency department of a secondary level hospital. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2012;28:489–92.
Bachur RG, Callahan MJ, Monuteaux MC, Rangel SJ. Integration of ultrasound findings and a clinical score in the diagnostic evaluation of pediatric appendicitis. J Pediatr. 2015;166:1134–9.
Aydin D, Turan C, Yurtseven A, et al. Integration of radiology and clinical score in pediatric appendicitis. Pediatr Int. 2018;60:173–8.
Lounis Y, Hugo J, Demarche M, Seghaye MC. Influence of age on clinical presentation, diagnosis delay and outcome in pre-school children with acute appendicitis. BMC Pediatr. 2020;20:151.
Bonadio W, Shahid S, Vardi L, et al. A pre-operative clinical scoring system to distinguish perforation risk with pediatric appendicitis. J Pediatr Surg. 2018;53:441–5.
Bickell NA, Aufses AH, Rojas M, Bodian C. How time affects the risk of rupture in appendicitis. J Am Coll Surg. 2006;202:401–6.
Carpenter JL, Orth RC, Zhang W, Lopez ME, Mangona KL, Guillerman RP. Diagnostic performance of us for differentiating perforated from nonperforated pediatric appendicitis: a prospective cohort study. Radiology. 2017;282:835–41.
Boomer LA, Cooper JN, Deans KJ, et al. Does delay in appendectomy affect surgical site infection in children with appendicitis? J Pediatr Surg. 2014;49:1026–9.
Fujii T, Tanaka A, Katami H, Shimono R. Usefulness of the pediatric appendicitis score for assessing the severity of acute appendicitis in children. Pediatr Int. 2020;62:70–3.
Feng W, Zhao XF, Li MM, Cui HL. A clinical prediction model for complicated appendicitis in children younger than five years of age. BMC Pediatr. 2020;20:401.
Dado G, Anania G, Baccarani U, et al. Application of a clinical score for the diagnosis of acute appendicitis in childhood: a retrospective analysis of 197 patients. J Pediatr Surg. 2000;35:1320–2.
Karakas SP, Guelfguat M, Leonidas JC, Springer S, Singh SP. Acute appendicitis in children: comparison of clinical diagnosis with ultrasound and CT imaging. Pediatr Radiol. 2000;30:94–8.
Smink DS, Finkelstein JA, Garcia Peña BM, Shannon MW, Taylor GA, Fishman SJ. Diagnosis of acute appendicitis in children using a clinical practice guideline. J Pediatr Surg. 2004;39:458–63.
Bullapur HM, Deshpande AV, Phin SJ, Cohen RC. Adjunct ultrasonography in children with suspected acute appendicitis: identifying the optimal target group. ANZ J Surg. 2014;84:326–30.
Scrimgeour DSG, Driver CP, Stoner RS, King SK, Beasley SW. When does ultrasonography influence management in suspected appendicitis? ANZ J Surg. 2014;84:331–4.
Gracey D, McClure MJ. The impact of ultrasound in suspected acute appendicitis. Clin Radiol. 2007;62:573–8.
Alaedeen DI, Cook M, Chwals WJ. Appendiceal fecalith is associated with early perforation in pediatric patients. J Pediatr Surg. 2008;43:889–92.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RN and MAK did the analysis and interpretation of data and drafted the work; AUS did the acquisition of data and drafted the work, SKA, PG, VJ, AKD designed the work, and revised it critically for important intellectual content; DKY did the conception of the work, interpretation of data, and revised it critically for important intellectual content. All authors approved the version to be published and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved. SKA will act as the guarantor for this paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
None.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nandan, R., Samie, A.U., Acharya, S.K. et al. Pediatric Appendicitis Score or Ultrasonography? In Search of a Better Diagnostic Tool in Indian Children with Lower Abdominal Pain. Indian J Pediatr 90, 1204–1209 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-022-04226-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-022-04226-9