Abstract
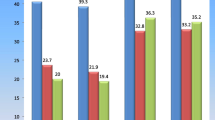
Ossicular discontinuity is one of the most common causes of conductive hearing loss. Ossicular chain reconstruction improves conductive hearing loss. With no additional cost, cartilage ossiculoplasty is easy to perform, and also the cartilage is well tolerated being an autograft. In this study we compared the audiological outcome in ossiculoplasty done by cartilage umbrella, cartilage boomerang and alloplastic TORP. 75 patients of age group 10–50 years clinically diagnosed with chronic otitis media with conductive hearing loss and an air bone gap (ABG) of at least 20 dB posted for surgery were included. Ossiculoplasty was done in three groups with autologous cartilage boomerang, cartilage umbrella and alloplastic TORP. In mucosal disease hearing gain was better in umbrella technique (17.66 ± 1.1) dB than Boomerang (16.9 ± 0.8) dB and TORP (10.68 ± 0.9) dB. ABG closure was higher in Boomerang and TORP. Hearing improvement in patients with squamosal disease managed by canal wall up surgery was 25.01 ± 1.1 dB, 27.73 ± 3.1 dB and 20.12 ± 1.8 dB in Boomerang, Umbrella and TORP group respectively showing that umbrella method gave maximum improvement. ABG closure was better in TORP group. In canal wall down surgery patient’s maximum improvement was seen in Boomerang (29.51 ± 0.9) dB followed by Umbrella (26.67 ± 1.2) dB and TORP (25.27 ± 0.8) dB group. ABG closure was higher in Boomerang group. Cartilage ossiculoplasty is a reliable and effective method of ossicular chain reconstruction for both mucosal and squamosal disease. Cartilage ossiculoplasty has the added advantage of reduced chances of prosthesis extrusion as compared to TORP.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mahanty S, Maiti AB, Naskar S, Das SK, Mandal S, Karmakar M (2015) A comparative study of outcome of ossicuoloplasty using cartilage graft, bone and different alloplasts in chronic otitis media. Indian J Otol 21(2):144–148
Wullstein H (1956) Theory and practice of tympanoplasty. Laryngoscope 66(8):1076–1093. https://doi.org/10.1288/00005537-195608000-00008
Sharma K, Gururani P, Arora A, Singh G (2017) Role of autologous versus homologous cartilage in ossicular reconstruction: a comparative study. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 69(2):137–141
Guler I, Kum RO (2019) Management of Incus defects in children: Comparison of Incus transposition versus glass inomer cement. Ear Nose Throat J. https://doi.org/10.1177/0145561319856325
Khan MM, Parab SR (2021) Endoscopic cartilage umberlla ossiculoplasty: as total ossicular replacement using endoscope holder. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-021-02518-8
Rana AK, Sharma R, Sharma VK, Mehrotra A, Upadhyay D (2020) Intraoperative tragal and conchal cartilage thickness: comparative study for cartilage tympanoplasty. Am J Otolaryngol 41(6):102690. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjoto.2020.102690
Parab SR, Khan MM, Rana AK (2020) Accurate and specific measuring grid for otorhinolaryngological surgeries. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-020-01886-x
Parab SR, Khan MM (2018) New cartilage slicer for slicing techniques in tympanoplasty: Design and applications. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 70(4):515–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-018-1467-4
Adhikari P, Joshi S, Baral D, Kharel B (2009) Chronic suppurative otitis media in urban private school of Nepal. Braz J Otolaryngol 75(5):669–672
Ayache D, Manach F, Teszler CB, Mathieu V, Bakkouri W, Corre A et al (2017) Cartilage ossiculoplasty from stapes to tympanic membrane in one stage intact canal wall tympanoplasty for cholesteatoma. J Int Adv Otol 13(2):171–175
Desarda KK, Bhisegaonkar DA, Gill S (2005) Tragal perichondrium and cartilage in reconstructive tympanoplasty. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 57(1):9–12
Singh VP, Sharma N, Bansal C (2017) Comparison of myringostapediopexy and malleostapediopexy tympanoplasty with sculptured incus in case of hearing reconstruction in tubotympanic chronic otitis media: a case series. Indian J Otol 23(3):189–192
Quaranta N, Taliente S, Coppola F, Salonna I (2015) Cartilage tympanoplasty in cholesteatoma surgery: hearing results and prognostic factors. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital 35:338–342
Bojrab DI, Kartush JM, Bouchard KR (1990) Surgery of the ear. WB Saunders Co., Philadelphia, pp 351–369
Brackmann DE, Sheely JL (1979) Tympanoplasty with TORP and PORPs. Laryngoscope 89:108–114
Jha S, Mehta K, Prajapati V, Patel D, Kharadi P (2011) A comparative study of ossiculoplasty by using various graft materials. National J Integrated Res Med 2(4):53–57
Gardner EK, Jackson CG, Kaylie DM (2004) Results with titanium ossicular reconstruction prostheses. Laryngoscope 114:65–70
Acharya SK, Pahuja OP, Chamyal PC (1994) Middle ear reconstruction- our experience. Med J Armed Forces India 50(2):113–116
Acknowledgements
Authors wish to thank Dr. Deviprasad Dosemane, Associate Professor, Department of ENT, Kasturba Medical College, Manipal Academy of Higher Education, Mangalore (India) for his valuable suggestions during preparation of this manuscript.
Funding
None received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed Consent
A written and explained consent was obtained from all the participants before enrolling them for the study.
Ethical Approval
Ethical clearance was obtained from institutional ethical clearance committee before starting the study involving human participants.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rana, A.K., Kumar, S., Kumar, A. et al. Comparative Evaluation of Hearing in Cartilage Umbrella, Boomerang and Torp in Chronic Otitis Media Cases with Absent Stapes Suprastructure: Our Experience. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 74 (Suppl 3), 4069–4076 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-021-02819-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-021-02819-y