Abstract
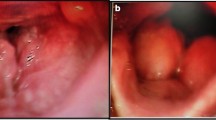
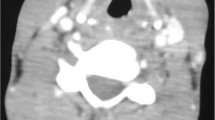
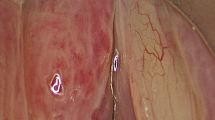
Laryngeal tuberculosis is a rare condition, isolated laryngeal tuberculosis without pulmonary manifestations is even more rare. Patients usually presents with voice change, difficulty in swallowing and other constitutional symptoms. The symptoms and findings can look like malignancy in most of the cases. Here, we present a case of primary laryngeal tuberculosis without pulmonary tuberculosis. A 24 year old man who presented to us with hoarseness of voice with 1 year duration. Laryngoscopic study showed a proliferative growth in the epiglottis, aryepiglottic folds and vocal cords and was diagnosed to have laryngeal tuberculosis on histopathology by the typical appearance of granuloma and caseous necrosis. The patient was started on standard antitubercular therapy and he had an excellent response to the same within 6 months. Isolated laryngeal tuberculosis should be suspected in patients with laryngeal complaints with no pulmonary symptoms, especially in a develo** country like India where pulmonary tuberculosis is prevalent. Even though isolated laryngeal tuberculosis cases are rare, we should keep in mind the possibility of tuberculosis in the differential diagnosis of laryngeal tumors, as the incidence of tuberculosis is steadily increasing.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rohwedder JJ (1974) Upper respiratory tract tuberculosis. Sixteen cases in a general hospital. Ann Intern Med 80:708–713
Richter B, Fradis M, Kohler G, Ridder GJ (2001) Epiglottic tuberculosis: differential diagnosis and treatment Case report and review of literature. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 110:197–201
Alonso PE, Mateos AM, Perez-Requena J, Serrano EA (2002) Laryngeal tuberculosis. Rev Laryngol Otol Rhinol 2002(14):352–356
Nishiike S, Irifune M, Sawada T, Doi K, Kubo T (2002) Laryngeal tuberculosis: a report of 15 cases. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 111(10):916–918
Verma SK, Verma SK, Sanjay (2007) Laryngeal tuberculosis clinically similar to laryngeal cancer. Lung India 24:87–89
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Research Involving Human Participants and/or Animal
Not applicable.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from the patient for use of data for publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pandiyan, H., Sivanand, N. & Sathish Kumar, S. Isolated Laryngeal Tuberculosis: a Diagnostic Dilemma. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 74 (Suppl 2), 2308–2310 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-020-02139-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-020-02139-7