Abstract
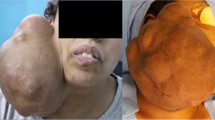
Salivary gland tumors are rare, comprising less than 3% of all neoplasia of head and neck region. Pleomorphic adenoma is the most common salivary gland tumor, accounting for 60–80% of benign tumors of salivary glands, which predominantly affect the superficial lobe of the parotid gland. The “pleomorphic” nature of the tumor can be explained on the basis of its epithelial and connective tissue origin. Usually they are found as solitary unilateral, firm and mobile, painless, slow growing mass. The tumor has a female predilection between 30 and 50 years of age. Utmost care is to be taken to preserve the facial nerve while performing superficial or total parotidectomy. We present 10 cases of pleomorphic adenoma of parotid gland over period of 2 years, highlighting the prognosis following surgical management.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gleeson M, Browning GG, Burton MJ, Clarke R, Hibbert J, Jones NS, Lund VJ, Luxon LM, Watkinson JC (2008) Scott-Brown’s otorhinolaryngology, head and neck surgery, 7th edn. Hodder Arnold, London, pp 2480–2481
Silva SJ, Costa GT, Filho ACB, Faria PR, Loyola AM (2006) Metachronous bilateral pleomorphic adenoma of the parotid gland. Oral Surg Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endodontol 101(3):333–338
Martinelli M, Martini F, Rinaldi E, Caramanico L, Magri E, Grandi E et al (2002) Simian virus 40 sequences and expression of the viral large T antigen oncoprotein in human pleomorphic adenomas of parotid glands. Am J Pathol 161(4):1127–1133
Traiger J, Rosen MB (1965) Mixed tumor of the cheek: report of a case. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 19:711–714
Berdal P, Hall JG (1969) Parapharyngeal growth of parotid tumours. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl 263:164–166
Dalati T, Hussein MR (2009) Juvenile pleomorphic adenoma of the cheek: a case report and review of literature. Diagn Pathol 4(32):1–5
Beunting JE, Smith TL, Holmes DK (1998) Giant pleomorphic adenoma of the parotid gland: case report and review of the literature. Ear Nose Throat J 77(8):643, 637–638, 640
Ellis GL, Auclair PL (1996) Tumors of the salivary glands (Atlas of Tumor Pathology) 3rd series. Fascicle 17. Armed Forces of Institute of Pathology, Washington, DC
Guerriere CN, Goff JJ, Cummings GH, Auber AE (1999) An unusually large, solid tumor of the parotid gland. Ann Plast Surg 43(5):529–532
Silva SJ, Costa GT, Filho ACB, Faria PR, Loyola AM (2006) Metachronous bilateral pleomorphic adenoma of the parotid gland. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endodontol 101(3):333–338
Takahama A Jr, Perez DEC, Magrin J, Almeida OP, Kowalski LP (2008) Giant pleomorphic adenoma of the parotid gland. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal 13(1):58–60
Sergi B, Limongelli A, Scarano E, Fetoni AR, Paludetti G (2008) Giant deep lobe parotid gland pleomorphic adenoma involving the parapharyngeal space. Report of three cases and review of the diagnostic and therapeutic approaches. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital 28:261–265
Contucci AM, Corina L, Sergi B, Fadda G, Paludetti G (2003) Correlation between fine needle aspiration biopsy and histologic findings in parotid masses. Personal experience. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital 23:314–318
Mehle ME, Krause DH, Wood BG, Benninger SM, Eliachar I, Levine HL et al (1993) Facial nerve morbidity following parotid surgery for benign disease. The Cleveland Clinic Foundation experience. Laryngoscope 103:386–388
Zarbo RJ (2002) Salivary gland neoplasia: a review for the practicing pathologist. Mod Pathol 15(3):298–323
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Dr. C.V. Srinivas and Dr. C. Shivani declared that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Srinivas, C.V., Shivani, C. Novice’s Sojourn to Parotid Surgery. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 71 (Suppl 1), 243–247 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-018-1245-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-018-1245-3