Abstract
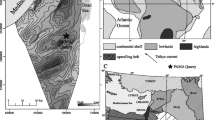
Deep biospheric anaerobic microbial sulfate reduction and oxidative sulfur cycling have been studied in long sediment cores mainly acquired as part of IODP explorations. The most remarkable observation in many of these studies is the existence of an active sulfur cycle in the deep subsurface sediments that have very low organic carbon content and are presumably refractory. Here, we investigate the interstitial sulfate concentrations and sulfur isotope ratios in a 290 m-long sediment core collected from the eastern Arabian Sea at a water depth of 2663 m. Continuous decrease in porewater-sulfate concentrations with depth (up to 75 mbsf) coupled with enrichment in δ34SSO4 values suggests organoclastic sulfate reduction (OSR) processes attributed to the activity of sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) and retention of labile organic substrates amenable to the SRBs. Below a depth of 75 mbsf, the absence of further reduction in sulfate concentration indicates insufficient labile substrate to drive sulfate-reduction activity. An increase in sulfate concentrations at the deeper subsurface (below 128.5 mbsf) coupled with decreasing δ34SSO4 values may be attributed to the oxidation of Fe-sulfide to sulfate. The increase in porewater alkalinity in the lower part of the core has been linked to the silicate degradation process by CO2 produced via the dissolution of CaCO3. Compilation of previous studies from this core, along with our investigation, intrigues future research on organic matter reactivity and microbiological activity in deeper subsurface under oligotrophic depositional regimes.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agatova A T and Bogdanov Y A 1972 Biochemical composition of suspended organic matter from the Tropical Pacific; Okeanologiya 12 267–276.
Aoki M, Kakiuchi R, Yamaguchi T, Takai K, Inagaki F and Imachi H 2015 Phylogenetic diversity of aprA genes in subseafloor sediments on the northwestern Pacific margin off Japan; Microbes Environ. 30(3) 276–280.
Arndt S, Jørgensen B B, LaRowe D E, Middelburg J J, Pancost R D and Regnier P 2013 Quantifying the degradation of organic matter in marine sediments: A review and synthesis; Earth Sci. Rev. 123 53–86.
Balci N, Brunner B and Turchyn A V 2017 Tetrathionate and elemental sulfur shape the isotope composition of sulfate in acid mine drainage; Front Microbiol. 8 1564.
Bergauer K, Fernandez-Guerra A, Garcia J A L, Sprenger R R, Stepanauskas R, Pachiadaki M G, Jensen O N and Herndl G J 2017 Organic matter processing by microbial communities throughout the Atlantic water column as revealed by metaproteomics; Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 115 E400–E408.
Berner R A 2004 The Phanerozoic carbon cycle: CO2 and O2; Oxford University Press on Demand.
Beulig F, Roy H, Glombitza C and Jørgensen B B 2018 Control on rate and pathway of anaerobic organic carbon degradation in the seabed; Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 115(2) 367–372.
Blazejak A and Schippers A 2011 Real-time PCR quantification and diversity analysis of the functional genes aprA and dsrA of sulfate-reducing prokaryotes in marine sediments of the Peru continental margin and the Black Sea; Front Microbiol. 2 253.
Boetius A, Ravenschlag K, Schubert C J, Rickert D, Widdel F, Giesecke A, Amann R, Jørgensen B B, Witte U and Pfannkuche O 2000 A marine microbial consortium apparently mediating anaerobic oxidation of methane; Nature 407 623–626.
Böttcher M, Khim B, Suzuki A, Gehre M, Wortmann U and Brumsack H 2004 Microbial sulfate reduction in deep sediments of the Southwest Pacific (ODP Leg 181, Sites 1119–1125): Evidence from stable sulfur isotope fractionation and pore water modelling; Mar. Geol. 205 249–260.
Böttcher M E, Brumsack H J and Dürselen C D 2007 The isotopic composition of modern seawater sulfate: I. Coastal waters with special regard to the North Sea; J. Mar. Syst. 67 73–82.
Bowles M W, Mogollon J M, Kasten S, Zabel M and Hinrichs K-U 2014 Global rates of marine sulfate reduction and implications for sub-sea-floor metabolic activities; Science 344 889–891.
Brophy J E and Carlson D J 1989 Production of biologically refractory dissolved organic carbon by natural seawater microbial populations; Deep-Sea Res. Part A: Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 36 497–507.
Brunner B, Arnold G L, Røy H, Müller I A and Jørgensen B B 2016 Off limits: Sulfate below the sulfate-methane transition; Front. Earth Sci. 4 75.
Burdige D J 2007 Preservation of organic matter in marine sediments: Controls, mechanisms, and an imbalance in sediment organic carbon budgets?; Chem. Rev. 107 467–485.
Canfield D 2001 Biogeochemistry of sulfur isotopes; Rev. Mineral Geochem. 43 607–636.
Canfield D and Thamdrup B 1994 The production of 34S-depleted sulfide during bacterial disproportionation of elemental sulphur; Science 266 1973–1975.
Canfield D, Kristensen E and Thamdrup B 2005 The sulfur cycle; Adv. Mar. Biol. 48 313–381.
Chaubey A K, Bhattacharya G C, Murty G P S and Desa M 1993 Spreading history of the Arabian Sea: Some new constraints; Mar. Geol. 112 343–352.
Claypool G 2004 Ventilation of marine sediments indicated by depth profiles of pore water sulfate and δ34S; Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ. 9 59–65.
Collett T, Riedel M, Cochran J, Boswell R, Presley J, Kumar P, Sathe A, Sethi A, Lall M and Sibal V 2008 Indian National Gas Hydrate Program: Expedition 01. Directorate General of Hydrocarbon; New Delhi India Initial Reports Vol. 1.
D’Hondt S, Jørgensen B B, Miller D J, Aiello I W and Bekins B 2003 Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Vol. 201 Initial Rep. Controls on microbial communities in deeply buried sediments, Eastern Equatorial Pacific and Peru Margin; College Station: Tex. A&M Univ. Ocean Drill. Program.
Danovaro R, Fabiano M and Della Croce N 1993 Labile organic matter and microbial biomasses in deep-sea sediments (Eastern Mediterranean Sea); Deep-Sea Res Part I: Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 40 953–965.
Dell’Anno A, Fabiano M, Mei M L and Danovaro R 2000 Enzymatically hydrolysed protein and carbohydrate pools in deep-sea sediments: Estimates of the potentially bioavailable fraction and methodological considerations; Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 196 15–23.
Detmers J, Bruchert V, Habicht K and Kuever J 2001 Diversity of sulfur isotope fractionations by sulfate-reducing prokaryotes; Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 67 888–894.
Ducklow H W, Steinberg D K and Buesseler K O 2001 Upper ocean carbon export and the biological pump; Oceanography 14 50–58.
Duncan R A 1981 Hotspots in the southern oceans – an absolute frame of reference for motion of the Gondwana continents; Tectonophysics 74 29–42.
Estes E R, Pockalny R, D’Hondt S, Inagaki F, Morono Y, Murray R W, Nordlund D, Spivack A J, Wankel S D, **ao N and Hansel C M 2019 Persistent organic matter in oxic subseafloor sediment; Nat. Geosci. 12 126–131.
Ferdelman T G, Ziebis W, Patel A, Krupke A, Expedition I and Party S S 2011 Autotrophic and heterotrophic microbial activity in sediments underlying the ultra-oligotrophic South Pacific Gyre; AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts B51K-0559.
Flores J A, Johnson J E, Mejia-Molina A E, Álvarez M C, Sierro F J, Singh S D, Mahanti S and Giosan L 2014 Sedimentation rates from calcareous nannofossil and planktonic foraminifera biostratigraphy in the Andaman Sea, northern Bay of Bengal, and eastern Arabian Sea; Mar. Pet. Geol. 58 425–437.
Froelich P, Klinkhammer G, Bender M, Luedtke N, Heath G, Cullen D, Dauphin P, Hammond D, Hartman B and Maynard V 1979 Early oxidation of organic matter in pelagic sediments of the eastern equatorial Atlantic: Suboxic diagenesis; Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 43 1075–1090.
Gieskes J M 1974 Interstitial Water Studies, LEG 35; In: Initial Reports DSDP (eds) Simpson E S W and Schlich R et al., U.S. Govt. Printing Office Washington DC 25 361–394.
Gieskes J M, Peretsman G and Rabinowitz P 1986 Water chemistry procedures aboard JOIDES resolution – some comments; ODP Tech. Note 5 1–46.
Glombitza C, Jaussi M, Roy H, Seidenkrantz M-S, Lomstein B A and Jorgensen B B 2015 Formate, acetate, and propionate as substrates for sulfate reduction in sub-arctic sediments of Southwest Greenland; Front Microbiol. 6 846.
Hedges J and Keil R 1995 Sedimentary organic matter preservation: An assessment and speculative synthesis; Mar. Chem. 49 81–115.
Hedges J I and Oades M 1997 A comparative study of marine and soil geochemistry; Org. Geochem. 27 319–361.
Hoehler T M and Jørgensen B B 2013 Microbial life under extreme energy limitation; Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 11 83–94.
Holland H D 1978 The chemistry of the atmosphere and oceans; John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Holmkvist L, Ferdelman T G and Jørgensen B B 2011 A cryptic sulfur cycle driven by iron in the methane zone of marine sediment (Aarhus Bay, Denmark); Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta. 75 3581–3599.
Johnson J E, Phillips S C, Torres M E, Pinero E, Rose K K and Giosan L 2014 Influence of total organic carbon deposition on the inventory of gas hydrate in the Indian continental margins; Mar. Petrol. Geol. 58 406–424.
Jørgensen B and Kasten S 2006 Sulfur cycling and methane oxidation; Mar. Geochem. 271–309.
Jørgensen B B and Marshall I P G 2016 Slow microbial life in the seabed; Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 8 311–332.
Jørgensen B B, Findlay A J and Pellerin A 2019 The biogeochemical sulfur cycle of marine sediments; Front Microbiol. 10 849.
Jørgensen B B, Wenzhöfer F, Egger M and Glud R N 2022 Sediment oxygen consumption: Role in the global marine carbon cycle; Earth Sci. Rev. 228 311–332.
Kharbush J J, Close H G, Van Mooy B A S, Arnosti C, Smittenberg R H, Le Moigne F A C, Mollenhauer G, Scholz-Bottcher B, Obreht I and Koch B P 2020 Particulate organic carbon deconstructed: Molecular and chemical composition of particulate organic carbon in the ocean; Front. Mar. Sci. 7 518.
Klemps R, Cypionka H, Widdel F and Pfennig N 1985 Growth with hydrogen, and further physiological characteristics of Desulfotomaculum species; Arch. Microbiol. 143 203–208.
Knittel K and Boetius A 2009 Anaerobic oxidation of methane: Progress with an unknown process; Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 63 311–334.
Kotelnikova S and Pedersen K 1997 Evidence for methanogenic Archaea and homoacetogenic bacteria in deep granitic rock aquifers; FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 20 339–349.
Kumar P, Collett T S, Boswell R, Cochran J R, Lall M, Mazumdar A, Ramana M V, Ramprasad T, Riedel M and Sain K 2014 Geologic implications of gas hydrates in the offshore of India: Krishna-Godavari Basin, Mahanadi Basin, Andaman Sea, Kerala-Konkan Basin; Mar. Petrol. Geol. 58 29–98.
LaRowe D E and Amend J P 2015 Power limits for microbial life; Front Microbiol. 6 718.
LaRowe D E, Arndt S, Bradley J A, Estes E R, Hoarfrost A, Lang S Q, Lloyd K G, Mahmoudi N, Orsi W D, Walter S S and Steen A D 2020 The fate of organic carbon in marine sediments – New insights from recent data and analysis; Earth Sci. Rev. 204 103146.
Lee C, Wakeham S and Arnosti C 2004 Particulate organic matter in the sea: The composition conundrum; AMBIO: J. Human Environ. 33 565–575.
Leloup J, Loy A, Knab N J, Borowski C, Wagner M and Jørgensen B B 2007 Diversity and abundance of sulfate-reducing microorganisms in the sulfate and methane zones of a marine sediment, Black Sea; Environ. Microbiol. 9 131–142.
Leloup J, Fossing H, Kohls K, Holmkvist L, Borowski C and Jørgensen B B 2009 Sulfate-reducing bacteria in marine sediment (Aarhus Bay, Denmark): Abundance and diversity related to geochemical zonation; Environ. Microbiol. 11 1278–1291.
Lever M A, Rogers K L, Lloyd K G, Overmann J R, Schink B, Thauer R K, Hoehler T M and Jørgensen B B 2015 Life under extreme energy limitation: A synthesis of laboratory-and field-based investigations; FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 39 688–728.
Luek J L, Thompson K E, Larsen R K, Heyes A and Gonsior M 2017 Sulfate reduction in sediments produces high levels of chromophoric dissolved organic matter; Sci. Rep. 7 1–8.
Malinverno A and Martinez E A 2015 The effect of temperature on organic carbon degradation in marine sediments; Sci. Rep. 5 1–10.
Malinverno A, Kastner M, Torres M E and Wortmann U G 2008 Gas hydrate occurrence from pore water chlorinity and downhole logs in a transect across the northern Cascadia margin (Integrated Ocean Drilling Program Expedition 311); J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 113(B8), https://doi.org/10.1029/2008JB005702.
Marra J and Barber R T 2005 Primary productivity in the Arabian Sea: A synthesis of JGOFS data; Prog. Oceanogr. 65 159–175.
Mazumdar A and Strauss H 2006 Sulfur and strontium isotopic compositions of carbonate and evaporite rocks from the late Neoproterozoic–early Cambrian Bilara Group (Nagaur–Ganganagar Basin, India): Constraints on intrabasinal correlation and global sulfur cycle; Precambrian Res. 149 217–230.
Mazumdar A, Paropkari A L, Borole D V, Rao B R, Khadge N H, Karisiddaiah S M, Kocherla M and Joao H M 2007 Pore-water sulfate concentration profiles of sediment cores from Krishna-Godavari and Goa basins, India; Geochem. J. 41 259–269.
Mazumdar A, Goldberg T and Strauss H 2008 Abiotic oxidation of pyrite by Fe (III) in acidic media and its implications for sulfur isotope measurements of lattice-bound sulfate in sediments; Chem. Geol. 253 30–37.
McKenzie D and Sclater J G 1971 The evolution of the Indian Ocean since the Late Cretaceous; Geophys. J. Int. 24 437–528.
McKibben M A and Barnes H L 1986 Oxidation of pyrite in low temperature acidic solutions: Rate laws and surface textures; Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta. 50 1509–1520.
Meister P, Brunner B, Picard A, Böttcher M E and Jørgensen B B 2019 Sulphur and carbon isotopes as tracers of past sub-seafloor microbial activity; Sci. Rep. 9 1–9.
Meister P, Herda G, Petrishcheva E, Gier S, Dickens G R, Bauer C and Liu B 2022 Microbial alkalinity production and silicate alteration in methane charged marine sediments: Implications for porewater chemistry and diagenetic carbonate formation; Front. Earth Sci. 9 756591.
Meyers P A and Shaw T J 1996 Organic matter accumulation, sulfate reduction, and methanogenesis in Pliocene-Pleistocene turbidites on the Iberia Abyssal Plain; Proc. Ocean Drill. Prog., Sci. Results 149 705–712.
Naini B R and Talwani M 1982 Structural framework and the evolutionary history of the continental margin of Western India: Rifted margins: Field investigations of margin structure and stratigraphy; AAPG Mem. 34.
Norton I O and Sclater J G 1979 A model for the evolution of the Indian Ocean and the breakup of Gondwanaland; J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 84 6803–6830.
Ouboter H T, Berben T, Berger S, Jetten M S M, Sleutels T, Ter Heijne A and Welte C U 2022 Methane-dependent extracellular electron transfer at the bioanode by the anaerobic archaeal methanotroph “Candidatus Methanoperedens”; Front. Microbiol. 13, https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.820989.
Parkes R J, Cragg B A, Bale S J, Getlifff J M, Goodman K, Rochelle P A, Fry J C, Weightman A J and Harvey S M 1994 Deep bacterial biosphere in Pacific Ocean sediments; Nature 371 410–413.
Rao Y, Subrahmanyam C, Rastogi A and Deka B 2001 Anomalous seismic reflections related to gas/gas hydrate occurrences along the western continental margin of India; Geo-Mar. Lett. 21 1–8.
Raven M R, Sessions A L, Fischer W W and Adkins J F 2016 Sedimentary pyrite δ34S differs from porewater sulfide in Santa Barbara Basin: Proposed role of organic sulphur; Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 186 120–134.
Reeburgh W 1980 Anaerobic methane oxidation: Rate depth distributions in Skan Bay sediments; Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 47 345–352.
Riedinger N, Brunner B, Formolo M J, Solomon E, Kasten S, Strasser M and Ferdelman T G 2010 Oxidative sulfur cycling in the deep biosphere of the Nankai Trough, Japan; Geology 38 851–854.
Riedinger N, Brunner B, Krastel S, Arnold G L, Wehrmann L, Formolo M J, Beck A, Bates S M, Henkel S and Kasten S 2017 Sulfur cycling in an iron oxide-dominated, dynamic marine depositional system: The Argentine continental margin; Front. Earth Sci. 5, https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2017.00033.
Sayles F L, Manheim F T and Waterman L S 1973 Interstitial water studies on small core samples, Leg 15; Ini. Rep. DSDP 20 783–804.
Schrenk M O, Brazelton W J and Lang S Q 2013 Serpentinization, carbon, and deep life; Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 75 575–606.
Solomon E A, Spivack A J, Kastner M, Torres M E and Robertson G 2014 Gas hydrate distribution and carbon sequestration through coupled microbial methanogenesis and silicate weathering in the Krishna–Godavari Basin, Offshore India; Mar. Pet. Geol. 58 233–253.
Sousa D Z, Visser M, Van Gelder A H, Boeren S, Pieterse M M, Pinkse M W H, Verhaert P D E M, Vogt C, Franke S and Kümmel S 2018 The deep-subsurface sulfate reducer Desulfotomaculum kuznetsovii employs two methanol-degrading pathways; Nat. Commun. 9 1–9.
Stevens T O and McKinley J P 1995 Lithoautotrophic microbial ecosystems in deep basalt aquifers; Science 270 450–455.
Torres M E, Hong W L, Solomon E A, Milliken K, Kim J H, Sample J C, Teichert B M and Wallmann K 2020 Silicate weathering in anoxic marine sediment as a requirement for authigenic carbonate burial; Earth Sci. Rev. 200 102960.
Treude T, Niggemann J, Kallmeyer J, Wintersteller P, Schubert C J, Boetius A and Jørgensen B B 2005 Anaerobic oxidation of methane and sulfate reduction along the Chilean continental margin; Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta. 69 2767–2779.
Valentine D and Reeburgh W 2000 New perspectives on anaerobic methane oxidation; Environ. Microbiol. 2 477–484.
Wallmann K, Aloisi G, Haeckel M, Tishchenko P, Pavlova G, Greinert J, Kutterolf S and Eisenhauer A 2008 Silicate weathering in anoxic marine sediments; Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 72 3067–3090.
Wasmund K, Cooper M, Schreiber L, Lloyd K G, Baker B J, Petersen D G, Jørgensen B B, Stepanauskas R, Reinhardt R and Schramm A 2016 Single-cell genome and group-specific dsrAB sequencing implicate marine members of the class Dehalococcoidia (phylum Chloroflexi) in sulfur cycling; MBio. 7 e00266–e1216.
Wasmund K, Mußmann M and Loy A 2017 The life sulfuric: Microbial ecology of sulfur cycling in marine sediments; Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 9 323–344.
Wellsbury P, Goodman K, Barth T, Cragg B A, Barnes S P and Parkes R J 1997 Deep marine biosphere fuelled by increasing organic matter availability during burial and heating; Nature 388 573–576.
Wellsbury P, Mather I and Parkes R J 2002 Geomicrobiology of deep low organic carbon sediments in the Woodlark Basin, Pacific Ocean; FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 42 59–70.
Wenk C B, Wing B A and Halevy I 2017 Electron carriers in microbial sulfate reduction inferred from experimental and environmental sulfur isotope fractionations; The ISME Journal 12 495–507.
Werne J P, Lyons T W, Hollander D J, Schouten S, Hopmans E C and Sinninghe Damste J S 2008 Investigating pathways of diagenetic organic matter sulfurization using compound-specific sulfur isotope analysis; Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 72 3489–3502.
Wing B A and Halevy I 2014 Intracellular metabolite levels shape sulfur isotope fractionation during microbial sulfate respiration; Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 111 18,116–18,125.
Zonneveld K A F, Versteegh G J M, Kasten S, Eglinton T I, Emeis K C, Huguet C, Koch B P, de Lange G J, de Leeuw J W and Middelburg J J 2010 Selective preservation of organic matter in marine environments; processes and impact on the sedimentary record; Biogeosciences 7 483–511.
Acknowledgements
We thank the director of CSIR-NIO for supporting this study. We thank NGHP for providing samples and onboarding the scientific team to obtain pore fluid data. We sincerely thank MOES for funding the program and CSIR for the research fellowship (SRF) to Kalyani Sivan, Ankita Ghosh and Mohd. Sadique. We thank Mrs Maria Desa for her contribution to making the figures. This study was funded by Ministry of Earth Sciences (GAP2303).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Aninda Mazumdar: Conceptualization, investigation, methodology, visualization, funding acquisition, formal analysis, writing – original draft; Aditya Peketi: Conceptualization, investigation, methodology, visualization, formal analysis, writing – original draft; Namrata Khadge: Data generation, methodology; Subhashree Mishra: Data generation, methodology; Kalyani Sivan: Data generation, methodology; A Ghosh: Data generation, methodology; S P K Pillutla: Data generation, methodology; Mohd. Sadique: Data generation, methodology; A Zatale: Data generation, methodology.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Ramananda Chakrabarti
All the authors belong to Methane Hydrate and Cold Seep Exploration Group.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mazumdar, A., Peketi, A., Khadke, N. et al. Evidence of deep subsurface carbon–sulfur geochemistry in a sediment core from the eastern Arabian Sea. J Earth Syst Sci 133, 121 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-024-02330-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-024-02330-2