Abstract
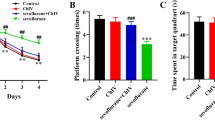
Postoperative cognitive dysfunction (POCD) is a major postoperative neurological complication in children and the elderly. However, the detailed mechanisms underlying this process remain unclear. This study aims to investigate the effect of pleiotrophin on sevoflurane-induced neuroinflammation and cognitive impairment. The novel object recognition test was performed to evaluate the cognitive and motor function of aged C57BL/6 (wild-type, WT) and pleiotrophin-knockout mice treated with sevoflurane. Small molecule inhibitors targeting receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase (RPTP) β/ζ, a pleiotrophin receptor, were used to ameliorate cognitive dysfunction. Sevoflurane treatment induced cognitive dysfunction and motor impairment in aged WT mice. Sevoflurane anesthesia induced the upregulation of certain inflammatory cytokines. Pleiotrophin knockout ameliorated the sevoflurane-induced cognitive dysfunction and motor impairment in vivo. Treatment with small molecule inhibitors targeting RPTP β/ζ inhibited sevoflurane-induced neuroinflammation. In summary, pleiotrophin was shown to potentiate sevoflurane anesthesia-induced cognitive dysfunction and learning deficits in mice.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Materials
Data are available from the authors by request.
References
Alalawi R, Yasmeen N (2018) Postoperative cognitive dysfunction in the elderly: a review comparing the effects of desflurane and sevflurane. J Perianesth Nurs 33:732–740. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jopan.2017.04.009
Chai D, Cheng Y, Jiang H (2019) Fundamentals of fetal toxicity relevant to sevoflurane exposures during pregnancy. Int J Dev Neurosci 72:31–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2018.11.001
Chen G, Gong M, Yan M, Zhang X (2013) Sevoflurane induces endoplasmic reticulum stress mediated apoptosis in hippocampal neurons of aging rats. PLoS One 8
Daiello LA et al (2019) Postoperative delirium and postoperative cognitive dysfunction: overlap and divergence. Anesthesiology 131:477–491. https://doi.org/10.1097/ALN.0000000000002729
Deuel TF, Zhang N, Yeh HJ, Silos-Santiago I, Wang ZY (2002) Pleiotrophin: a cytokine with diverse functions and a novel signaling pathway. Arch Biochem Biophys 397:162–171. https://doi.org/10.1006/abbi.2001.2705
Evered LA, Silbert BS (2018) Postoperative Cognitive Dysfunction and Noncardiac Surgery. Anesth Analg 127:496–505. https://doi.org/10.1213/ANE.0000000000003514
Ferrario JE, Rojas-Mayorquin AE, Saldana-Ortega M, Salum C, Gomes MZ, Hunot S, Raisman-Vozari R (2008) Pleiotrophin receptor RPTP-zeta/beta expression is up-regulated by L-DOPA in striatal medium spiny neurons of parkinsonian rats. J Neurochem 107:443–452. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2008.05640.x
Gaba V (2007) Correlation of the depth of anesthesia with POCD (postoperative cognitive dysfunction). Anesth Analg 104:1298; author reply 1298–1299. https://doi.org/10.1213/01.ane.0000260372.38206.b3
Himburg HA et al (2010) Pleiotrophin regulates the expansion and regeneration of hematopoietic stem cells. Nat Med 16:475–482. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2119
Huang L, Cichon J, Ninan I, Yang G (2016) Post-anesthesia AMPA receptor potentiation prevents anesthesia-induced learning and synaptic deficits. Sci Transl Med 8:344ra385. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.aaf7151
Ju LS et al (2019) Intergenerational Effects of Sevoflurane in Young Adult Rats. Anesthesiology 131:1092–1109. https://doi.org/10.1097/ALN.0000000000002920
Jungwirth B, Zieglgansberger W, Kochs E, Rammes G (2009) Anesthesia and postoperative cognitive dysfunction (POCD). Mini Rev Med Chem 9:1568–1579. https://doi.org/10.2174/138955709791012229
Kadomatsu K, Muramatsu T (2004) Midkine and pleiotrophin in neural development and cancer. Cancer Lett 204:127–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3835(03)00450-6
Le Freche H et al (2012) Tau phosphorylation and sevoflurane anesthesia: an association to postoperative cognitive impairment. Anesthesiology 116:779–787. https://doi.org/10.1097/ALN.0b013e31824be8c7
Li Y, **a H, Chen L, Zhang X (2017) Sevoflurane induces endoplasmic reticulum stress mediated apoptosis inmouse hippocampal neuronal HT22 cells via modulating miR-15b-5p/Rab1A signaling pathway. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 10:8270–8280
Liebert AD, Chow RT, Bicknell BT, Varigos E (2016) Neuroprotective effects against POCD by photobiomodulation: evidence from assembly/disassembly of the cytoskeleton. J Exp Neurosci 10:1–19. https://doi.org/10.4137/JEN.S33444
Lu C et al (2015) Neuron-restrictive silencer factor in periaqueductal gray contributes to remifentanil-induced postoperative hyperalgesia via repression of the mu-opioid receptor. J Neurol Sci 352:48–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2015.03.018
Luo C, Zou W (2018) Cerebral monitoring of anaesthesia on reducing cognitive dysfunction and postoperative delirium: a systematic review. J Int Med Res 46:4100–4110. https://doi.org/10.1177/0300060518786406
Needham MJ, Webb CE, Bryden DC (2017) Postoperative cognitive dysfunction and dementia: what we need to know and do. Br J Anaesth 119:i115–i125. https://doi.org/10.1093/bja/aex354
Palanca BJA, Avidan MS, Mashour GA (2017) Human neural correlates of sevoflurane-induced unconsciousness. Br J Anaesth 119:573–582. https://doi.org/10.1093/bja/aex244
Peng L, Xu L, Ouyang W (2013) Role of peripheral inflammatory markers in postoperative cognitive dysfunction (POCD): a meta-analysis. PLoS One 8:e79624. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0079624
Potapov EV et al (2001) Postoperative course of S-100B protein and neuron-specific enolase in patients after implantation of continuous and pulsatile flow LVADs. J Heart Lung Transplant 20:1310–1316. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1053-2498(01)00351-5
Shoair OA, Grasso II MP, Lahaye LA, Daniel R, Biddle CJ, Slattum PW (2015) Incidence and risk factors for postoperative cognitive dysfunction in older adults undergoing major noncardiac surgery: a prospective study. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol 31:30–36. https://doi.org/10.4103/0970-9185.150530
Urits I, Orhurhu V, Jones M, Hoyt D, Seats A, Viswanath O (2019) Current perspectives on postoperative cognitive dysfunction in the ageing population . Turk J Anaesthesiol Reanim 47:439–447. https://doi.org/10.5152/TJAR.2019.75299
Wang C, Li L, Xu H, Lv H, Zhang H (2019) Effect of desflurane-remifentanil or sevoflurane-remifentanil on early recovery in elderly patients: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Pharmazie 74:201–205. https://doi.org/10.1691/ph.2019.8935
Wang Y, Cao M, Cao G, Liu Y, Zhang Y (2020) Effect of combined intravenous-inhalation anesthesia on postoperative cognitive dysfunction after laparoscopic radical resection of cervical cancer: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (baltimore) 99:e23124. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000023124
** G, Demambro VE, D'Costa S, **a SK, Cox ZC, Rosen CJ, Clemmons DR (2020) Estrogen stimulation of pleiotrophin enhances osteoblast differentiation and maintains bone mass in IGFBP-2 null mice. Endocrinology 161. https://doi.org/10.1210/endocr/bqz007
**e H, She GM, Wang C, Zhang LY, Liu CF (2015) The gender difference in effect of sevoflurane exposure on cognitive function and hippocampus neuronal apoptosis in rats. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 19:647–657
**ong B, Shi Q, Fang H (2016) Dexmedetomidine alleviates postoperative cognitive dysfunction by inhibiting neuron excitation in aged rats Am J. Transl Res 8:70–80
Zhao H, Wang W, Liu L, Wang J, Yan Q (2020) Functional Modular Network Identifies the Key Genes of Preoperative Inhalation Anesthesia and Intravenous Anesthesia in off-Pump Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting. Comput Math Methods Med 2020:4574792. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/4574792
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Data curation, analysis: Shunhong Mao, Jian Yu, Lei Wang and Chunhua Zhu; Drafting of the manuscript: Shunhong Mao and Chunhua Zhu; Concept, design of the study: Shunhong Mao and Chunhua Zhu. All authors approved the publication the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Animal studies were approved by the ethics commitment of Cangzhou Central Hospital.
Consent to Participate
The current study is available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Consent for Publication
The current study is available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Conflict of Interest
All of the authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mao, S., Yu, J., Wang, L. et al. Pleiotrophin Potentiates Sevoflurane Anesthesia-induced Learning Deficits in Mice. J Mol Neurosci 72, 48–55 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-021-01885-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-021-01885-9