Abstract
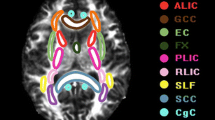
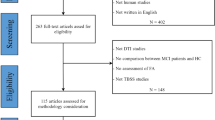
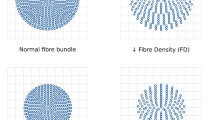
Patients with subcortical ischemic vascular disease (SIVD) may exhibit a high risk of cognitive impairment (CI) by disruption of white matter (WM) integrity. Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) is recommended as a sensitive method to explore whole brain WM alterations at an asymptomatic stage of the disease, which might be correlated with underlying cognitive disorders. We aim to investigate alterations in WM microstructures and evaluate the relationships between the mean values of diffusion metrics (FA, MD, AD, and RD) and cognitive assessments in SIVD patients. Fifty SIVD patients with (SVCI, N = 25) and without (pre-SVCI, N = 25) cognitive impairments and normal controls (NC, N = 23) underwent DTI and neuropsychological examinations. DTI data were analyzed via TBSS to detect significant changes in WM tracts. Spearman correlation analysis was performed to evaluate relationships between the mean values of diffusion indices and the cognitive assessments. In general, extensive symmetrically altered areas that involved approximately the entire cerebral WM were noted in the pre-SVCI group but were less distinct than that noted in the SVCI group compared with NCs. The genu of corpus callosum exhibited the most damaged WM fiber. Throughout WM, FA was decreased, whereas MD, AD, and RD were increased. Some specific WM tracts in patient groups were significantly correlated with the severity of white matter hyperintensity (WMH), cognitive assessments about executive functions and processing speed. WM integrity has already been damaged at the pre-SVCI stage, which would be associate with future cognitive dysfunction. DTI could potentially establish early biomarkers to detect underlying mechanisms of SIVD.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alves GS, Knöchel VO, Knöchel C, Carvalho AF, Pantel J, Engelhardt E, Laks J (2015) Integrating retrogenesis theory to Alzheimer’s disease pathology: insight from DTI-TBSS investigation of the white matter microstructural integrity Biomed Research International 2015
Amlien IK, Fjell AM (2014) Diffusion tensor imaging of white matter degeneration in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. Neuroscience 276:206–215
Benjamin P, Zeestraten E, Lambert C, Chis Ster I, Williams OA, Lawrence AJ, Patel B, MacKinnon AD, Barrick TR, Markus HS (2016) Progression of MRI markers in cerebral small vessel disease: sample size considerations for clinical trials. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 36:228–240. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2015.113
Biesbroek JM, Weaver NA, Biessels GJ (2017) Lesion location and cognitive impact of cerebral small vessel disease. Clin Sci (London, England : 1979) 131:715–728. https://doi.org/10.1042/cs20160452
Ciulli S, Citi L, Salvadori E, Valenti R, Poggesi A, Inzitari D, Mascalchi M, Toschi N, Pantoni L, Diciotti S (2016) Prediction of impaired performance in trail making test in MCI patients with small vessel disease using DTI data. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 20:1026–1033. https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2016.2537808
D'Souza MM, Gorthi SP, Vadwala K, Trivedi R, Vijayakumar C, Kaur P, Khushu S (2018) Diffusion tensor tractography in cerebral small vessel disease: correlation with cognitive function. Neuroradiol J 31:83–89. https://doi.org/10.1177/1971400916682753
Duering M, Gonik M, Malik R, Zieren N, Reyes S, Jouvent E, Hervé D, Gschwendtner A, Opherk C, Chabriat H, Dichgans M (2013) Identification of a strategic brain network underlying processing speed deficits in vascular cognitive impairment. Neuroimage 66:177–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.10.084
Duering M, Gesierich B, Seiler S, Pirpamer L, Gonik M, Hofer E, Jouvent E, Duchesnay E, Chabriat H, Ropele S, Schmidt R, Dichgans M (2014) Strategic white matter tracts for processing speed deficits in age-related small vessel disease. Neurology 82:1946–1950
Fazekas F, Chawluk JB, Alavi A, Hurtig HI, Zimmerman RA (1987) MR signal abnormalities at 1.5 T in Alzheimer’s dementia and normal aging. AJR Am J Roentgenol 149:351–356. https://doi.org/10.2214/ajr.149.2.351
Galluzzi S, Sheu CF, Zanetti O, Frisoni GB (2005) Distinctive clinical features of mild cognitive impairment with subcortical cerebrovascular disease. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 19:196–203. https://doi.org/10.1159/000083499
Huang J et al (2018) White matter microstructural alterations in clinically isolated syndrome and multiple sclerosis. J Clin Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2018.01.007
Hulst HE, Steenwijk MD, Versteeg A, Pouwels PJW, Vrenken H, Uitdehaag BMJ, Polman CH, Geurts JJG, Barkhof F (2013) Cognitive impairment in MS: impact of white matter integrity, gray matter volume, and lesions. Neurology 80:1025–1032
Joutel A, Chabriat H (2017) Pathogenesis of white matter changes in cerebral small vessel diseases: beyond vessel-intrinsic mechanisms. Clin Sci (London, England : 1979) 131:635–651. https://doi.org/10.1042/CS20160380
Kim YJ, Kwon HK, Lee JM, Kim YJ, Kim HJ, Jung NY, Kim ST, Lee KH, Na DL, Seo SW (2015) White matter microstructural changes in pure Alzheimer’s disease and subcortical vascular dementia. Eur J Neurol 22:709–716. https://doi.org/10.1111/ene.12645
Lawrence AJ, Patel B, Morris RG, Mackinnon AD, Rich PM, Barrick TR, Markus HS (2013) Correction: mechanisms of cognitive impairment in cerebral small vessel disease: multimodal MRI results from the St George’s cognition and neuroimaging in stroke (SCANS) study. PLoS One 8:e61014
Lyoubi-Idrissi AL, Jouvent E, Poupon C, Chabriat H (2017) Diffusion magnetic resonance imaging in cerebral small vessel disease. Rev Neurol (Paris) 173:201–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurol.2017.03.005
Nitkunan A, Barrick TR, Charlton RA, Clark CA, Markus HS (2008) Multimodal MRI in cerebral small vessel disease: its relationship with cognition and sensitivity to change over time. Stroke 39:1999–2005
Palta P, Snitz B, Carlson MC (2016) Neuropsychologic assessment. In: Neuroepidemiology. Handb Clin Neurol:107–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-802973-2.00007-0
Reginold W, Itorralba J, Luedke AC, Fernandez-Ruiz J, Reginold J, Islam O, Garcia A (2016) Tractography at 3T MRI of corpus callosum tracts crossing white matter hyperintensities. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 37:1617–1622. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A4788
Reijmer YD, Fotiadis P, Piantoni G, Boulouis G, Kelly KE, Gurol ME, Leemans A, O’Sullivan MJ, Greenberg SM, Viswanathan A (2016) Small vessel disease and cognitive impairment: the relevance of central network connections. Hum Brain Mapp 37:2446–2454
Roman GC, Erkinjuntti T, Wallin A, Pantoni L, Chui HC (2002) Subcortical ischaemic vascular dementia. The Lancet Neurology 1:426–436
Rosenberg GA, Bjerke M, Wallin A (2014) Multimodal markers of inflammation in the subcortical ischemic vascular disease type of vascular cognitive impairment. Stroke 45:1531–1538. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.113.004534
Sachdev P, Kalaria R, O'Brien J, Skoog I, Alladi S, Black SE, Blacker D, Blazer DG, Chen C, Chui H, Ganguli M, Jellinger K, Jeste DV, Pasquier F, Paulsen J, Prins N, Rockwood K, Roman G, Scheltens P, Internationlal Society for Vascular Behavioral and Cognitive Disorders (2014) Diagnostic criteria for vascular cognitive disorders: a VASCOG statement. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 28:206–218. https://doi.org/10.1097/wad.0000000000000034
Shu N, Wang Z, Qi Z, Li K, He Y (2011) Multiple diffusion indices reveals white matter degeneration in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment: a tract-based spatial statistics study. J Alzheimers Dis 26(Suppl 3):275–285. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-2011-0024
Smith SM (2002) Fast robust automated brain extraction. Hum Brain Mapp 17:143–155. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.10062
Smith SM, Jenkinson M, Johansen-Berg H, Rueckert D, Nichols TE, Mackay CE, Watkins KE, Ciccarelli O, Cader MZ, Matthews PM, Behrens TEJ (2006) Tract-based spatial statistics: voxelwise analysis of multi-subject diffusion data. Neuroimage 31:1487–1505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.02.024
Soares JM, Paulo M, Victor A, Nuno S (2013) A hitchhiker’s guide to diffusion tensor imaging. Front Neurosci 7:31
Sun Y, Cao W, Ding W, Wang Y, Han X, Zhou Y, Xu Q, Zhang Y, Xu J (2016) Cerebral blood flow alterations as assessed by 3D ASL in cognitive impairment in patients with subcortical vascular cognitive impairment: a marker for disease severity. Front Aging Neurosci 8:211. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2016.00211
Sun Q, Chen GQ, Wang XB, Yu Y, Hu YC, Yan LF, Zhang X, Yang Y, Zhang J, Liu B, Wang CC, Ma Y, Wang W, Han Y, Cui GB (2018) Alterations of white matter integrity and hippocampal functional connectivity in type 2 diabetes without mild cognitive impairment. Front Neuroanat 12:21. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnana.2018.00021
Tuladhar AM, van Norden AG, de Laat KF, Zwiers MP, van Dijk EJ, Norris DG, de Leeuw FE (2015) White matter integrity in small vessel disease is related to cognition. Neuroimage Clin 7:518–524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2015.02.003
Tuladhar AM, Lawrence A, Norris DG, Barrick TR, Markus HS, de Leeuw FE (2017) Disruption of rich club organisation in cerebral small vessel disease. Hum Brain Mapp 38:1751–1766. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.23479
van der Holst HM, Tuladhar AM, Zerbi V, van Uden IWM, de Laat KF, van Leijsen EMC, Ghafoorian M, Platel B, Bergkamp MI, van Norden AGW, Norris DG, van Dijk EJ, Kiliaan AJ, de Leeuw FE (2018) White matter changes and gait decline in cerebral small vessel disease. Neuroimage Clin 17:731–738. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2017.12.007
Wang B, Niu Y, Miao L, Cao R, Yan P, Guo H, Li D, Guo Y, Yan T, Wu J, **. Front Aging Neurosci 9:378
Wardlaw JM, Smith EE, Biessels GJ, Cordonnier C, Fazekas F, Frayne R, Lindley RI, O’Brien JT, Barkhof F, Benavente OR, Black SE, Brayne C, Breteler M, Chabriat H, Decarli C, de Leeuw FE, Doubal F, Duering M, Fox NC, Greenberg S, Hachinski V, Kilimann I, Mok V, Oostenbrugge Rv, Pantoni L, Speck O, Stephan BC, Teipel S, Viswanathan A, Werring D, Chen C, Smith C, van Buchem M, Norrving B, Gorelick PB, Dichgans M, STandards for ReportIng Vascular changes on nEuroimaging (STRIVE v1) (2013) Neuroimaging standards for research into small vessel disease and its contribution to ageing and neurodegeneration. Lancet Neurol 12:822–838
Winkler AM, Ridgway GR, Webster MA, Smith SM, Nichols TE (2014) Permutation inference for the general linear model. NeuroImage 92:381–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.01.060
Xu Q, Zhou Y, Cao W, Lin Y, Pan Y, Li Y, Chen S (2010) Diffusion tensor imaging correlates with cognition better than conventional MRI in patients with subcortical ischemic vascular disease. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 30:317–326
Yew B, Nation DA, Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging I (2017) Cerebrovascular resistance: effects on cognitive decline, cortical atrophy, and progression to dementia. Brain 140:1987–2001. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awx112
Yuan JL, Wang SK, Guo XJ, Teng LL, Jiang H, Gu H, Hu WL (2017) Disconnections of cortico-subcortical pathways related to cognitive impairment in patients with Leukoaraiosis: a preliminary diffusion tensor imaging study. Eur Neurol 78:41–47. https://doi.org/10.1159/000477899
Zeestraten EA, Lawrence AJ, Lambert C, Benjamin P, Brookes RL, Mackinnon AD, Morris RG, Barrick TR, Markus HS (2017) Change in multimodal MRI markers predicts dementia risk in cerebral small vessel disease. Neurology 89:1869–1876. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.0000000000004594
Zhou X, Hu X, Zhang C, Wang H, Zhu X, Xu L, Sun Z, Yu Y (2016) Aberrant functional connectivity and structural atrophy in subcortical vascular cognitive impairment: relationship with cognitive impairments. Front Aging Neurosci 8:14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2016.00014
Acknowledgments
Our team thank all patients and healthy volunteers for their participation.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation of China (NO.81671666), the Doctoral Scientific Funds of North Sichuan Medical College (CBY16-QD04), and the Key Project Sichuan Provincial Department of Education (18ZA0211).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 71 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Cheng, R., Chen, L. et al. Alterations of White Matter Integrity in Subcortical Ischemic Vascular Disease with and Without Cognitive Impairment: a TBSS Study. J Mol Neurosci 67, 595–603 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-019-01266-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-019-01266-3