Abstract
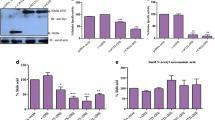
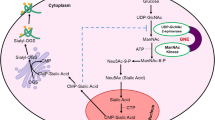
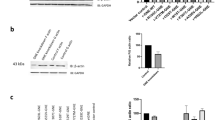
GNE myopathy is a rare neuromuscular genetic disorder characterized by early adult onset and muscle weakness due to mutation in sialic acid biosynthetic enzyme, UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase (GNE). More than 180 different GNE mutations are known all over the world with unclear pathomechanism. Although hyposialylation of glycoproteins is speculated to be the major cause, but cellular mechanism leading to loss of muscle mass has not yet been deciphered. Besides sialic acid biosynthesis, GNE affects other cellular functions such as cell adhesion and apoptosis. In order to understand the effect of mutant GNE protein on cellular functions, differential proteome profile of HEK293 cells overexpressing pathologically relevant recombinant mutant GNE protein (D207V and V603L) was analyzed. These cells, along with vector control and wild-type GNE-overexpressing cells, were subjected to two-dimensional gel electrophoresis coupled with mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF/TOF MS/MS). In the study, 10 differentially expressed proteins were identified. Progenesis same spots software revealed downregulation of peroxiredoxin IV (PrdxIV), an ER-resident H2O2 sensor that regulates neurogenesis. Significant reduction in mRNA and protein levels of PrdxIV was observed in GNE mutant cell lines compared with vector control. However, neither total reactive oxygen species was altered nor H2O2 accumulation was observed in GNE mutant cell lines. Interestingly, ER redox state was significantly affected due to reduced normal GNE enzyme activity. Our study indicates that downregulation of PrdxIV affects ER redox state that may contribute to misfolding and aggregation of proteins in GNE myopathy.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GNE:
-
UDP-N-acetylglucosamine-2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase
- ROS:
-
Reactive Oxygen Species
- PrdxIV:
-
Peroxiredoxin-4
- PrdxIII:
-
Peroxiredoxin-3
- PDI:
-
Protein Disulfide Isomerase
- 2D-GE:
-
Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis
- Ero1:
-
Endoplasmin reticulum oxidoreductase
- H2O2 :
-
Hyderogen peroxide
- MERO-GFP:
-
Mammalian endoplasmic reticulum-localized RedOx-sensitive Green Fluorescent Protein
References
Abbasi, A., Corpeleijn, E., et al. (2012). Peroxiredoxin 4, a novel circulating biomarker for oxidative stress and the risk of incident cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality. Journal of the American Heart Association, 1(5), e002956.
Amsili, S., Zer, H., et al. (2008). UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase (GNE) binds to alpha-actinin 1: Novel pathways in skeletal muscle? PLoS ONE, 3(6), e2477.
Baik, S. C., Kim, K. M., et al. (2004). Proteomic analysis of the sarcosine-insoluble outer membrane fraction of Helicobacter pylori strain 26695. Journal of Bacteriology, 186(4), 949–955.
Broccolini, A., & Mirabella, M. (2015). Hereditary inclusion-body myopathies. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1852(4), 644–650.
Choi, M. H., Ow, J. R., et al. (2016). Oxidative stress-mediated skeletal muscle degeneration: Molecules, mechanisms, and therapies. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2016, 6842568.
Fischer, C., Kleinschnitz, K., et al. (2013). Cell stress molecules in the skeletal muscle of GNE myopathy. BMC Neurology, 13, 24.
Galeano, B., Klootwijk, R., et al. (2007). Mutation in the key enzyme of sialic acid biosynthesis causes severe glomerular proteinuria and is rescued by N-acetylmannosamine. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 117(6), 1585–1594.
Grover, S., & Arya, R. (2014). Role of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase (GNE) in beta1-integrin-mediated cell adhesion. Molecular Neurobiology, 50(2), 257–273.
Harazi, A., Becker-Cohen, M., et al. (2017). The interaction of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase (GNE) and alpha-actinin 2 Is altered in GNE myopathy M743T mutant. Molecular Neurobiology, 54(4), 2928–2938.
Hinderlich, S., Salama, I., et al. (2004). The homozygous M712T mutation of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase results in reduced enzyme activities but not in altered overall cellular sialylation in hereditary inclusion body myopathy. FEBS Letters, 566(1–3), 105–109.
Kanekura, K., Ishigaki, S., et al. (2013). Establishment of a system for monitoring endoplasmic reticulum redox state in mammalian cells. Laboratory Investigation, 93(11), 1254–1258.
Kwofie, M. A., & Skowronski, J. (2008). Specific recognition of Rac2 and Cdc42 by DOCK2 and DOCK9 guanine nucleotide exchange factors. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 283(6), 3088–3096.
Li, H., Chen, Q., et al. (2013). Unfolded protein response and activated degradative pathways regulation in GNE myopathy. PLoS ONE, 8(3), e58116.
Ling, L. U., Tan, K. B., et al. (2011). The role of reactive oxygen species and autophagy in safingol-induced cell death. Cell Death and Disease, 2, e129.
Merksamer, P. I., Trusina, A., et al. (2008). Real-time redox measurements during endoplasmic reticulum stress reveal interlinked protein folding functions. Cell, 135(5), 933–947.
Milman Krentsis, I., Sela, I., et al. (2011). GNE is involved in the early development of skeletal and cardiac muscle. PLoS ONE, 6(6), e21389.
Oka, O. B., & Bulleid, N. J. (2013). Forming disulfides in the endoplasmic reticulum. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1833(11), 2425–2429.
Padhy, G., Sethy, N. K., et al. (2013). Abundance of plasma antioxidant proteins confers tolerance to acute hypobaric hypoxia exposure. High Altitude Medicine & Biology, 14(3), 289–297.
Poynton, R. A., & Hampton, M. B. (2014). Peroxiredoxins as biomarkers of oxidative stress. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1840(2), 906–912.
Roussel, B. D., Kruppa, A. J., et al. (2013). Endoplasmic reticulum dysfunction in neurological disease. Lancet Neurology, 12(1), 105–118.
Schwarzkopf, M., Knobeloch, K. P., et al. (2002). Sialylation is essential for early development in mice. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 99(8), 5267–5270.
Sela, I., Milman Krentsis, I., et al. (2011). The proteomic profile of hereditary inclusion body myopathy. PLoS ONE, 6(1), e16334.
Singh, R., & Arya, R. (2016). GNE myopathy and cell apoptosis: A comparative mutation analysis. Molecular Neurobiology, 53(5), 3088–3101.
Tateyama, M., Takeda, A., et al. (2003). Oxidative stress and predominant Abeta 42(43) deposition in myopathies with rimmed vacuoles. Acta Neuropathologica, 105(6), 581–585.
Tavender, T. J., & Bulleid, N. J. (2010). Peroxiredoxin IV protects cells from oxidative stress by removing H2O2 produced during disulphide formation. Journal of Cell Science, 123(Pt 15), 2672–2679.
Tavender, T. J., Sheppard, A. M., et al. (2008). Peroxiredoxin IV is an endoplasmic reticulum-localized enzyme forming oligomeric complexes in human cells. Biochemical Journal, 411(1), 191–199.
Trachootham, D., Lu, W., et al. (2008). Redox regulation of cell survival. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling, 10(8), 1343–1374.
Tsuruta, Y., Furuta, A., et al. (2002). Increased expression of manganese superoxide dismutase is associated with that of nitrotyrosine in myopathies with rimmed vacuoles. Acta Neuropathologica, 103(1), 59–65.
Valko, M., Leibfritz, D., et al. (2007). Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology, 39(1), 44–84.
Varki, A. (2008). Sialic acids in human health and disease. Trends in Molecular Medicine, 14(8), 351–360.
Varki, N. M., & Varki, A. (2007). Diversity in cell surface sialic acid presentations: Implications for biology and disease. Laboratory Investigation, 87(9), 851–857.
Wang, Z., Sun, Z., et al. (2006). Roles for UDP-GlcNAc 2-epimerase/ManNAc 6-kinase outside of sialic acid biosynthesis: Modulation of sialyltransferase and BiP expression, GM3 and GD3 biosynthesis, proliferation, and apoptosis, and ERK1/2 phosphorylation. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 281(37), 27016–27028.
Weidemann, W., Stelzl, U., et al. (2006). The collapsin response mediator protein 1 (CRMP-1) and the promyelocytic leukemia zinc finger protein (PLZF) bind to UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase (GNE), the key enzyme of sialic acid biosynthesis. FEBS Letters, 580(28–29), 6649–6654.
Yan, Y., Wladyka, C., et al. (2015). Prdx4 is a compartment-specific H2O2 sensor that regulates neurogenesis by controlling surface expression of GDE2. Nature Communications, 6, 7006.
Zito, E., Melo, E. P., et al. (2010). Oxidative protein folding by an endoplasmic reticulum-localized peroxiredoxin. Molecular Cell, 40(5), 787–797.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge Prof Fumihiko Urano, Department of Pathology and Immunology, Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, MO, USA, for MERO-GFP construct. We also thank Prof. Alok Bhattacharya (School of Life Sciences, Jawaharlal Nehru University, New Delhi) and Prof. Sudha Bhattacharya (School of Environmental Sciences, Jawaharlal Nehru University, New Delhi) for thoughtful discussions and progressive comments during the project. We thank Mr. Ashok Kumar Sahu, Technical Officer, Advanced Instrumentation Research Facility, JNU for confocal facility.
Funding
This work was supported by the Department of Science and Technology-PURSE-II (DST/SR/PURSE Phase II/11) and University Grants Commission-UPOE II (Project ID: 16), Govt. of India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare no conflict interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chanana, P., Padhy, G., Bhargava, K. et al. Mutation in GNE Downregulates Peroxiredoxin IV Altering ER Redox Homeostasis. Neuromol Med 19, 525–540 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-017-8467-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-017-8467-5