Abstract
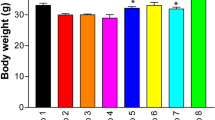
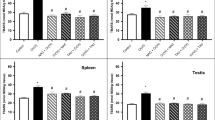
Hexavalent chromium [Cr(VI)] has emerged as a prevailing environmental and occupational contaminant over the past few decades. However, the knowledge is sparse regarding Cr(VI)-induced neurological aberrations, and its remediation through natural bioactive compounds has not been fully explored. This study intended to probe the possible invigorative effects of nutraceuticals such as coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10), biochanin A (BCA), and phloretin (PHL) on Cr(VI) intoxicated Swiss albino mice with special emphasis on Nrf2/HO-1/NQO1 gene expressions. Mice received potassium dichromate (75 ppm) through drinking water and were simultaneously co-treated intraperitoneally with CoQ10 (10 mg/kg), BCA, and PHL (50 mg/kg) each for 30-day treatment period. The statistics highlight the elevated levels of lipid peroxidation (LPO) and protein carbonyl content (PCC) with a concomitant reduction in the superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione-S-transferase (GST), reduced glutathione (GSH), total thiols (TT), catalase (CAT), and cholinesterase activities in the Cr(VI)-exposed mice. The collateral assessment of DNA fragmentation, DNA breakages, and induced histological alterations was in conformity with the above findings in conjugation with the dysregulation in the Nrf2 and associated downstream HO-1 and NQO1 gene expressions. Co-treatment with the selected natural compounds reversed the above-altered parameters significantly, thereby bringing cellular homeostasis in alleviating the Cr(VI)-induced conciliated impairments. Our study demonstrated that the combination of different bioactive compounds shields the brain better against Cr(VI)-induced neurotoxicity by revoking the oxidative stress-associated manifestations. These compounds may represent a new potential combination therapy due to their ability to modulate the cellular antioxidant responses by upregulating the Nrf2/HO-1/NQO1 signaling pathway against Cr(VI)-exposed population.
Highlights
-
Cr(VI)-associated heavy metal exposure poses a significant threat to the environment, especially to living organisms.
-
Cr(VI) exposure for 30 days resulted in the free radical’s generation that caused neurotoxicity in the Swiss albino mice.
-
Natural compounds such as coenzyme Q10, biochanin A, and phloretin counteracted the neurotoxic effect due to Cr(VI) exposure in scavenging of free radicals by enhancing Nrf2/HO-1/NQO1 gene expressions in maintaining the cellular homeostasis.
Graphical abstract













Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article. Data will be available on request. Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to Gyanendra Singh.
References
Aebi H (1974) Catalase. Academic Press, Methods Of Enzymatic Analysis. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-091302-2.50032-3
Aldhahri RS, Alghamdi BS, Alzahrani NA, Bahaidrah KA, Alsufiani HM, Mansouri RA and Ashraf GM (2022) Biochanin A Improves Memory Decline And Brain Pathology In Cuprizone-Induced Mouse Model Of Multiple Sclerosis. Behav Sci (Basel) 12
Atici S, Cinel L, Cinel I, Doruk N, Aktekin M, Akca A, Camdeviren H, Oral U (2004) Opioid Neurotoxicity: Comparison Of Morphine And Tramadol In An Experimental Rat Model. Int J Neurosci 114:1001–1011
Atsdr U (2012) Toxicological Profile For Chromium. Us Department Of Health And Human Services, Public Health Service. https://wwwn.Cdc.Gov/Tsp/Toxprofiles/Toxprofiles.Aspx
Bagchi D, Balmoori J, Bagchi M, Ye X, Williams CB, Stohs SJ (2002) Comparative Effects Of Tcdd, Endrin, Naphthalene And Chromium (Vi) On Oxidative Stress And Tissue Damage In The Liver And Brain Tissues Of Mice. Toxicology 175:73–82
Bagchi D, Stohs SJ, Downs BW, Bagchi M, Preuss HG (2002) Cytotoxicity And Oxidative Mechanisms Of Different Forms Of Chromium. Toxicology 180:5–22
Bagchi D, Vuchetich PJ, Bagchi M, Hassoun EA, Tran MX, Tang L, Stohs SJ (1997) Induction Of Oxidative Stress By Chronic Administration Of Sodium Dichromate [Chromium Vi] And Cadmium Chloride [Cadmium Ii] To Rats. Free Radic Biol Med 22:471–478
Bailey MM, Boohaker JG, Jernigan PL, Townsend MB, Sturdivant J, Rasco JF, Vincent JB, Hood RD (2008) Effects Of Pre- And Postnatal Exposure To Chromium Picolinate Or Picolinic Acid On Neurological Development In Cd-1 Mice. Biol Trace Elem Res 124:70–82
Barceloux DG (1999) Chromium. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol 37:173–194
Bosgelmez Ii, Soylemezoglu T, Guvendik G (2008) The Protective And Antidotal Effects Of Taurine On Hexavalent Chromium-Induced Oxidative Stress In Mice Liver Tissue. Biol Trace Elem Res 125:46–58
Buege JA, Aust SD (1978) Microsomal Lipid Peroxidation. Methods Enzymol 52:302–310
Chen H, Mu L, Cao J, Mu J, Klerks PL, Luo Y, Guo Z, **e L (2016) Accumulation And Effects Of Cr(Vi) In Japanese Medaka (Oryzias Latipes) During Chronic Dissolved And Dietary Exposures. Aquat Toxicol 176:208–216
Dashti A, Soodi M, Amani N (2016) Cr (Vi) Induced Oxidative Stress And Toxicity In Cultured Cerebellar Granule Neurons At Different Stages Of Development And Protective Effect Of Rosmarinic Acid. Environ Toxicol 31:269–277
Ellman GL (1959) Tissue Sulfhydryl Groups. Arch Biochem Biophys 82:70–77
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres V Jr, Feather-Stone RM (1961) A New And Rapid Colorimetric Determination Of Acetylcholinesterase Activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7:88–95
Guilhermino L, Soares AM, Carvalho AP, Lopes MC (1998) Correlation Between Whole Blood Cholinesterase Activity And Cerebral Cortex Cholinesterase Activity In Rats Treated With Parathion. Chemosphere 37:1385–1393
Guo M, Lu H, Qin J, Qu S, Wang W, Guo Y, Liao W, Song M, Chen J, Wang Y (2019) Biochanin A Provides Neuroprotection Against Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury By Nrf2-Mediated Inhibition Of Oxidative Stress And Inflammation Signaling Pathway In Rats. Med Sci Monit 25:8975–8983
Habig WH, Pabst MJ, Jakoby WB (1974) Glutathione S-Transferases. The First Enzymatic Step In Mercapturic Acid Formation. J Biol Chem 249:7130–7139
Han B, Li S, Lv Y, Yang D, Li J, Yang Q, Wu P, Lv Z, Zhang Z (2019) Dietary Melatonin Attenuates Chromium-Induced Lung Injury Via Activating The Sirt1/Pgc-1alpha/Nrf2 Pathway. Food Funct 10:5555–5565
Hao P, Zhu Y, Wang S, Wan H, Chen P, Wang Y, Cheng Z, Liu Y, Liu J (2017) Selenium Administration Alleviates Toxicity Of Chromium(Vi) In The Chicken Brain. Biol Trace Elem Res 178:127–135
Hu ML (1994) Measurement Of Protein Thiol Groups And Glutathione In Plasma. Methods Enzymol 233:380–385
Itoh K, Wakabayashi N, Katoh Y, Ishii T, Igarashi K, Engel JD, Yamamoto M (1999) Keap1 Represses Nuclear Activation Of Antioxidant Responsive Elements By Nrf2 Through Binding To The Amino-Terminal Neh2 Domain. Genes Dev 13:76–86
** Y, Zhang S, Tao R, Huang J, He X, Qu L, Fu Z (2016) Oral Exposure Of Mice To Cadmium (Ii), Chromium (Vi) And Their Mixture Induce Oxidative- And Endoplasmic Reticulum-Stress Mediated Apoptosis In The Livers. Environ Toxicol 31:693–705
Kadiiska MB, ** Investigation. Chem Res Toxicol 7:800–805
Levine RL, Berlett BS, Moskovitz J, Mosoni L, Stadtman ER (1999) Methionine Residues May Protect Proteins From Critical Oxidative Damage. Mech Ageing Dev 107:323–332
Li J, Yu Z, Han B, Li S, Lv Y, Wang X, Yang Q, Wu P, Liao Y, Qu B, Zhang Z (2022) Activation Of The Gpx4/Tlr4 Signaling Pathway Participates In The Alleviation Of Selenium Yeast On Deltamethrin-Provoked Cerebrum Injury In Quails. Mol Neurobiol 59:2946–2961
Li S, Wu P, Han B, Yang Q, Wang X, Li J, Deng N, Han B, Liao Y, Liu Y, Zhang Z (2022) Deltamethrin Induces Apoptosis In Cerebrum Neurons Of Quail Via Promoting Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress And Mitochondrial Dysfunction. Environ Toxicol 37:2033–2043
Li X, He S, Zhou J, Yu X, Li L, Liu Y, Li W (2021) Cr (Vi) Induces Abnormalities In Glucose And Lipid Metabolism Through Ros/Nrf2 Signaling. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 219:112320
Liu Y, Zhang L, Liang J (2015) Activation Of The Nrf2 Defense Pathway Contributes To Neuroprotective Effects Of Phloretin On Oxidative Stress Injury After Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion In Rats. J Neurol Sci 351:88–92
Lu J, Jiang H, Liu B, Baiyun R, Li S, Lv Y, Li D, Qiao S, Tan X, Zhang Z (2018) Grape Seed Procyanidin Extract Protects Against Pb-Induced Lung Toxicity By Activating The Ampk/Nrf2/P62 Signaling Axis. Food Chem Toxicol 116:59–69
Mahmoud AM, Abd El-Twab SM (2017) Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester Protects The Brain Against Hexavalent Chromium Toxicity By Enhancing Endogenous Antioxidants And Modulating The Jak/Stat Signaling Pathway. Biomed Pharmacother 91:303–311
Majumdar A, Nirwane A, Kamble R (2014) New Evidences Of Neurotoxicity Of Aroclor 1254 In Mice Brain: Potential Of Coenzyme Q10 In Abating The Detrimental Outcomes. Environ Health Toxicol 29:E2014001
Marklund S, Marklund G (1974) Involvement Of The Superoxide Anion Radical In The Autoxidation Of Pyrogallol And A Convenient Assay For Superoxide Dismutase. Eur J Biochem 47:469–474
Mary Momo CM, Ferdinand N, Omer Bebe NK, Alexane Marquise MN, Augustave K, Bertin Narcisse V, Herve T and Joseph T (2019) Oxidative Effects Of Potassium Dichromate On Biochemical, Hematological Characteristics, And Hormonal Levels In Rabbit Doe (Oryctolagus Cuniculus). Vet Sci 6
Michiels C, Raes M, Toussaint O, Remacle J (1994) Importance Of Se-Glutathione Peroxidase, Catalase, And Cu/Zn-Sod For Cell Survival Against Oxidative Stress. Free Radic Biol Med 17:235–248
Nyariki JN, Ochola LA, Jillani NE, Nyamweya NO, Amwayi PE, Yole DS, Azonvide L, Isaac AO (2019) Oral Administration Of Coenzyme Q10 Protects Mice Against Oxidative Stress And Neuro-Inflammation During Experimental Cerebral Malaria. Parasitol Int 71:106–120
O’flaherty EJ, Kerger BD, Hays SM, Paustenbach DJ (2001) A Physiologically Based Model For The Ingestion Of Chromium(Iii) And Chromium(Vi) By Humans. Toxicol Sci 60:196–213
Patlolla AK, Barnes C, Yedjou C, Velma VR, Tchounwou PB (2009) Oxidative Stress, Dna Damage, And Antioxidant Enzyme Activity Induced By Hexavalent Chromium In Sprague-Dawley Rats. Environ Toxicol 24:66–73
Pratush A, Kumar A, Hu Z (2018) Adverse Effect Of Heavy Metals (As, Pb, Hg, And Cr) On Health And Their Bioremediation Strategies: A Review. Int Microbiol 21:97–106
Prince PD, Rodriguez Lanzi C, Fraga CG, Galleano M (2019) Dietary (-)-Epicatechin Affects Nf-Kappab Activation And Nadph Oxidases In The Kidney Cortex Of High-Fructose-Fed Rats. Food Funct 10:26–32
Ray RR (2016) Adverse Hematological Effects Of Hexavalent Chromium: An Overview. Interdiscip Toxicol 9:55–65
Salama A, Hegazy R, Hassan A (2016) Intranasal Chromium Induces Acute Brain And Lung Injuries In Rats: Assessment Of Different Potential Hazardous Effects Of Environmental And Occupational Exposure To Chromium And Introduction Of A Novel Pharmacological And Toxicological Animal Model. PLoS ONE 11:E0168688
Sanchez-Diaz G, Escobar F, Badland H, Arias-Merino G, Posada De La Paz M, and Alonso-Ferreira V (2018) Geographic Analysis Of Motor Neuron Disease Mortality And Heavy Metals Released To Rivers In Spain. Int J Environ Res Public Health 15
Shipkowski KA, Sheth CM, Smith MJ, Hooth MJ, White KL Jr, Germolec DR (2017) Assessment Of Immunotoxicity In Female Fischer 344/N And Sprague Dawley Rats And Female B6c3f1 Mice Exposed To Hexavalent Chromium Via The Drinking Water. J Immunotoxicol 14:215–227
Singh G, Thaker R, Sharma A, Parmar D (2021) Therapeutic Effects Of Biochanin A, Phloretin, And Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate In Reducing Oxidative Stress In Arsenic-Intoxicated Mice. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 28:20517–20536
Singh NP, Mccoy MT, Tice RR, Schneider EL (1988) A Simple Technique For Quantitation Of Low Levels Of Dna Damage In Individual Cells. Exp Cell Res 175:184–191
Singh P, Chowdhuri DK (2017) Environmental Presence Of Hexavalent But Not Trivalent Chromium Causes Neurotoxicity In Exposed Drosophila Melanogaster. Mol Neurobiol 54:3368–3387
Sirvio J, Soininen HS, Kutvonen R, Hyttinen JM, Helkala EL, Riekkinen PJ (1987) Acetyl- And Butyrylcholinesterase Activity In The Cerebrospinal Fluid Of Patients With Parkinson’s Disease. J Neurol Sci 81:273–279
Soudani N, Troudi A, Amara IB, Bouaziz H, Boudawara T, Zeghal N (2012) Ameliorating Effect Of Selenium On Chromium (Vi)-Induced Oxidative Damage In The Brain Of Adult Rats. J Physiol Biochem 68:397–409
Suzuki YJ, Carini M, Butterfield DA (2010) Protein Carbonylation. Antioxid Redox Signal 12:323–325
Thompson CM, Proctor DM, Haws LC, Hebert CD, Grimes SD, Shertzer HG, Kopec AK, Hixon JG, Zacharewski TR, Harris MA (2011) Investigation Of The Mode Of Action Underlying The Tumorigenic Response Induced In B6c3f1 Mice Exposed Orally To Hexavalent Chromium. Toxicol Sci 123:58–70
Travacio M, Polo JM, Llesuy S (2001) Chromium (Vi) Induces Oxidative Stress In The Mouse Brain. Toxicology 162:139–148
Tripathi S, Fhatima S, Parmar D, Singh DP, Mishra S, Mishra R and Singh G (2022) Therapeutic Effects Of Coenzymeq10, Biochanin A And Phloretin Against Arsenic And Chromium Induced Oxidative Stress In Mouse (Mus Musculus) Brain. 3 Biotech 12:1–13
Wang J, He C, Wu WY, Chen F, Wu YY, Li WZ, Chen HQ, Yin YY (2015) Biochanin A Protects Dopaminergic Neurons Against Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Damage And Oxidative Stress In A Rat Model Of Parkinson’s Disease. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 138:96–103
Wang XF, **ng ML, Shen Y, Zhu X, Xu LH (2006) Oral Administration Of Cr(Vi) Induced Oxidative Stress, Dna Damage And Apoptotic Cell Death In Mice. Toxicology 228:16–23
Wise JP Jr, Young JL, Cai J, Cai L (2022) Current Understanding Of Hexavalent Chromium [Cr(Vi)] Neurotoxicity And New Perspectives. Environ Int 158:106877
Witt KL, Stout MD, Herbert RA, Travlos GS, Kissling GE, Collins BJ, Hooth MJ (2013) Mechanistic Insights From The Ntp Studies Of Chromium. Toxicol Pathol 41:326–342
Yang X, Fang Y, Hou J, Wang X, Li J, Li S, Zheng X, Liu Y, Zhang Z (2022) The Heart As A Target For Deltamethrin Toxicity: Inhibition Of Nrf2/Ho-1 Pathway Induces Oxidative Stress And Results In Inflammation And Apoptosis. Chemosphere 300:134479
Yang X, Zhang Y, Xu H, Luo X, Yu J, Liu J, Chang RC (2016) Neuroprotection Of Coenzyme Q10 In Neurodegenerative Diseases. Curr Top Med Chem 16:858–866
Zendehdel R, Shetab-Boushehri SV, Azari MR, Hosseini V, Mohammadi H (2015) Chemometrics Models For Assessment Of Oxidative Stress Risk In Chrome-Electroplating Workers. Drug Chem Toxicol 38:174–179
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the Director, ICMR-NIOH Ahmedabad, for providing the necessary infrastructure for conducting this study. The authors acknowledge the help from the Animal House Facility staff in carrying out the study. The authors are also grateful to the Zydus Research Center (ZRC), Ahmedabad, for gifting the Swiss albino mice for the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study objectives. Swapnil Tripathi: investigation, visualization, writing — original draft preparation. Shabrin Fhatima: investigation, visualization; Dharati Parmar: investigation, visualization; Samir Raval: investigation, visualization, resources; Gyanendra Singh: conceptualization, visualization, supervision, writing — reviewing and editing. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
The present study on animals was conducted as per the compliance with the Institutional Animal Ethics Committee (IAEC) of the ICMR-National Institute of Occupational Health (NIOH), Ahmedabad wide approval no. IAEC/NIOH/2018–19/21/02/M.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable
Consent for Publication
Not applicable
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tripathi, S., Parmar, D., Fathima, S. et al. Coenzyme Q10, Biochanin A and Phloretin Attenuate Cr(VI)-Induced Oxidative Stress and DNA Damage by Stimulating Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway in the Experimental Model. Biol Trace Elem Res 201, 2427–2441 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-022-03358-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-022-03358-5