Abstract
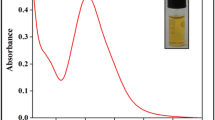
Chemical interactions between nanoparticles and biomolecules are vital for applying nanoparticles in medicine and life science. Development of sensitive, rapid, low-cost, and eco-friendly sensors for the detection of molecules acting as disease indicator is need of an hour. In the present investigation, a green trend for silver nanoparticle synthesis was followed using leaf extract of Calotropis procera. Silver nanoparticles exhibited surface plasmon absorption peak at 421 nm, spherical shape with average size of 10 nm, and zeta potential of −22.4 mV. The as-synthesized silver nanoparticles were used for selective and sensitive detection of cysteine. Cysteine induces aggregation in stable silver nanoparticles owing to selective and strong interaction of –SH group of cysteine with silver nanoparticle surface. Cysteine-induced silver nanoparticle aggregation can be observed visually by change in color of silver nanoparticles from yellow to pink. Cysteine concentration was estimated colorimetrically by measuring absorption at surface plasmon wavelength. Limit of detection for cysteine using silver nanoparticles is ultralow, i.e., 100 nM. The mechanistic insight into cysteine detection by silver nanoparticles was investigated using FT-IR, TEM, DLS, and TLC analysis. Proposed method can be applied for the detection of cysteine in blood plasma and may give rise to a new insight into development of eco-friendly fabricated nanodiagnostic device in future.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wei, X., Qia, L., Tan, J., Liu, R., & Wang, F. (2010). Analytica Chimica Acta, 671, 80–84.
Gazit, V., Ben-Abraham, R., Coleman, R., Weizman, A., & Katz, Y. (2004). Amino Acids, 26, 163–168.
Shahrokhian, S. (2001). Analytical Chemistry, 73, 5972–5978.
Jacob, C., Giles, G. I., Giles, N. M., & Sies, H. (2003). Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 42, 4742–4758.
Chen, W., Kennedy, D. O., Kojima, A., & Matsui-Yuasa, I. (2000). Amino Acids, 18, 319–327.
Nikiforova, V., Kempa, S., Zeh, M., Maimann, S., Kreft, O., Casazza, A. P., Riedel, K., Tauberger, E., Hoefgen, R., & Hesse, H. (2002). Amino Acids, 22, 259–278.
Moreira, P. I., Harris, P. L. R., Zhu, X. W., Santos, M. S., Oliveira, C. R., Smith, M. A., & Perry, G. (2007). Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, 12, 195–206.
Wang, W., Rusin, O., Xu, X., Kim, K. K., Escobedo, J. O., Fakayode, S. O., Fletcher, K. A., Lowry, M., Schowalter, C. M., Lawrence, C. M., Fronczek, F. R., Warner, I. M., & Strongin, R. M. (2005). Journal of the American Chemical Society, 127, 15949–15958.
Droge, W., & Holm, E. (1997). The Journal of Federation of American Society for Experimental Biology, 11, 1077–1089.
The Research Council of Norway. “Obesity: Cysteine plays a key role: Amino acid may be at root of obesity.” Science Daily. 14 June 2011. www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2011/06/110614095649.htm.
Li, L., & Li, B. (2009). Analyst, 134, 1361–1365.
Tcherkas, Y. V., & Denisenko, A. D. (2001). Journal of Chromatography A., 913, 309–313.
Leung, K. H., He, H. Z., Ma, V. P. Y., Chan, D. S. H., Leung, C. H., & Ma, D. L. (2013). Chemical Communications, 49, 771–773.
Chand, R., Han, D. W., Islam, K., Yeon, I. J., Ko, S. S., & Kim, Y. S. (2013). Advanced Materials Research, 647, 482–486.
Vieira, I. C., & Fatibello-Filho, O. (1999). Analytica Chimica Acta, 399, 287–293.
Lin, M., Pei, H., Yang, F., Fan, C., & Zuo, X. (2013). Advanced Materials, 25, 3490–3496.
Brede, C., & Labhasetwar, V. (2013). Advances in Chronic Kidney Disease, 20, 454–465.
Borase, H. P., Patil, C. D., Salunkhe, R. B., Suryawanshi, R. K., Salunke, B. K., & Patil, S. V. (2014). Bioprocess Biosystems Engineering, 37(11), 2223–33.
Rohit, J. V., & Kailasa, S. K. (2014). Analytical Methods, 6, 5934–5941.
Borase, H. P., Patil, C. D., Salunkhe, R. B., Suryawanshi, R. K., Salunke, B. K., & Patil, S. V. (2014). Biotechnology and Applied Biochemistry. doi:10.1002/bab.1306.
Serra, A., Filippo, E., Re, M., Palmisano, M., Vittori-Antisari, M., Buccolieri, A., & Manno, D. (2009). Nanotechnology, 165501, 1–7.
Borase, H. P., Salunke, B. K., Salunkhe, R. B., Patil, C. D., Hallsworth, J. E., Kim, B. S., & Patil, S. V. (2014). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 173, 1–29.
Wang, J., Li, Y. F., Huang, C. Z., & Wu, T. (2008). Analytica Chimica Acta, 626, 37–43.
Han, C., Xu, K., Liu, Q., Liu, X., & Li, J. (2014). Sensors and Actuators B, 202, 574–582.
Ravindran, A., Mani, V., Chandrasekaran, N., & Mukherjee, A. (2011). Talanta, 85, 533–540.
Prasad, G. (1985). Journal of National Integrated Medical Association, 27, 7–10.
Dieye, A. M., Tidjani, M. A., Diouf, A., Bassene, E., & Faye, B. (1993). Dakar Med, 38, 69–72.
Jain, P. K., Verma, R., Kumar, N., & Kumar, A. (1985). Journal of Research in Ayurveda and Sidha, 6, 88–91.
Samy, R. P., Rajendran, P., Li, F., Anandi, N. M., Stiles, B. G., Ignacimuthu, S., Sethi, G., & Chow, V. T. (2007). PLoS ONE, e48514, 1–14.
Kakkar, A., Verma, D. R., Suryavanshi, S., & Dubey, P. (2012). Chemistry of Natural Compound, 48, 155–157.
Moustafa, A. M., Ahmed, S. H., Nabil, Z. I., Hussein, A. A., & Omran, M. A. (2010). Pharmaceutical Biology, 48, 1080–1090.
Chaplin, M. F. (1976). Biochemical Journal, 155, 457–459.
Haiss, W., Thanh, N. T. K., Aveyard, J., & Fernig, D. G. (2007). Analytical Chemistry, 79, 4215–4221.
Martínez, J. C., Chequer, N. A., González, J. L., & Cordova, T. (2012). Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 2, 184–189.
Valodkar, M., Jadeja, R. N., Thounaojam, M. C., Devkar, R. V., & Thakore, S. (2011). Materials Science and Engineering C, 31, 1723–1728.
Baker, D. H., & Czarnecki-Maulden, G. L. (1987). Journal of Nutrition, 117, 1003–1010.
Uvdal, K., Bodo, P., & Liedberg, B. J. (1992). Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 149, 162–173.
Aryal, S., Remant, B. K. C., Dharmaraj, N., Bhattarai, N., Kim, C. H., & Kim, H. Y. (2006). Spectrochimica Acta A, 63, 160–163.
Qian, Q., Deng, J., Wang, D., Yang, L., Yu, P., & Mao, X. (2012). Analytical Chemistry, 84, 9579–9584.
Chen, Z., Luo, S., Liu, C., & Cai, Q. (2009). Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 395, 489–494.
Zhang, F. X., Han, L., Israel, L. B., Daras, J. G., Maye, M. M., Ly, N. K., & Zhong, C. J. (2002). Analyst, 127, 462–465.
Bahram, M., & Mohammadzadeh, E. (2014). Analytical Methods, 6, 6916–6924.
Acknowledgments
Present research was supported by the Department of Science and Technology, Government of India, under the DST INSPIRE Ph.D. fellowship to Mr. Hemant P. Borase. Authors are thankful to anonymous reviewers for critical evaluation of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary 1
Eppendorf tubes showing interaction of amino acids with silver nanoparticles(1- Silver nanoparticles, 2- Cysteine, 3-alanine, 4-arginine, 5- methionine, 6-asparagine, 7-aspartic acid, 8-glutamine, 9-glutamic acid, 10-glycine, 11-histidine, 12-isoleucine, 13-leucine, 14-lysine, 15-phenylalanine, 16-proline, 17-serine, 18-threonine, 19-tryptophan, 20-tyrosine, 21-valine). (JPEG 1026 kb)
Supplementary 2
Parameters studied during cysteine detection using bio functionalized silver nanoparticles. (DOCX 13 kb)
Supplementary 3
TLC analysis of 1. cysteine, 2. Silver nanoparticles and 3. cysteine- silver nanoparticles complex. The develo** system is Butanol: Acetic acid: Water (4:1:5). (JPEG 610 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Borase, H.P., Patil, C.D., Salunkhe, R.B. et al. Bio-Functionalized Silver Nanoparticles: a Novel Colorimetric Probe for Cysteine Detection. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 175, 3479–3493 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1519-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1519-0