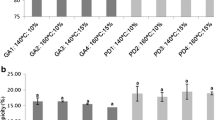
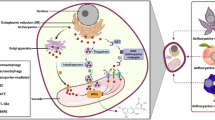
Abstract
Blueberries are an important source of bioactive compounds such as phenolic compounds. The growing interest in these berries is associated with their composition rich in anthocyanins, which represent the most widely studied class of phenolic compounds in blueberry. In addition, anthocyanins are known to bringing benefits to consumers’ health, and are also responsible for their attractive and intense blue coloration. In total, forty-three anthocyanins have been identified, being found cyaninidins, delphinidins, malvidins, petunidins, and peonidins with different ligands. However, these compounds are sensitive to light, oxygen, temperature, and pH variations and are highly unstable and susceptible to degradation. An alternative to increase anthocyanin stability is microencapsulation. Different methods are used in the microencapsulation of blueberry compounds, with spray drying being the most widely used. Several studies showed that microencapsulation was efficient and promising method that incorporates and protects bioactive compounds, thereby prolonging their half-life, in addition to increasing their bioavailability and their controlled release in the gastrointestinal system.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Askar, K. A., Alsawad, Z. H., & Khalaf, M. N. (2015). Evaluation of the pH and thermal stabilities of rosella anthocyanin extracts under solar light. Beni-Suef University Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 4(3), 262–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjbas.2015.06.001
Araujo-Díaz, S. B., Leyva-Porras, C., Aguirre-Bañuelos, P., Álvarez-Salas, C., & Saavedra-Leos, Z. (2017). Evaluation of the physical properties and conservation of the antioxidants content, employing inulin and maltodextrin in the spray drying of blueberry juice. Carbohydrate Polymers, 167, 317–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.03.065
Berg, S., Bretz, M., Hubbermann, E. M., & Schwarz, K. (2012). Influence of different pectins on powder characteristics of microencapsulated anthocyanins and their impact on drug retention of shellac coated granulate. Journal of Food Engineering, 108(1), 158–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2011.06.035
Betz, M., & Kulozik, U. (2011). Whey protein gels for the entrapment of bioactive anthocyanins from bilberry extract. International Dairy Journal, 21(9), 703–710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.idairyj.2011.04.003
Bhatt, D. S., & Debnath, S. C. (2021). Genetic diversity of blueberry genotypes estimated by antioxidant properties and molecular markers. Antioxidants, 10(3), 1–30. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10030458
Bora, A. F. M., Ma, S., Li, X., & Liu, L. (2018). Application of microencapsulation for the safe delivery of green tea polyphenols in food systems: Review and recent advances. Food Research International, 105, 241–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2017.11.047
Buckow, R., Kastell, A., Terefe, N. S., & Versteeg, C. (2010). Pressure and temperature effects on degradation kinetics and storage stability of total anthocyanins in blueberry juice. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 58(18), 10076–10084. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf1015347
Cai, X., Du, X., Cui, D., Wang, X., Yang, Z., & Zhu, G. (2019). Improvement of stability of blueberry anthocyanins by carboxymethyl starch/xanthan gum combinations microencapsulation. Food Hydrocolloids, 91, 238–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2019.01.034
Castañeda-Ovando, A., Pacheco-Hernández, M. D. L., Páez-Hernández, M. E., Rodríguez, J. A., & Galán-Vidal, C. A. (2009). Chemical studies of anthocyanins: A review. Food Chemistry, 113(4), 859–871. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.09.001
Celli, G. B., Dibazar, R., Ghanem, A., & Su-Ling, M. (2016). Degradation kinetics of anthocyanins in freeze-dried microencapsulates from lowbush blueberries (Vaccinium angustifolium Aiton) and prediction of shelf-life. Drying Technology, 34(10), 1175–1184. https://doi.org/10.1080/07373937.2015.1099546
Chen, B. -H., & Inbaraj, B. S. (2019). Nanoemulsion and nanoliposome based strategies for improving anthocyanin stability and bioavailability. Nutrients. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11051052
Colak, N., Torun, H., Gruz, J., Strnad, M., Hermosín-Gutiérrez, I., Hayirlioglu-Ayaz, S., & Ayaz, F. A. (2016). Bog bilberry phenolics, antioxidant capacity and nutrient profile. Food Chemistry, 201, 339–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.01.062
Correia, R., Grace, M. H., Esposito, D., & Lila, M. A. (2017). Wild blueberry polyphenol-protein food ingredients produced by three drying methods: Comparative physico-chemical properties, phytochemical content, and stability during storage. Food Chemistry, 235, 76–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.05.042
Costa, D. V. T. A., Almeida, D. P. F., & Pintado, M. (2015). Effect of atmosphere composition on phenolic phytochemicals of two cultivars of Northern Highbush blueberry. Acta Horticulturae, 1071, 675–680. https://doi.org/10.17660/ActaHortic.2015.1071.89
da Rosa, J. R., Nunes, G. L., Motta, M. H., Fortes, J. P., Weis, G. C. C., Hecktheuer, L. H. R., et al. (2019). Microencapsulation of anthocyanin compounds extracted from blueberry (Vaccinium spp.) by spray drying: Characterization, stability and simulated gastrointestinal conditions. Food Hydrocolloids, 89, 742–748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2018.11.042
da Rosa, J. R., Weis, G. C. C., Moro, K. I. B., Robalo, S. S., Assmann, C. E., da Silva, L. P., et al. (2021). Effect of wall materials and storage temperature on anthocyanin stability of microencapsulated blueberry extract. LWT - Food Science and Technology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2021.111027
de Azevedo Bittencourt, L. L., Silva, K. A., de Sousa, V. P., Fontes-Sant’Ana, G. C., & Rocha-Leão, M. H. (2018). Blueberry residue encapsulation by ionotropic gelation. Plant Foods for Human Nutrition, 73(4), 278–286. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11130-018-0685-y
De Rosso, V. V., & Mercadante, A. Z. (2007). The high ascorbic acid content is the main cause of the low stability of anthocyanin extracts from acerola. Food Chemistry, 103(3), 935–943. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2006.09.047
Debnath-Canning, M., Unruh, S., Vyas, P., Daneshtalab, N., Igamberdiev, A. U., & Weber, J. T. (2020). Fruits and leaves from wild blueberry plants contain diverse polyphenols and decrease neuroinflammatory responses in microglia. Journal of Functional Foods. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2020.103906
Driscoll, K., Deshpande, A., Datta, R., & Ramakrishna, W. (2020). Anti-inflammatory effects of Northern Highbush blueberry extract on an in vitro inflammatory bowel disease model. Nutrition and Cancer, 72(7), 1178–1190. https://doi.org/10.1080/01635581.2019.1673449
Falagán, N., Miclo, T., & Terry, L. A. (2020). Graduated controlled atmosphere: A novel approach to increase “Duke” blueberry storage life. Frontiers in Plant Science. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.00221
Flores, F. P., Singh, R. K., Kerr, W. L., Pegg, R. B., & Kong, F. (2014a). Total phenolics content and antioxidant capacities of microencapsulated blueberry anthocyanins during in vitro digestion. Food Chemistry, 153, 272–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.12.063
Flores, F. P., Singh, R. K., Kerr, W. L., Phillips, D. R., & Kong, F. (2015). In vitro release properties of encapsulated blueberry (Vaccinium ashei) extracts. Food Chemistry, 168, 225–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.07.059
Flores, F. P., Singh, R. K., & Kong, F. (2014b). Physical and storage properties of spray-dried blueberry pomace extract with whey protein isolate as wall material. Journal of Food Engineering, 137, 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2014.03.034
Fracassetti, D., Del Bo’, C., Simonetti, P., Gardana, C., Klimis-Zacas, D., & Ciappellano, S. (2013). Effect of time and storage temperature on anthocyanin decay and antioxidant activity in wild blueberry (Vaccinium angustifolium) powder. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 61(12), 2999–3005. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf3048884
Furtado, P., Figueiredo, P., das Neves, H. C., & Pina, F. (1993). Photochemical and thermal degradation of anthocyanidins. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology, A: Chemistry, 75(2), 113–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/1010-6030(93)80191-B
Giusti, M. M., & Wrolstad, R. E. (2001). Characterization and measurement of anthocyanins by UV-visible spectroscopy. In Current Protocols in Food Analytical Chemistry (pp. 19–31). https://doi.org/10.1002/0471142913.faf0102s00
González-Cruz, E. M., Calderón-Santoyo, M., Barros-Castillo, J. C., & Ragazzo-Sánchez, J. A. (2020). Evaluation of biopolymers in the encapsulation by electrospraying of polyphenolic compounds extracted from blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum L.) variety Biloxi. Polymer Bulletin. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-020-03292-3
Grace, M. H., **ong, J., Esposito, D., Ehlenfeldt, M., & Lila, M. A. (2019). Simultaneous LC-MS quantification of anthocyanins and non-anthocyanin phenolics from blueberries with widely divergent profiles and biological activities. Food Chemistry, 277, 336–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.10.101
Gündüz, K., Serçe, S., & Hancock, J. F. (2015). Variation among highbush and rabbiteye cultivars of blueberry for fruit quality and phytochemical characteristics. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis, 38, 69–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2014.09.007
Guo, J., Giusti, M. M., & Kaletunç, G. (2018). Encapsulation of purple corn and blueberry extracts in alginate-pectin hydrogel particles: Impact of processing and storage parameters on encapsulation efficiency. Food Research International, 107, 414–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2018.02.035
Howard, L. R., Brownmiller, C., Mauromoustakos, A., & Prior, R. L. (2016). Improved stability of blueberry juice anthocyanins by acidification and refrigeration. Journal of Berry Research, 6(2), 189–201. https://doi.org/10.3233/JBR-160133
Huang, W., Yao, L., He, X., Wang, L., Li, M., Yang, Y., & Wan, C. (2018). Hypoglycemic activity and constituents analysis of blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum) fruit extracts. Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy, 11, 357–366. https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S166728
Istek, N., & Gurbuz, O. (2017). Investigation of the impact of blueberries on metabolic factors influencing health. Journal of Functional Foods, 38, 298–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2017.09.039
Jamei, R., & Babaloo, F. (2017). Stability of blueberry (Cornus mas–Yulyush) anthocyanin pigment under pH and co-pigment treatments. International Journal of Food Properties, 20(9), 2128–2133. https://doi.org/10.1080/10942912.2016.1233116
Jiao, X., Wang, Y., Lin, Y., Lang, Y., Li, E., Zhang, X., et al. (2019). Blueberry polyphenols extract as a potential prebiotic with anti-obesity effects on C57BL/6 J mice by modulating the gut microbiota. Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry, 64, 88–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2018.07.008
Jiménez-Aguilar, D. M., Ortega-Regules, A. E., Lozada-Ramírez, J. D., Pérez-Pérez, M. C. I., Vernon-Carter, E. J., & Welti-Chanes, J. (2011). Color and chemical stability of spray-dried blueberry extract using mesquite gum as wall material. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis, 24(6), 889–894. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2011.04.012
Kim, A. N., Lee, K. Y., Kim, B. G., Cha, S. W., Jeong, E. J., Kerr, W. L., & Choi, S. G. (2021). Thermal processing under oxygen–free condition of blueberry puree: Effect on anthocyanin, ascorbic acid, antioxidant activity, and enzyme activities. Food Chemistry. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128345
Kurozawa, L. E., & Hubinger, M. D. (2017). Hydrophilic food compounds encapsulation by ionic gelation. Current Opinion in Food Science, 15, 50–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cofs.2017.06.004
Lang, Y., Li, E., Meng, X., Tian, J., Ran, X., Zhang, Y., et al. (2019). Protective effects of bovine serum albumin on blueberry anthocyanins under illumination conditions and their mechanism analysis. Food Research International, 122, 487–495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2019.05.021
Lamdan, H., Garcia-Lazaro, R. S., Lorenzo, N., Caligiuri, L. G., Alonso, D. F., & Farina, H. G. (2020). Anti-proliferative effects of a blueberry extract on a panel of tumor cell lines of different origin. Experimental Oncology, 42(2), 101–108. https://doi.org/10.32471/exp-oncology.2312-8852.vol-42-no-2.14766
Laokuldilok, T., & Kanha, N. (2015). Effects of processing conditions on powder properties of black glutinous rice (Oryza sativa L.) bran anthocyanins produced by spray drying and freeze drying. LWT - Food Science and Technology, 64(1), 405–411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2015.05.015
Li, D., Li, B., Ma, Y., Sun, X., Lin, Y., & Meng, X. (2017). Polyphenols, anthocyanins, and flavonoids contents and the antioxidant capacity of various cultivars of highbush and half-high blueberries. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis, 62, 84–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2017.03.006
Li, D., Meng, X., & Li, B. (2016). Profiling of anthocyanins from blueberries produced in China using HPLC-DAD-MS and exploratory analysis by principal component analysis. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis, 47, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2015.09.005
Liao, M., Ma, L., Miao, S., Hu, X., Liao, X., Chen, F., & Ji, J. (2021). The in-vitro digestion behaviors of milk proteins acting as wall materials in spray-dried microparticles: Effects on the release of loaded blueberry anthocyanins. Food Hydrocolloids. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.106620
Lim, K., Ma, M., & Dolan, K. D. (2011). Effects of spray drying on antioxidant capacity and anthocyanidin content of blueberry by-products. Journal of Food Science, 76(7), H156–H164. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1750-3841.2011.02286.x
Lin, Y., Huang, G., Zhang, Q., Wang, Y., Dia, V. P., & Meng, X. (2020). Ripening affects the physicochemical properties, phytochemicals and antioxidant capacities of two blueberry cultivars. Postharvest Biology and Technology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2019.111097
Liu, Y., Liu, Y., Tao, C., Liu, M., Pan, Y., & Lv, Z. (2018). Effect of temperature and pH on stability of anthocyanin obtained from blueberry. Journal of Food Measurement and Characterization, 12(3), 1744–1753. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-018-9789-1
Lopes, T. J., Xavier, M. F., Quadri, M. G. N., & Quadri, M. B. (2007). Antocianinas: Uma breve revisão das características estruturais e da estabilidade. Revista Brasileira De Agrociência, 13(3), 291–297.
Lou, H., Yao, J., Sun, Y., Sun, H., Song, Z., Li, H., et al. (2021). Role of blueberry anthocyanin extract in the expression of SIRT1 and NF-κB in rat lens epithelial cells in experimentally induced DM. Current Eye Research, 46(1), 45–51. https://doi.org/10.1080/02713683.2020.1776879
Lu, Y., Liang, X., Cheng, L., & Fang, S. (2020). Microencapsulation of pigments by directly spray-drying of anthocyanins extracts from blueberry pomace: Chemical characterization and extraction modeling. International Journal of Food Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1515/ijfe-2019-0247
Machado, A. P. D., Rezende, C. A., Rodrigues, R. A., Barbero, G. F., Rosa, P. D. V. E., & Martínez, J. (2018). Encapsulation of anthocyanin-rich extract from blackberry residues by spray-drying, freeze-drying and supercritical antisolvent. Powder Technology, 340, 553–562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2018.09.063
Mahdavi, S. A., Jafari, S. M., Ghorbani, M., & Assadpoor, E. (2014). Spray-drying microencapsulation of anthocyanins by natural biopolymers: A review. Drying Technology, 32(5), 509–518. https://doi.org/10.1080/07373937.2013.839562
Malacrida, C. R., & Motta, S. D. (2005). Compostos fenólicos totais e antocianinas em suco de uva. Ciência e Tecnologia De Alimentos, 25(4), 659–664. https://doi.org/10.1590/s0101-20612005000400006
Mar, J. M., Silva, L. S., RabeloMuniz, M. D. S. M. P., Nunomura, S. M., Correa, R. F., et al. (2020). Encapsulation of Amazonian blueberry juices: Evaluation of bioactive compounds and stability. LWT - Food Science and Technology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2020.109152
Mueller, D., Jung, K., Winter, M., Rogoll, D., Melcher, R., Kulozik, U., et al. (2018). Encapsulation of anthocyanins from bilberries—Effects on bioavailability and intestinal accessibility in humans. Food Chemistry, 248, 217–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.12.058
Muñoz-Shugulí, C., Vidal, C. P., Cantero-López, P., & Lopez-Polo, J. (2021). Encapsulation of plant extract compounds using cyclodextrin inclusion complexes, liposomes, electrospinning and their combinations for food purposes. Trends in Food Science and Technology, 108, 177–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2020.12.020
Ochoa, M. R., Kesseler, A. G., Michelis, A. D., Mugridge, A., & Chaves, A. R. (2001). Kinetics of colour change of raspberry, sweet (Prunus avium) and sour (Prunus cerasus) cherries preserves packed in glass containers: Light and room temperature effects. Journal of Food Engineering, 49(1), 55–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0260-8774(00)00184-9
Ozkan, G., Franco, P., de Marco, I., **ao, J., & Capanoglu, E. (2019). A review of microencapsulation methods for food antioxidants: Principles, advantages, drawbacks and applications. Food Chemistry, 272, 494–506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.07.205
Patil, J. S., Kamalapur, M. V., Marapur, S. C., & Kadam, D. V. (2010). Ionotropic gelation and polyelectrolyte complexation: The novel techniques to design hydrogel particulate sustained, modulated drug delivery system: A review. Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures, 5(1), 241–248.
Patras, A., Brunton, N. P., O’Donnell, C., & Tiwari, B. K. (2010). Effect of thermal processing on anthocyanin stability in foods; mechanisms and kinetics of degradation. Trends in Food Science and Technology, 21(1), 3–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2009.07.004
Peng, K., Liu, C., & Wang, S. (2016). Study on stability of anthocyanin from blueberry peel. American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers. https://doi.org/10.13031/aim.20162460709
Pertuzatti, P. B., Barcia, M. T., Gómez-Alonso, S., Godoy, H. T., & Hermosin-Gutierrez, I. (2021). Phenolics profiling by HPLC-DAD-ESI-MSn aided by principal component analysis to classify Rabbiteye and Highbush blueberries. Food Chemistry. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127958
Pertuzatti, P. B., Barcia, M. T., Rebello, L. P. G., Gómez-Alonso, S., Duarte, R. M. T., Duarte, M. C. T., et al. (2016). Antimicrobial activity and differentiation of anthocyanin profiles of rabbiteye and highbush blueberries using HPLC–DAD–ESI-MSn and multivariate analysis. Journal of Functional Foods, 26, 506–516. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2016.07.026
Pieczykolan, E., & Kurek, M. A. (2019). Use of guar gum, gum arabic, pectin, beta-glucan and inulin for microencapsulation of anthocyanins from chokeberry. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 129, 665–671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.02.073
Pires, T. C. S. P., Caleja, C., Santos-Buelga, C., Barros, L., & Ferreira, I. C. F. R. (2020). Vaccinium myrtillus L. fruits as a novel source of phenolic compounds with health benefits and industrial applications—A review. Current Pharmaceutical Design, 26(16), 1917–1928. https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612826666200317132507
Rahaiee, S., Assadpour, E., Esfanjani, A. F., Silva, A. S., & Jafari, S. M. (2020). Application of nano/microencapsulated phenolic compounds against cancer. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2020.102153
Rocha, J. D. C. G., de Barros, F. A. R., Perrone, Í. T., Viana, K. W. C., Tavares, G. M., Stephani, R., & Stringheta, P. C. (2019). Microencapsulation by atomization of the mixture of phenolic extracts. Powder Technology, 343, 317–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2018.11.040
Rodriguez-Amaya, D. B. (2019). Update on natural food pigments—A mini-review on carotenoids, anthocyanins, and betalains. Food Research International, 124, 200–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2018.05.028
Santos-Buelga, C., & González-Paramás, A. M. (2018). Anthocyanins. Encyclopedia of Food Chemistry. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-814026-0.21609-0
Sater, H. M., Bizzio, L. N., Tieman, D. M., & Muñoz, P. D. (2020). A review of the fruit volatiles found in blueberry and other vaccinium species. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 68(21), 5777–5786. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.0c01445
Sezer, E. D., Oktay, L. M., Karadadaş, E., Memmedov, H., Gunel, N. S., & Sözmen, E. (2019). Assessing anticancer potential of blueberry flavonoids, quercetin, kaempferol, and gentisic acid, through oxidative stress and apoptosis parameters on HCT-116 cells. Journal of Medicinal Food, 22(11), 1118–1126. https://doi.org/10.1089/jmf.2019.0098
Shao, X., Zhao, B., Wang, B., Zhao, B., Zhu, Y., Yuan, Z., & Zhang, J. (2019). Neuroprotective effects of blueberry anthocyanins against perfluorooctanoic sulfonate on planarian Dugesia japonica. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 175, 39–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.03.023
Sharif, N., Khoshnoudi-Nia, S., & Jafari, S. M. (2020). Nano/microencapsulation of anthocyanins; a systematic review and meta-analysis. Food Research International. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109077
Shi, M., Loftus, H., McAinch, A. J., & Su, X. Q. (2017). Blueberry as a source of bioactive compounds for the treatment of obesity, type 2 diabetes and chronic inflammation. Journal of Functional Foods, 30, 16–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2016.12.036
Silva, P. I., Stringheta, P. C., Teof́ilo, R. F., & de Oliveira, I. R. N. (2013). Parameter optimization for spray-drying microencapsulation of jaboticaba (Myrciaria jaboticaba) peel extracts using simultaneous analysis of responses. Journal of Food Engineering, 117(4), 538–544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2012.08.039
Silva, S., Costa, E. M., Veiga, M., Morais, R. M., Calhau, C., & Pintado, M. (2020). Health promoting properties of blueberries: A review. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 60(2), 181–200. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2018.1518895
Song, H. -N., Ji, S. -A., Park, H. -R., Kim, H. -H., & Hogstrand, C. (2018). Impact of various factors on color stability of fresh blueberry juice during storage. Preventive Nutrition and Food Science, 23(1), 46–51. https://doi.org/10.3746/pnf.2018.23.1.46
Song, Y., Huang, L., & Yu, J. (2016). Effects of blueberry anthocyanins on retinal oxidative stress and inflammation in diabetes through Nrf2/HO-1 signaling. Journal of Neuroimmunology, 301, 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneuroim.2016.11.001
Sun, J., Bai, W., Zhang, Y., Liao, X., & Hu, X. (2011). Identification of degradation pathways and products of cyanidin-3-sophoroside exposed to pulsed electric field. Food Chemistry, 126(3), 1203–1210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.12.002
Sun, X., Zhou, T., Wei, C., Lan, W., Zhao, Y., Pan, Y., & Wu, V. C. H. (2018). Antibacterial effect and mechanism of anthocyanin rich Chinese wild blueberry extract on various foodborne pathogens. Food Control, 94, 155–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2018.07.012
Sun, Y., Nemec-Bakk, A. S., Mallik, A. U., Bagchi, A. K., Singal, P. K., & Khaper, N. (2019). Blueberry extract attenuates doxorubicin-induced damage in h9c2 cardiac cells. Canadian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology, 97(9), 880–884. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjpp-2019-0031
Svanberg, L., Malmberg, K., Gustinelli, G., Öhgren, C., Persson, I., Brive, L., & Wassén, S. (2019). Effect of anthocyanins on lipid oxidation and microbial spoilage in value-added emulsions with bilberry seed oil, anthocyanins and cold set whey protein hydrogels. Food Chemistry, 272, 273–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.06.064
Taiz, L., & Zeiger, E. (2006). Plant physiology (4th ed., 481 p.). Wadsworth Publishing Company, Beverly.
Tao, Y., Wang, P., Wang, J., Wu, Y., Han, Y., & Zhou, J. (2017). Combining various wall materials for encapsulation of blueberry anthocyanin extracts: Optimization by artificial neural network and genetic algorithm and a comprehensive analysis of anthocyanin powder properties. Powder Technology, 311, 77–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2017.01.078
Tarone, A. G., Cazarin, C. B. B., & Junior, M. R. M. (2020). Anthocyanins: New techniques and challenges in microencapsulation. Food Research International. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109092
Tran, P. H. L., & Tran, T. T. D. (2021). Blueberry supplementation in neuronal health and protective technologies for efficient delivery of blueberry anthocyanins. Biomolecules, 11(1), 1–20. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11010102
Trost, K., Golc-Wondra, A., Prosek, M., & Milivojevic, L. (2008). Anthocyanin degradation of blueberry-Aronia nectar in glass compared with carton during storage. Journal of Food Science, 73(8), S405–S411. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1750-3841.2008.00909.x
Trucillo, P., Campardelli, R., & Reverchon, E. (2018). Production of liposomes loaded with antioxidants using a supercritical CO2 assisted process. Powder Technology, 323, 155–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2017.10.007
Turan, F. T., Cengiz, A., & Kahyaoglu, T. (2015). Evaluation of ultrasonic nozzle with spray-drying as a novel method for the microencapsulation of blueberry’s bioactive compounds. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 32, 136–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2015.09.011
Turan, F. T., & Kahyaoglu, T. (2021). The effect of an ultrasonic spray nozzle on carbohydrate and protein-based coating materials for blueberry extract microencapsulation. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 101(1), 120–130. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.10622
Wang, H., Guo, X., Hu, X., Li, T., Fu, X., & Liu, R. H. (2017a). Comparison of phytochemical profiles, antioxidant and cellular antioxidant activities of different varieties of blueberry (Vaccinium spp.). Food Chemistry, 217, 773–781. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.09.002
Wang, W., Jung, J., & Zhao, Y. (2017b). Chitosan-cellulose nanocrystal microencapsulation to improve encapsulation efficiency and stability of entrapped fruit anthocyanins. Carbohydrate Polymers, 157, 1246–1253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.11.005
Wang, Z., Li, Y., Chen, L., **n, X., & Yuan, Q. (2013). A study of controlled uptake and release of anthocyanins by oxidized starch microgels. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 61(24), 5880–5887. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf400275m
Whyte, A. R., Rahman, S., Bell, L., Edirisinghe, I., Krikorian, R., Williams, C. M., & Burton-Freeman, B. (2021). Improved metabolic function and cognitive performance in middle-aged adults following a single dose of wild blueberry. European Journal of Nutrition, 60(3), 1521–1536. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-020-02336-8
Wilkowska, A., Ambroziak, W., Czyzowska, A., & Adamiec, J. (2016). Effect of microencapsulation by spray-drying and freeze-drying technique on the antioxidant properties of blueberry (Vaccinium myrtillus) juice polyphenolic compounds. Polish Journal of Food and Nutrition Sciences, 66(1), 11–16. https://doi.org/10.1515/pjfns-2015-0015
Wrolstad, R. E., Durst, R. W., & Lee, J. (2005). Tracking color and pigment changes in anthocyanin products. Trends in Food Science and Technology, 16(9), 423–428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2005.03.019
Wu, Y., Zhou, Q., Chen, X., Li, X., Wang, Y., & Zhang, J. (2017a). Comparison and screening of bioactive phenolic compounds in different blueberry cultivars: Evaluation of anti-oxidation and α-glucosidase inhibition effect. Food Research International, 100, 312–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2017.07.004
Wu, Y., Yang, J., Wang, Q., Jiang, N., Tao, Y., & Han, Y. (2017b). Effects of storage time and temperature on quality of blueberry anthocyanin microcapsules. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 33(8), 301–308. https://doi.org/10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.08.040
Wu, Y., Han, Y., Tao, Y., Li, D., **e, G., Show, P. L., & Lee, S. Y. (2020). In vitro gastrointestinal digestion and fecal fermentation reveal the effect of different encapsulation materials on the release, degradation and modulation of gut microbiota of blueberry anthocyanin extract. Food Research International. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109098
Xu, Q., Li, B., Wang, D., Luo, L., Liu, G., & Zhou, Y. (2019). Microencapsulation and stability analysis of blueberry anthocyanins. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/252/5/052133
Zang, Z., Chou, S., Geng, L., Si, X., Ding, Y., Lang, Y., et al. (2021). Interactions of blueberry anthocyanins with whey protein isolate and bovine serum protein: Color stability, antioxidant activity, in vitro simulation, and protein functionality. LWT - Food Science and TechnologyFood Science and Technology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2021.112269
Zhao, C. L., Yu, Y. Q., Chen, Z. J., Wen, G. S., Wei, F. G., Zheng, Q., et al. (2017a). Stability-increasing effects of anthocyanin glycosyl acylation. Food Chemistry, 214, 119–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.07.073
Zhao, L., & Temelli, F. (2017). Preparation of anthocyanin-loaded liposomes using an improved supercritical carbon dioxide method. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 39, 119–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2016.11.013
Zhao, L., Temelli, F., & Chen, L. (2017b). Encapsulation of anthocyanin in liposomes using supercritical carbon dioxide: Effects of anthocyanin and sterol concentrations. Journal of Functional Foods, 34, 159–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2017.04.021
Zheng, Y., Wang, S. Y., Wang, C. Y., & Zheng, W. (2010). Effect of superatmospheric oxygen on anthocyanins, phenolics and antioxidant activity of blueberries and strawberries. Acta Horticulturae, 857, 475–482. https://doi.org/10.17660/ActaHortic.2010.857.59
Zheng, Y., Wang, C. Y., Wang, S. Y., & Zheng, W. (2003). Effect of high-oxygen atmospheres on blueberry phenolics, anthocyanins, and antioxidant capacity. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 51(24), 7162–7169. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf030440k
Zhou, L., **e, M., Yang, F., & Liu, J. (2020a). Antioxidant activity of high purity blueberry anthocyanins and the effects on human intestinal microbiota. LWT - Food Science and Technology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2019.108621
Zhou, T., Wei, C., Lan, W., Zhao, Y., Pan, Y., Sun, X., & Wu, V. C. H. (2020b). The effect of Chinese wild blueberry fractions on the growth and membrane integrity of various foodborne pathogens. Journal of Food Science, 85(5), 1513–1522. https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.15077
Zhu, H., Yangun, Z., Jianwen, T., & Chu, Z. (2018). Effect of a new shell material-jackfruit seed starch on novel flavor microcapsules containg vanilla oil. Industrial Crops and Products, 112, 47–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2017.10.060
Zorenc, Z., Veberic, R., Stampar, F., Koron, D., & Mikulic-Petkovsek, M. (2017). Thermal stability of primary and secondary metabolites in highbush blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum L.) purees. LWT - Food Science and Technology, 76, 79–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2016.10.048
Acknowledgements
The authors also thank Atlas Assessoria Linguística for help with the English language.
Funding
Research support was provided by Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) and the Fundação Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal Nível Superior (CAPES).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Neuenfeldt, N.H., de Moraes, D.P., de Deus, C. et al. Blueberry Phenolic Composition and Improved Stability by Microencapsulation. Food Bioprocess Technol 15, 750–767 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-021-02749-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-021-02749-1