Abstract
Purpose of review
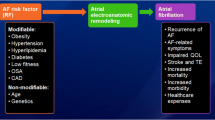
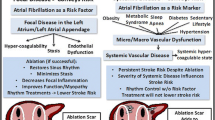
Atrial fibrillation (AF) predisposes to embolic strokes and reduced quality of life. Ablation (catheter-based or surgically performed) can be employed to promote the maintenance of sinus rhythm in a carefully selected subset of patients with AF. The goal of this review is to discuss the indications and techniques for AF ablation, as well as post-procedural outcomes.
Recent findings
Atrial fibrillation ablation improves quality of life in patients with atrial fibrillation although no clear reduction in stroke or overall mortality has been shown.
Summary
Familiarity with the indications for AF ablation is important for all cardiologists, as is having a sound understanding of the efficacy of the procedure and potential complications. Furthermore, acquiring a grasp of the different modalities of AF ablation (including percutaneous endocardial techniques and surgical ablation approaches) will help to facilitate effective and appropriate referrals.

Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Chugh SS, Havmoeller R, Narayanan K, et al. Worldwide epidemiology of atrial fibrillation: a global burden of disease 2010 study. Circulation. 2014;129:837–47.
Colilla S, Crow A, Petkun W, Singer DE, Simon T, Liu X. Estimates of current and future incidence and prevalence of atrial fibrillation in the U.S. adult population. Am J Cardiol. 2013;112:1142–7.
Calkins H, Reynolds MR, Spector P, Sondhi M, Xu Y, Martin A, et al. Treatment of atrial fibrillation with antiarrhythmic drugs or radiofrequency ablation. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2009;2:349–61.
Kuck K-H, Brugada J, Fürnkranz A, et al. Cryoballoon or radiofrequency ablation for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:2235–45.
Wilber DJ, Pappone C, Neuzil P, et al. Comparison of antiarrhythmic drug therapy and radiofrequency catheter ablation in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. JAMA. 2010;303:333.
• Packer DL, Mark DB, Robb RA, et al. Effect of catheter ablation vs antiarrhythmic drug therapy on mortality, stroke, bleeding, and cardiac arrest among patients with atrial fibrillation. JAMA. 2019;321:1261 Recent large randomized clinical trail that did not show a mortality benefit with catheter ablation in patients with symptomatic AF. However, catheter ablation did significantly reduce AF recurrence and improve quality of life.
Graves KG, Jacobs V, May HT, Cutler MJ, Day JD, Bunch TJ. Atrial fibrillation ablation and its impact on stroke. Curr Treat Options Cardiovasc Med. 2018;20:2.
Bunch TJ, May HT, Bair TL, Crandall BG, Cutler MJ, Day JD, et al. Five-year impact of catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation in patients with a prior history of stroke. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2018;29:221–6.
Barra S, Baran J, Narayanan K, et al. Association of catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation with mortality and stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Cardiol. 2018;266:136–42.
Mark DB, Anstrom KJ, Sheng S, et al. Effect of catheter ablation vs medical therapy on quality of life among patients with atrial fibrillation. JAMA. 2019;321:1275.
Blomström-Lundqvist C, Gizurarson S, Schwieler J, et al. Effect of catheter ablation vs antiarrhythmic medication on quality of life in patients with atrial fibrillation. JAMA. 2019;321:1059.
January CT, Wann LS, Calkins H, et al. 2019 AHA/ACC/HRS Focused update of the 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS guideline for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000000665.
• Marrouche NF, Brachmann J, Andresen D, et al. Catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation with heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:417–27 Small randomized clinical trial which showed a mortality benefit in patients with heart failure and AF who underwent catheter ablation. First randomized clinical trial to show this benefit.
Fink T, Rexha E, Schlüter M, et al. Positive impact of pulmonary vein isolation on biventricular pacing in nonresponders to cardiac resynchronization therapy. Heart Rhythm. 2019;16:416–23.
Cheng DCH, Ad N, Martin J, Berglin EE, Chang B-C, Doukas G, et al. Surgical ablation for atrial fibrillation in cardiac surgery. Innov Technol Tech Cardiothorac Vasc Surg. 2010;5:84–96.
Badhwar V, Rankin JS, Ad N, et al. Surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation in the United States: trends and propensity matched outcomes. Ann Thorac Surg. 2017;104:493–500.
Ad N, Damiano RJ, Badhwar V, Calkins H, La Meir M, Nitta T, et al. Expert consensus guidelines: examining surgical ablation for atrial fibrillation. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2017;153:1330–1354.e1.
Zipes DP, Jalife J, Stevenson WG, William G Cardiac electrophysiology: from cell to bedside
Haines DE. The biophysics of radiofrequency catheter ablation in the heart: the importance of temperature monitoring. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 1993;16:586–91.
Arentz T, Weber R, Bürkle G, Herrera C, Blum T, Stockinger J, et al. Small or large isolation areas around the pulmonary veins for the treatment of atrial fibrillation? Circulation. 2007;115:3057–63.
Oral H, Scharf C, Chugh A, Hall B, Cheung P, Good E, et al. Catheter ablation for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 2003;108:2355–60.
Haïssaguerre M, Jaïs P, Shah DC, Garrigue S, Takahashi A, Lavergne T, et al. Electrophysiological end point for catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation initiated from multiple pulmonary venous foci. Circulation. 2000;101:1409–17.
Mantovan R, Macle L, De Martino G, et al. Relationship of quality of life with procedural success of atrial fibrillation (AF) ablation and postablation AF burden: substudy of the STAR AF randomized trial. Can J Cardiol. 2013;29:1211–7.
Kochhäuser S, Jiang C-Y, Betts TR, et al. Impact of acute atrial fibrillation termination and prolongation of atrial fibrillation cycle length on the outcome of ablation of persistent atrial fibrillation: a substudy of the STAR AF II trial. Heart Rhythm. 2017;14:476–83.
Sau A, Al-Aidarous S, Howard J, et al. Optimum lesion set and predictors of outcome in persistent atrial fibrillation ablation: a meta-regression analysis. Europace. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1093/europace/euz108.
Tse H-F, Lee KLF, Fan K, Lau C-P. Nonfluoroscopic magnetic electroanatomic map** to facilitate focal pulmonary veins ablation for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2002;25:57–61.
Pappone C, Oreto G, Lamberti F, et al. Catheter ablation of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation using a 3D map** system. Circulation. 1999;100:1203–8.
Jaïs P, Haïssaguerre M, Shah DC, Takahashi A, Hocini M, Lavergne T, et al. Successful irrigated-tip catheter ablation of atrial flutter resistant to conventional radiofrequency ablation. Circulation. 1998;98:835–8.
Kobza R, Hindricks G, Tanner H, Schirdewahn P, Dorszewski A, Piorkowski C, et al. Late recurrent arrhythmias after ablation of atrial fibrillation: incidence, mechanisms, and treatment. Heart Rhythm. 2004;1:676–83.
Macle L, Jaïs P, Weerasooriya R, Hocini M, Shah DC, Choi K-J, et al. Irrigated-tip catheter ablation of pulmonary veins for treatment of atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2002;13:1067–73.
Natale A, Reddy VY, Monir G, et al. Paroxysmal AF catheter ablation with a contact force sensing catheter. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;64:647–56.
Reddy VY, Dukkipati SR, Neuzil P, et al. Randomized, controlled trial of the safety and effectiveness of a contact force–sensing irrigated catheter for ablation of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 2015;132:907–15.
•• Calkins H, Hindricks G, Cappato R, et al. 2017 HRS/EHRA/ECAS/APHRS/SOLAECE Expert consensus statement on catheter and surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation. Europace. 2018;20:157–208 Recent guidelines on both catheter and surgical ablation of AF. Summarizes relevant research and literature related to AF ablation.
Ganesan AN, Shipp NJ, Brooks AG, Kuklik P, Lau DH, Lim HS, et al. Long-term outcomes of catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Heart Assoc. 2013. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.112.004549.
Baman TS, Jongnarangsin K, Chugh A, et al. Prevalence and predictors of complications of radiofrequency catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2011;22:626–31.
Cappato R, Calkins H, Chen S-A, et al. Updated worldwide survey on the methods, efficacy, and safety of catheter ablation for human atrial fibrillation. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2010;3:32–8.
Neumann T, Vogt J, Schumacher B, et al. Circumferential pulmonary vein isolation with the cryoballoon technique. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008;52:273–8.
Packer DL, Kowal RC, Wheelan KR, et al. Cryoballoon ablation of pulmonary veins for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;61:1713–23.
Guhl EN, Siddoway D, Adelstein E, et al. Incidence and predictors of complications during cryoballoon pulmonary vein isolation for atrial fibrillation. J Am Heart Assoc. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.116.003724.
Mugnai G, de Asmundis C, Ciconte G, et al. Incidence and characteristics of complications in the setting of second-generation cryoballoon ablation: a large single-center study of 500 consecutive patients. Heart Rhythm. 2015;12:1476–82.
Cardoso R, Mendirichaga R, Fernandes G, Healy C, Lambrakos LK, Viles-Gonzalez JF, et al. Cryoballoon versus radiofrequency catheter ablation in atrial fibrillation: a meta-analysis. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2016;27:1151–9.
Di Biase L, Burkhardt JD, Santangeli P, et al. Periprocedural stroke and bleeding complications in patients undergoing catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation with different anticoagulation management. Circulation. 2014;129:2638–44.
Hakalahti A, Uusimaa P, Ylitalo K, Raatikainen MJP. Catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation in patients with therapeutic oral anticoagulation treatment. Europace. 2011;13:640–5.
Wazni OM, Beheiry S, Fahmy T, et al. Atrial fibrillation ablation in patients with therapeutic international normalized ratio. Circulation. 2007;116:2531–4.
Calkins H, Willems S, Gerstenfeld EP, et al. Uninterrupted Dabigatran versus warfarin for ablation in atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2017;376:1627–36.
Cappato R, Marchlinski FE, Hohnloser SH, et al. Uninterrupted rivaroxaban vs. uninterrupted vitamin K antagonists for catheter ablation in non-valvular atrial fibrillation. Eur Heart J. 2015;36:1805–11.
Scherr D, Dalal D, Chilukuri K, et al. Incidence and predictors of left atrial thrombus prior to catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2009;20:379–84.
McCready JW, Nunn L, Lambiase PD, Ahsan SY, Segal OR, Rowland E, et al. Incidence of left atrial thrombus prior to atrial fibrillation ablation: is pre-procedural transoesophageal echocardiography mandatory? Europace. 2010;12:927–32.
Santangeli P, Zado ES, Hutchinson MD, et al. Prevalence and distribution of focal triggers in persistent and long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm. 2016;13:374–82.
Shah D, Haissaguerre M, Jais P, Hocini M. Nonpulmonary vein foci: do they exist? Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2003;26:1631–5.
Chen S-A, Tai C-T. Catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation originating from the non-pulmonary vein foci. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2005;16:229–32.
Di Biase L, Burkhardt JD, Mohanty P, et al. Left atrial appendage. Circulation. 2010;122:109–18.
He X, Zhou Y, Chen Y, Wu L, Huang Y, He J. Left atrial posterior wall isolation reduces the recurrence of atrial fibrillation: a meta-analysis. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2016;46:267–74.
Tamborero D, Mont L, Berruezo A, et al. Left atrial posterior wall isolation does not improve the outcome of circumferential pulmonary vein ablation for atrial fibrillation. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2009;2:35–40.
Kim YG, Shim J, Oh S-K, Lee K-N, Choi J-I, Kim Y-H. Electrical isolation of the left atrial appendage increases the risk of ischemic stroke and transient ischemic attack regardless of postisolation flow velocity. Heart Rhythm. 2018;15:1746–53.
Cox JL, Boineau JP, Schuessler RB, Ferguson TB, Cain ME, Lindsay BD, et al. Successful surgical treatment of atrial fibrillation. JAMA. 1991;266:1976.
Chiappini B, Martìn-Suàrez S, LoForte A, Arpesella G, Di Bartolomeo R, Marinelli G. Cox/Maze III operation versus radiofrequency ablation for the surgical treatment of atrial fibrillation: a comparative study. Ann Thorac Surg. 2004;77:87–92.
•• Badhwar V, Rankin JS, Damiano RJ, et al. The Society of Thoracic Surgeons 2017 Clinical practice guidelines for the surgical treatment of atrial fibrillation. Ann Thorac Surg. 2017;103:329–41 Recent update from the Thoracic Surgeons Society which supports the AF ablation in most surgical interventions. Summarizes research relating to AF ablation and mortality, stroke, and quality of stroke.
Kim WK, Kim HJ, Kim JB, Jung S-H, Choo SJ, Chung CH, et al. Concomitant ablation of atrial fibrillation in rheumatic mitral valve surgery. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2019;157:1519–1528.e5.
Ad N, Holmes SD, Rongione AJ, Badhwar V, Wei L, Fornaresio LM, et al. The long-term safety and efficacy of concomitant Cox maze procedures for atrial fibrillation in patients without mitral valve disease. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2019;157:1505–14.
Rankin JS, Grau-Sepulveda MV, Ad N, et al. Associations between surgical ablation and operative mortality after mitral valve procedures. Ann Thorac Surg. 2018;105:1790–6.
Damiano RJ, Gaynor SL, Bailey M, Prasad S, Cox JL, Boineau JP, et al. The long-term outcome of patients with coronary disease and atrial fibrillation undergoing the cox maze procedure. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2003;126:2016–21.
Akpinar B, Sanisoglu I, Guden M, Sagbas E, Caynak B, Bayramoglu Z. Combined off-pump coronary artery bypass grafting surgery and ablative therapy for atrial fibrillation: early and mid-term results. Ann Thorac Surg. 2006;81:1332–7.
Phan K, **e A, La Meir M, Black D, Yan TD. Surgical ablation for treatment of atrial fibrillation in cardiac surgery: a cumulative meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Heart. 2014;100:722–30.
Barnett SD, Ad N. Surgical ablation as treatment for the elimination of atrial fibrillation: a meta-analysis. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2006;131:1029–35.
Budera P, Straka Z, Osmancik P, et al. Comparison of cardiac surgery with left atrial surgical ablation vs. cardiac surgery without atrial ablation in patients with coronary and/or valvular heart disease plus atrial fibrillation: final results of the PRAGUE-12 randomized multicentre study. Eur Heart J. 2012;33:2644–52.
Suwalski P, Kowalewski M, Jasiński M, et al. Survival after surgical ablation for atrial fibrillation in mitral valve surgery: analysis from the Polish National Registry of Cardiac Surgery Procedures (KROK). J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2019;157:1007–18 e4.
• Iribarne A, DiScipio AW, McCullough JN, et al. Surgical atrial fibrillation ablation improves long-term survival: a multicenter analysis. Ann Thorac Surg. 2019;107:135–42 Retrospective multicenter analysis of >20,000 patients that addresses the issue of mortality benefit for surgical ablation in AF. Suggests that surgical ablation improves mortality.
Ad N, Holmes SD, Friehling T. Minimally invasive stand-alone cox maze procedure for persistent and long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCEP.117.005352.
Pasic M, Musci M, Siniawski H, Grauhan O, Edelmann B, Tedoriya T, et al. The cox maze III procedure: parallel normalization of sinus node dysfunction, improvement of atrial function, and recovery of the cardiac autonomic nervous system. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1999;118:287–96.
Gammie JS, Haddad M, Milford-Beland S, Welke KF, Ferguson TB, O’Brien SM, et al. Atrial fibrillation correction surgery: lessons from the society of thoracic surgeons national cardiac database. Ann Thorac Surg. 2008;85:909–14.
Buber J, Luria D, Sternik L, et al. Left atrial contractile function following a successful modified maze procedure at surgery and the risk for subsequent thromboembolic stroke. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;58:1614–21.
Rankin JS. Amiodarone and cardiac surgery. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2007;134:271.
Ad N, Holmes SD, Shuman DJ, Pritchard G, Miller CE. Amiodarone after surgical ablation for atrial fibrillation: is it really necessary? A prospective randomized controlled trial. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2016;151:798–803.
Kiser AC, Landers M, Horton R, Hume A, Natale A, Gersak B. The convergent procedure: a multidisciplinary atrial fibrillation treatment. Heart Surg Forum. 2010;13:E317–21.
Honarbakhsh S, Birch S, Baker V, O’Brien B, Lowe M, Hunter R, et al. Radiofrequency balloon catheter ablation for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation, radiance study—a UK experience. EP Eur. 2017;19:i21.
Wojtaszczyk A, Caluori G, Pešl M, Melajova K, Stárek Z. Irreversible electroporation ablation for atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2018;29:643–51.
Wittkampf FHM, van Es R, Neven K. Electroporation and its relevance for cardiac catheter ablation. JACC Clin Electrophysiol. 2018;4:977–86.
Reddy VY, Neuzil P, Koruth JS, Petru J, Funosako M, Cochet H, Sediva L, Chovanec M, Dukkipati SR, Jais P (2019) Pulsed field ablation for pulmonary vein isolation in atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol 26225.
DeSimone CV, Kapa S, Asirvatham SJ. Electroporation: past and future of catheter ablation. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2014;7:573–5.
von Oppell UO, Masani N, O’Callaghan P, Wheeler R, Dimitrakakis G, Schiffelers S. Mitral valve surgery plus concomitant atrial fibrillation ablation is superior to mitral valve surgery alone with an intensive rhythm control strategy. Eur J Cardio-Thoracic Surg. 2009;35:641–50.
Jessurun ER, van Hemel NM, Defauw JJ, Brutel De La Rivière A, Stofmeel MAM, Kelder JC, et al. A randomized study of combining maze surgery for atrial fibrillation with mitral valve surgery. J Cardiovasc Surg. 2003;44:9–18.
Verma A, Ha ACT, Kirchhof P, et al. The optimal anti-coagulation for enhanced-risk patients post–catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation (OCEAN) trial. Am Heart J. 2018;197:124–32.
Huxley RR, Lopez FL, Folsom AR, Agarwal SK, Loehr LR, Soliman EZ, et al. Absolute and attributable risks of atrial fibrillation in relation to optimal and borderline risk factors: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study. Circulation. 2011;123:1501–8.
Munger TM, Dong Y-X, Masaki M, et al. Electrophysiological and hemodynamic characteristics associated with obesity in patients with atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;60:851–60.
Holmqvist F, Guan N, Zhu Z, et al. Impact of obstructive sleep apnea and continuous positive airway pressure therapy on outcomes in patients with atrial fibrillation—results from the Outcomes Registry for Better Informed Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation (ORBIT-AF). Am Heart J. 2015;169:647–654.e2.
Trembley-Gravel M, White M, Roy D, et al. Blood pressure and atrial fibrillation: a combined AF-CHF and AFFIRM analysis. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2015;26:509–14.
Huxley RR, Alonso A, Lopez FL, Filion KB, Agarwal SK, Loehr LR, et al. Type 2 diabetes, glucose homeostasis and incident atrial fibrillation: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities study. Heart. 2012;98:133–8.
Ettinger PO, Wu CF, De La Cruz C, Weisse AB, Ahmed SS, Regan TJ. Arrhythmias and the “Holiday Heart”: alcohol-associated cardiac rhythm disorders. Am Heart J. 1978;95:555–62.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Arrhythmia
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patel, N.J., Maradey, J.A. & Bhave, P.D. Atrial Fibrillation Ablation: Indications and Techniques. Curr Treat Options Cardio Med 21, 43 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11936-019-0747-y
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11936-019-0747-y