Abstract
Psoriatic arthritis is a form of inflammatory arthritis that is frequently associated with psoriasis. Individuals with this disease present with heterogeneous clinical manifestations, making it challenging to diagnose and select optimal treatment strategies. Perhaps, not unsurprisingly, there are currently no molecular diagnostic or prognostic tests to confirm if a patient has the disease or predict how they may respond to therapy. Instead, a range of classification criteria have been developed, and the experience of the treating clinician is heavily relied upon. It is therefore widely accepted that there is a significant and as yet unmet need for effective molecular markers in psoriatic arthritis. Protein mediators drive disease pathogenesis and, therefore, represent logical potential biomarkers. Indeed, significant advances have recently been made by the introduction of multiplexed protein biomarker tests for monitoring disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. At the same time, recent advances in proteomics have enhanced the capabilities for the detection and discovery of protein biomarkers. These advances offer renewed opportunities for the development of multi-protein biomarker signatures to support clinical decision-making in the diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of psoriatic arthritis. This review summarises the pathogenesis of psoriatic arthritis, highlighting specific areas of unmet clinical need. Furthermore, it seeks to illustrate how the latest developments in proteomic technologies could be used to enhance our understanding of the molecular pathology of psoriatic arthritis and improve clinical outcomes and quality of life for patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hirsch JHK, Burlingame AL, Matthey MA. Proteomics: current techniques and potential applications to lung disease. Am J Physiol. 2004;28(7):17–23.
Whiteaker JR, Halusa GN, Hoofnagle AN, Sharma V, MacLean B, Yan P, et al. CPTAC assay Portal: a repository of targeted proteomic assays. Nat Methods. 2014;7:703–4.
Yates JR, Ruse CI, Nakorchevsky A. Proteomics by mass spectrometry: approaches, advances, and applications. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2009;11:49–79.
Helliwell PS, FitzGerald O, Fransen J, Gladman DD, Kreuger GG, Callis-Duffin K, et al. The development of candidate composite disease activity and responder indices for psoriatic arthritis (GRACE project). Ann Rheum Dis. 2013;72(6):986–91.
LaFramboise WA, Dhir R, Kelly LA, Petrosko P, Krill-Burger JM, Sciulli CM, et al. Serum protein profiles predict coronary artery disease in symptomatic patients referred for coronary angiography. BMC Med. 2012;10:157.
Curtis JR, van der Helm-van Mil AH, Knevel R, Huizinga TW, Haney DJ, Shen Y, et al. Validation of a novel multibiomarker test to assess rheumatoid arthritis disease activity. Arthritis Care Res. 2012;64(12):1794–803.
Eastman PS, Manning WC, Qureshi F, Haney D, Cavet G, Alexander C, et al. Characterization of a multiplex, 12-biomarker test for rheumatoid arthritis. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2012;70:415–24.
Punzi L, Podswiadek M, Sfriso P, Oliviero F, Fiocco U, Todesco S. Pathogenetic and clinical rationale for TNF-blocking therapy in psoriatic arthritis. Autoimmun Rev. 2007;6:524–8.
Duarte GV, Faillace C. Freire de Carvalho J: Psoriatic arthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2012;26:147–56.
Moll JMWV. Psoriatic Arthritis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1973;3(1):55–78.
Taylor W, Gladman D, Helliwell P, Marchesoni A, Mease P, Mielants H. Classification criteria for psoriatic arthritis: development of new criteria from a large international study. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54:2665–73.
Alamanos Y, Voulgari PV. Drosos Aa: Incidence and prevalence of psoriatic arthritis: a systematic review. J Rheumatol. 2008;35:1354–8.
Leung YY, Tam LS, Ho KW, Lau WM, Li TK-Y, Zhu TY, et al. Evaluation of the CASPAR criteria for psoriatic arthritis in the Chinese population. Rheumatology (Oxford, England). 2010;49:112–5.
Coates LC, Conaghan PG, Emery P, Green MJ, Ibrahim G, MacIver H, et al. Sensitivity and specificity of the classification of psoriatic arthritis criteria in early psoriatic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64:3150–5.
Eder L, Chandran V, Shen H, Cook RJ, Shanmugarajah S, Rosen CF, et al. Incidence of arthritis in a prospective cohort of psoriasis patients. Arthritis Care Res. 2011;63:619–22.
Ogdie A, Langan S, Love T, Haynes K, Shin D, Seminara N, et al. Prevalence and treatment patterns of psoriatic arthritis in the UK. Rheumatology (Oxford, England). 2013;52:568–75.
Winchester R. Epidemiology, genetics and management of psoriatic arthritis 2013: focus on developments of who develops the disease, its clinical features, and emerging treatment options. Psoriasis: Targets Ther. 2013;11.
Reich K, Krüger K, Mössner R, Augustin M. Epidemiology and clinical pattern of psoriatic arthritis in Germany: a prospective interdisciplinary epidemiological study of 1511 patients with plaque-type psoriasis. Br j dermatol. 2009;160:1040–7.
Yang Q, Qu L, Tian H, Hu Y, Peng J, Yu X, et al. Prevalence and characteristics of psoriatic arthritis in Chinese patients with psoriasis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol: JEADV. 2011;25:1409–14.
Y-y L, L-s T, Li EK. The Perspective on Psoriatic Arthritis in Asia. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2011;369–375.
Costello PJ, Winchester RJ, Curran SA, Peterson KS, Kane DJ, Bresnihan B, et al. Psoriatic Arthritis Joint Fluids Are Characterized by CD8 and CD4 T Cell Clonal Expansions that Appear Antigen Driven. J Immunol. 2001;166:2878–86.
Borgato LPA, Beri R, Codella O, Frigo A, Simeoni S, Pacor ML, et al. The T cell receptor repertoire in psoriatic synovitis is restricted and T lymphocytes expressing the same TCR are present in joint and skin lesions. J Rheumatol. 2002;29:1914–9.
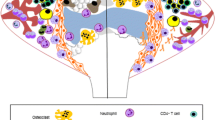
Veale DJ, Ritchlin C, FitzGerald O. Immunopathology of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005;64 Suppl 2:ii26–9.
Menon B, Gullick NJ, Walter GJ, Rajasekhar M, Garrood T, Evans HG, et al. Interleukin-17+CD8+ T cells are enriched in the joints of patients with psoriatic arthritis and correlate with disease activity and joint damage progression. Arthritis Rheumatol (Hoboken, NJ). 2014;66:1272–81.
van Kuijk AWR, Reinders-Blankert P, Smeets TJM, Dijkmans BC, Tak PP. Detailed analysis of the cell infiltrate and the expression of mediators of synovial inflammation and joint destruction in the synovium of patients with psoriatic arthritis: implications for treatment. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006;65:1551–7.
Lande R, Giacomini E, Serafini B, Rosicarelli B, Sebastiani GD, Minisola G, et al. Characterization and Recruitment of Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells in Synovial Fluid and Tissue of Patients with Chronic Inflammatory Arthritis. J Immunol. 2004;173:2815–24.
Veale DJ, FitzGerald O. Psoriatic arthritis-pathogenesis and epidemiology. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2002;20:S27–33.
van Kuijk AW, Tak PP. Synovitis in psoriatic arthritis: immunohistochemistry, comparisons with rheumatoid arthritis, and effects of therapy. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2011;13(4):353–9.
Chimenti MS, Ballanti E, Perricone C, Cipriani P, Giacomelli R, Perricone R. Immunomodulation in psoriatic arthritis: focus on cellular and molecular pathways. Autoimmun Rev. 2013;12:599–606.
Gladman DD. Clinical, radiological, and functional assessment in psoriatic arthritis: is it different from other inflammatory joint diseases? Ann Rheum Dis. 2006;65 Suppl 3:iii22–4.
Yy L, Ls T, Ew K, Ek L. Psoriatic arthritis as a distinct disease entity. J Postgrad Med. 2007;53:63–72.
Nash P, Clegg DO. Psoriatic arthritis therapy: NSAIDs and traditional DMARDs. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005;64 Suppl 2:ii74–7.
Gossec L, Smolen JS, Gaujoux-Viala C, Ash Z, Marzo-Ortega H, van der Heijde D, et al. European League Against Rheumatism recommendations for the management of psoriatic arthritis with pharmacological therapies. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012;71(1):4–12.
Lie E, van der Heijde D, Uhlig T, Heiberg MS, Koldingsnes W, Rødevand E, et al. Effectiveness and retention rates of methotrexate in psoriatic arthritis in comparison with methotrexate-treated patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69:671–6.
Gladman DD. Adalimumab, etanercept and infliximab are equally effective treatments for patients with psoriatic arthritis. Nautre Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2008;4(10):510–1.
Mease PJ, Fleischmann R, Deodhar AA, Wollenhaupt J, Khraishi M, Kielar D, et al. Effect of certolizumab pegol on signs and symptoms in patients with psoriatic arthritis: 24-week results of a Phase 3 double-blind randomised placebo-controlled study (RAPID-PsA). Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(1):48–55.
Girolomoni G, Mrowietz U, Paul C. Psoriasis: rationale for targeting interleukin-17. Br J Dermatol. 2012;167(4):717–24.
Gaffen SL, Jain R, Garg AV, Cua DJ. The IL-23-IL-17 immune axis: from mechanisms to therapeutic testing. Nat Rev Immunol. 2014;14(9):585–600.
Novelli L, Chimenti MS, Chiricozzi A, Perricone R. The new era for the treatment of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: perspectives and validated strategies. Autoimmun Rev. 2014;13:64–9.
Gottlieb A, Menter A, Mendelsohn A, Shen Y-K, Li S, Guzzo C, et al. Ustekinumab, a human interleukin 12/23 monoclonal antibody, for psoriatic arthritis: randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial. Lancet. 2009;373:633–40.
McInnes IB, Sieper J, Braun J, Emery P, van der Heijde D, Isaacs JD, et al. Efficacy and safety of secukinumab, a fully human anti-interleukin-17A monoclonal antibody, in patients with moderate-to-severe psoriatic arthritis: a 24-week, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase II proof-of-concept trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73:349–56.
Leonardi C, Matheson R, Zachariae C, Cameron G, Li L, Edson-Heredia E, et al. Anti-interleukin-17 monoclonal antibody ixekizumab in chronic plaque psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:1190–9.
Helliwell P, Taylor W. Classification and diagnostic criteria orpsoriatic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005;64:ii3–8.
Helliwell PS, Fitzgerald O, Mease PJ, Gladman DD. GRAPPA Responder Index Project (GRACE): a report from the GRAPPA 2011 annual meeting. J Rheumatol. 2012;39(11):2196–7.
Ortea I, Pascoal A, Canas B, Gallardo JM, Barros-Velazquez J, Calo-Mata P. Food authentication of commercially-relevant shrimp and prawn species: from classical methods to Foodomics. Electrophoresis. 2012;33(15):2201–11.
Bowes J, Barton A. The genetics of psoriatic arthritis: lessons from genome-wide association studies. Discov Med. 2010;10(52):177–83.
Wetie AG, Woods AG, Darie CC. Mass spectrometric analysis of posttranslational modifications (PTMs) and protein-protein interactions (PPIs). Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014;806:205–35.
Lories RJU, Derese I, de Vlam K. Mitogen-activated kinases in psoriatic arthritis: differences in activation and distinct regulation by etanercept therapy. Arthritis Res Ther. 2005;7 Suppl 1:88.
Mavropoulos A, Rigopoulou EI, Liaskos C, Bogdanos DP, Sakkas LI. The role of p38 MAPK in the aetiopathogenesis of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Clin Develop Immunol. 2013;2013:569751.
Lizzul PF, Aphale A, Malaviya R, Sun Y, Masud S, Dombrovskiy V, et al. Differential expression of phosphorylated NF-kappaB/RelA in normal and psoriatic epidermis and downregulation of NF-kappaB in response to treatment with etanercept. J Invest Dermatol. 2005;124(6):1275–83.
Raychaudhuri SK, Raychaudhuri SP. mTOR Signaling Cascade in Psoriatic Disease: Double Kinase mTOR Inhibitor a Novel Therapeutic Target. Ind J Dermatol. 2014;59(1):67–70.
Doyle MS, Collins ES, FitzGerald OM, Pennington SR. New insights into the role of interllukin-17 receptor adaptor protein Act1 in psoriatic arthrtisi. Arthritis Res Ther. 2012;14:226.
Bensimon A, Heck AJ, Aebersold R. Mass spectrometry-based proteomics and network biology. Annu Rev Biochem. 2012;81:379–405.
Cox J, Mann M. Quantitative, high-resolution proteomics for data-driven systems biology. Annu Rev Biochem. 2011;80:273–99.
Gstaiger M, Aebersold R. Applying mass spectrometry-based proteomics to genetics, genomics and network biology. Nat Rev Genet. 2009;10(9):617–27.
Kim MS, Pinto SM, Getnet D, Nirujogi RS, Manda SS, Chaerkady R, et al. A draft map of the human proteome. Nature. 2014;509(7502):575–81.
Wilhelm M, Schlegl J, Hahne H, Moghaddas Gholami A, Lieberenz M, Savitski MM, et al. Mass-spectrometry-based draft of the human proteome. Nature. 2014;509(7502):582–7.
Uhlen M, Bjorling E, Agaton C, Szigyarto CA, Amini B, Andersen E, et al. A human protein atlas for normal and cancer tissues based on antibody proteomics. Mol Cell Proteomics: MCP. 2005;4(12):1920–32.
Uhlen M, Fagerberg L, Hallstrom BM, Lindskog C, Oksvold P, Mardinoglu A, et al. Proteomics. Tissue-based map of the human proteome. Science. 2015;347(6220):1260419.
Uhlen M, Oksvold P, Fagerberg L, Lundberg E, Jonasson K, Forsberg M, et al. Towards a knowledge-based Human Protein Atlas. Nat Biotechnol. 2010;28(12):1248–50.
Guerrero C, Tagwerker C, Kaiser P, Huang L. An integrated mass spectrometrybased proteomic approach: quantitative analysis of tandem affinity-purified in vivo cross-linked protein complexes (QTAX) to decipher the 26 S proteasomeinteracting network. MolCell Proteomics: MCP. 2006;5(2):366–78.
Gygi SP, Rist B, Gerber SA, Turecek F, Gelb MH, Aebersold R. Quantitative analysis of complex protein mixtures using isotope-coded affinity tags. Nat Biotechnol. 1999;17(10):994–9.
Jiang X, Coffino P, Li X. Development of a method for screening short-lived proteins using green fluorescent protein. Genome Biol. 2004;5(10):R81.
Wang X, Chen CF, Baker PR, Chen PL, Kaiser P, Huang L. Mass spectrometric characterization of the affinity-purified human 26S proteasome complex. Biochemistry. 2007;46(11):3553–65.
Dixon DP, Skipsey M, Grundy NM, Edwards R. Stress-induced protein Sglutathionylation in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2005;138(4):2233–44.
Kusch H, Engelmann S, Albrecht D, Morschhauser J, Hecker M. Proteomic analysis of the oxidative stress response in Candida albicans. Proteomics. 2007;7(5):686–97.
**ao GG, Recker RR, Deng HW. Recent advances in proteomics and cancer biomarker discovery. Clin Med Oncol. 2008;2:63–72.
Graves PR, Haystead TA. Molecular biologist's guide to proteomics. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev: MMBR. 2002;66(1):39–63. table of contents.
Aggarwal K, Choe LH, Lee KH. Shotgun proteomics using the iTRAQ isobaric tags. Brief Funct Genomics Proteomics. 2006;5(2):112–20.
Maurya P, Meleady P, Dowling P, Clynes M. Proteomic approaches for serum biomarker discovery in cancer. Anticancer Res. 2007;27(3A):1247–55.
Ross PL, Huang YN, Marchese JN, Williamson B, Parker K, Hattan S, et al. Multiplexed protein quantitation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae using amine-reactive isobaric tagging reagents. Mol Cell Proteomics: MCP. 2004;3(12):1154–69.
Gronborg M, Kristiansen TZ, Iwahori A, Chang R, Reddy R, Sato N, et al. Biomarker discovery from pancreatic cancer secretome using a differential proteomic approach. Mol Cell Proteomics: MCP. 2006;5(1):157–71.
Guerrera IC, Keep NH, Godovac-Zimmermann J. Proteomics study reveals crosstalk between Rho guanidine nucleotide dissociation inhibitor 1 post-translational modifications in epidermal growth factor stimulated fibroblasts. J Proteome Res. 2007;6(7):2623–30.
Bose R, Molina H, Patterson AS, Bitok JK, Periaswamy B, Bader JS, et al. Phosphoproteomic analysis of Her2/neu signaling and inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103(26):9773–8.
Foster LJ, Rudich A, Talior I, Patel N, Huang X, Furtado LM, et al. Insulin-dependent interactions of proteins with GLUT4 revealed through stable isotope labeling by amino acids in cell culture (SILAC). J Proteome Res. 2006;5(1):64–75.
Selbach M, Mann M. Protein interaction screening by quantitative immunoprecipitation combined with knockdown (QUICK). Nat Methods. 2006;3(12):981–3.
Waanders LF, Hanke S, Mann M. Top-down quantitation and characterization of SILAC-labeled proteins. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2007;18(11):2058–64.
Liang X, Fonnum G, Hajivandi M, Stene T, Kjus NH, Ragnhildstveit E, et al. Quantitative comparison of IMAC and TiO2 surfaces used in the study of regulated, dynamic protein phosphorylation. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2007;18(11):1932–44.
Soufi B, Jers C, Hansen ME, Petranovic D, Mijakovic I. Insights from site-specific phosphoproteomics in bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008;1784(1):186–92.
**ao GG, Garg M, Lim S, Wong D, Go VL, Lee WN. Determination of protein synthesis in vivo using labeling from deuterated water and analysis of MALDITOF spectrum. J Appl Physiol. 2008;104(3):828–36.
Megger DA, Bracht T, Meyer HE, Sitek B. Label-free quantification in clinical proteomics. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013;1834(8):1581–90.
Old WM, Meyer-Arendt K, Aveline-Wolf L, Pierce KG, Mendoza A, Sevinsky JR, et al. Comparison of label-free methods for quantifying human proteins by shotgun proteomics. Mol Cell Proteomics: MCP. 2005;4(10):1487–502.
Liu J, Bell AW, Bergeron JJ, Yanofsky CM, Carrillo B, Beaudrie CE, et al. Methods for peptide identification by spectral comparison. Proteome Sci. 2007;5:3.
Chelius D, Bondarenko PV. Quantitative profiling of proteins in complex mixtures using liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry. J Proteome Res. 2002;1(4):317–23.
Bantscheff M, Schirle M, Sweetman G, Rick J, Kuster B. Quantitative mass spectrometry in proteomics: a critical review. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2007;389(4):1017–31.
Westermeier R, Marouga R. Protein detection methods in proteomics research. Biosci Rep. 2005;25(1–2):19–32.
Eng JK, McCormack AL, Yates JR. An approach to correlate tandem mass spectral data of peptides with amino acid sequences in a protein database. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 1994;5(11):976–89.
Geer LY, Markey SP, Kowalak JA, Wagner L, Xu M, Maynard DM, et al. Open mass spectrometry search algorithm. J Proteome Res. 2004;3(5):958–64.
Perkins DN, Pappin DJ, Creasy DM, Cottrell JS. Probability-based protein identification by searching sequence databases using mass spectrometry data. Electrophoresis. 1999;20(18):3551–67.
Dancik V, Addona TA, Clauser KR, Vath JE, Pevzner PA. De novo peptide sequencing via tandem mass spectrometry. J Comput Biol: J Comput Mol Cell Biol. 1999;6(3–4):327–42.
Pitzer E, Masselot A, Colinge J. Assessing peptide de novo sequencing algorithms performance on large and diverse data sets. Proteomics. 2007;7(17):3051–4.
Shevchenko A, Chernushevich I, Ens W, Standing KG, Thomson B, Wilm M, et al. Rapid 'de novo' peptide sequencing by a combination of nanoelectrospray, isotopic labeling and a quadrupole/time-of-flight mass spectrometer. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom: RCM. 1997;11(9):1015–24.
Craig R, Cortens JC, Fenyo D, Beavis RC. Using annotated peptide mass spectrum libraries for protein identification. J Proteome Res. 2006;5(8):1843–9.
Frewen BE, Merrihew GE, Wu CC, Noble WS, MacCoss MJ. Analysis of peptide MS/MS spectra from large-scale proteomics experiments using spectrum libraries. Anal Chem. 2006;78(16):5678–84.
Yates 3rd JR, Morgan SF, Gatlin CL, Griffin PR, Eng JK. Method to compare collision-induced dissociation spectra of peptides: potential for library searching and subtractive analysis. Anal Chem. 1998;70(17):3557–65.
Buts K, Michielssens S, Hertog ML, Hayakawa E, Cordewener J, America AH, et al. Improving the identification rate of data independent label-free quantitative proteomics experiments on non-model crops: a case study on apple fruit. J Proteome. 2014;105:31–45.
Plumb RS, Johnson KA, Rainville P, Smith BW, Wilson ID, Castro-Perez JM, et al. UPLC/MS(E); a new approach for generating molecular fragment information for biomarker structure elucidation. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom: RCM. 2006;20(13):1989–94.
Vertommen A, Moller AL, Cordewener JH, Swennen R, Panis B, Finnie C, et al. A workflow for peptide-based proteomics in a poorly sequenced plant: a case study on the plasma membrane proteome of banana. J Proteome. 2011;74(8):1218–29.
Gillet LC, Navarro P, Tate S, Rost H, Selevsek N, Reiter L, et al. Targeted data extraction of the MS/MS spectra generated by data-independent acquisition: a new concept for consistent and accurate proteome analysis. Mol Cell Proteomics: MCP. 2012;11(6):O111.016717.
Egertson JD, Kuehn A, Merrihew GE, Bateman NW, MacLean BX, Ting YS, et al. Multiplexed MS/MS for improved data-independent acquisition. Nat Methods. 2013;10(8):744–6.
Fan Y, Thompson JW, Dubois LG, Moseley MA, Wernegreen JJ. Proteomic analysis of an unculturable bacterial endosymbiont (Blochmannia) reveals high abundance of chaperonins and biosynthetic enzymes. J Proteome Res. 2013;12(2):704–18.
Elliott MH, Smith DS, Parker CE, Borchers C. Current trends in quantitative proteomics. J Mass Spectrom: JMS. 2009;44(12):1637–60.
Lange V, Picotti P, Domon B, Aebersold R. Selected reaction monitoring for quantitative proteomics: a tutorial. Mol Syst Biol. 2008;4:222.
Gerber SA, Rush J, Stemman O, Kirschner MW, Gygi SP. Absolute quantification of proteins and phosphoproteins from cell lysates by tandem MS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100(12):6940–5.
Qian WJ, Jacobs JM, Liu T, Camp 2nd DG, Smith RD. Advances and challenges in liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry-based proteomics profiling for clinical applications. Mol Cell Proteom: MCP. 2006;5(10):1727–44.
Wasinger VC, Zeng M, Yau Y. Current status and advances in quantitative proteomic mass spectrometry. Int J Proteom. 2013;2013:180605.
Anderson L, Hunter CL. Quantitative mass spectrometric multiple reaction monitoring assays for major plasma proteins. Mol Cell Proteom: MCP. 2006;5(4):573–88.
Huillet C, Adrait A, Lebert D, Picard G, Trauchessec M, Louwagie M, et al. Accurate quantification of cardiovascular biomarkers in serum using Protein Standard Absolute Quantification (PSAQ) and selected reaction monitoring. Mol Cell Proteom: MCP. 2012;11(2):M111.008235.
Keshishian H, Addona T, Burgess M, Kuhn E, Carr SA. Quantitative, multiplexed assays for low abundance proteins in plasma by targeted mass spectrometry and stable isotope dilution. Mol Cell Proteom: MCP. 2007;6(12):2212–29.
Keshishian H, Addona T, Burgess M, Mani DR, Shi X, Kuhn E, et al. Quantification of cardiovascular biomarkers in patient plasma by targeted mass spectrometry and stable isotope dilution. Mol Cell Proteom: MCP. 2009;8(10):2339–49.
Kirsch S, Widart J, Louette J, Focant JF, De Pauw E. Development of an absolute quantification method targeting growth hormone biomarkers using liquid chromatography coupled to isotope dilution mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A. 2007;1153(1–2):300–6.
Kuhn E, Addona T, Keshishian H, Burgess M, Mani DR, Lee RT, et al. Develo** multiplexed assays for troponin I and interleukin-33 in plasma by peptide immunoaffinity enrichment and targeted mass spectrometry. Clin Chem. 2009;55(6):1108–17.
Kuhn E, Wu J, Karl J, Liao H, Zolg W, Guild B. Quantification of C-reactive protein in the serum of patients with rheumatoid arthritis using multiple reaction monitoring mass spectrometry and 13C-labeled peptide standards. Proteomics. 2004;4(4):1175–86.
McKay MJ, Sherman J, Laver MT, Baker MS, Clarke SJ, Molloy MP. The development of multiple reaction monitoring assays for liver-derived plasma proteins. Proteomics Clin Appl. 2007;1(12):1570–81.
Picard G, Lebert D, Louwagie M, Adrait A, Huillet C, Vandenesch F, et al. PSAQ standards for accurate MS-based quantification of proteins: from the concept to biomedical applications. J Mass Spectrom: JMS. 2012;47(10):1353–63.
Schmidt A, Kellermann J, Lottspeich F. A novel strategy for quantitative proteomics using isotope-coded protein labels. Proteomics. 2005;5(1):4–15.
Stahl-Zeng J, Lange V, Ossola R, Eckhardt K, Krek W, Aebersold R, et al. High sensitivity detection of plasma proteins by multiple reaction monitoring of Nglycosites. Mol Cell Proteom: MCP. 2007;6(10):1809–17.
Zhang Y, Zhao C, Liu H, Hou H, Zhang H. Multiple metastasis-like bone lesions in scintigraphic imaging. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012;2012:957364.
Titz B, Elamin A, Martin F, Schneider T, Dijon S, Ivanov NV, et al. Proteomics for systems toxicology. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2014;11(18):73–90.
S Ademowo BH, E Collins, C Rooney, U Fearon AWvK, P Tak, D M Gerlag, O FitzGerald, SR Pennington: Discovery and confirmation of a protein biomarker panel with poteinal to predict reponse to biological therapy in psoriatic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014:1–8.
Cretu D, Prassas I, Saraon P, Batruch I, Gandhi R, Diamandis EP, et al. Identification of psoriatic arthritis mediators in synovial fluid by quantitative mass spectrometry. Clin Proteom. 2014;11(1):27.
Balakrishnan L, Bhattacharjee M, Ahmad S, Nirujogi RS, Renuse S, Subbannayya Y, et al. Differential proteomic analysis of synovial fluid from rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis patients. Clin Proteom. 2014;11(1):1.
Gibson DS, Finnegan S, Jordan G, Scaife C, Brockbank S, Curry J, et al. Stratification and monitoring of juvenile idiopathic arthritis patients by synovial proteome analysis. J Proteome Res. 2009;8(12):5601–9.
Finnegan S, Robson J, Scaife C, McAllister C, Pennington SR, Gibson DS, et al. Synovial membrane protein expression differs between juvenile idiopathic arthritis subtypes in early disease. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16(1):R8.
Lau TY, Collins BC, Stone P, Tang N, Gallagher WM, Pennington SR. Absolute quantification of toxicological biomarkers by multiple reaction monitoring. Methods Mol Biol. 2011;691:417–27.
Oe T, Ackermann BL, Inoue K, Berna MJ, Garner CO, Gelfanova V, et al. Quantitative analysis of amyloid beta peptides in cerebrospinal fluid of Alzheimer's disease patients by immunoaffinity purification and stable isotope dilution liquid chromatography/negative electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom: RCM. 2006;20(24):3723–35.
Collins BC, Miller CA, Sposny A, Hewitt P, Wells M, Gallagher WM, et al. Development of a pharmaceutical hepatotoxicity biomarker panel using a discovery to targeted proteomics approach. Mol Cell Proteom: MCP. 2012;11(8):394–410.
Morrissey B, O'Shea C, Armstrong J, Rooney C, Staunton L, Sheehan M, et al. Development of a label-free LC-MS/MS strategy to approach the identification of candidate protein biomarkers of disease recurrence in prostate cancer patients in a clinical trial of combined hormone and radiation therapy. Proteomics Clin Appl. 2013;7(5–6):316–26.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
Conflict of Interest
Aisha Q. Butt, Angela McArdle, David S. Gibson and Stephen R. Pennington declare no conflicts of interest. Oliver FitzGerald declares the receipt of research grant support from Pfizer, Abbott, Roche, MSD, Amgen and UCB.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Psoriatic Arthritis
Aisha Q. Butt and Angela McArdle contributed equally to this manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Butt, A.Q., McArdle, A., Gibson, D.S. et al. Psoriatic Arthritis Under a Proteomic Spotlight: Application of Novel Technologies to Advance Diagnosis and Management. Curr Rheumatol Rep 17, 35 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11926-015-0509-0
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11926-015-0509-0