Abstract
Purpose of Review
We review the recent practice-changing trials of anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapies in large B cell lymphoma (LBCL) including phase 3 comparisons with second-line standard-of-care (SOC) and phase 2 investigations in transplant-ineligible patients or as part of first-line treatment.
Recent Findings
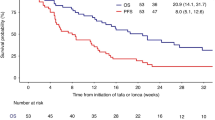
ZUMA-7 found significantly improved overall survival and event-free survival (EFS) with axicabtagene ciloleucel (axi-cel) versus SOC of salvage chemotherapy followed by autologous stem-cell transplantation. This represents the first such survival improvement in nearly 30 years for early-relapsed or refractory (r/r) LBCL. TRANSFORM demonstrated prolonged EFS for lisocabtagene maraleucel (liso-cel) versus SOC but BELINDA did not for tisagenlecleucel. Second-line CAR T cell was a viable curative-intent therapy in elderly (ZUMA-7; axi-cel) and/or transplant-ineligible (PILOT; liso-cel) patients. ZUMA-12 demonstrated effectiveness for axi-cel as part of first-line treatment for high-risk LBCL.
Summary
These results support a role for CAR T cell therapy as new second-line SOC for r/r LBCL and highlight its potential evolution into future first-line treatment for high-risk disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Sehn LH, Salles G. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(9):842–58.
Coiffier B, Lepage E, Briere J, Herbrecht R, Tilly H, Bouabdallah R, et al. CHOP chemotherapy plus rituximab compared with CHOP alone in elderly patients with diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2002;346(4):235–42.
Nastoupil LJ, Bartlett NL. Navigating the evolving treatment landscape of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2023;41(4):903–13. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.22.01848.
Westin J, Sehn LH. CAR T cells as a second-line therapy for large B-cell lymphoma: a paradigm shift? Blood. 2022;139(18):2737–46. This comprehensive review describes in detail the three randomized phase 3 trials in second line LBCL, and why they represent a true paradigm shift in management.
Crump M, Kuruvilla J, Couban S, MacDonald DA, Kukreti V, Kouroukis CT, et al. Randomized comparison of gemcitabine, dexamethasone, and cisplatin versus dexamethasone, cytarabine, and cisplatin chemotherapy before autologous stem-cell transplantation for relapsed and refractory aggressive lymphomas: NCIC-CTG LY12. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32(31):3490–6.
Flowers CR, Odejide OO. Sequencing therapy in relapsed DLBCL. Hematol Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2022;2022(1):146–54.
Philip T, Guglielmi C, Hagenbeek A, Somers R, Van der Lelie H, Bron D, et al. Autologous bone marrow transplantation as compared with salvage chemotherapy in relapses of chemotherapy-sensitive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 1995;333(23):1540–5.
Gisselbrecht C, Glass B, Mounier N, Singh Gill D, Linch DC, Trneny M, et al. Salvage regimens with autologous transplantation for relapsed large B-cell lymphoma in the rituximab era. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(27):4184–90.
Crump M, Neelapu SS, Farooq U, Van Den Neste E, Kuruvilla J, Westin J, et al. Outcomes in refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: results from the international SCHOLAR-1 study. Blood. 2017;130(16):1800–8.
Gordon MJ, Sureda A, Westin JR. Novel strategies for relapsed/refractory DLBCL; navigating the immunotherapy era in aggressive lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma. 2022;63(9):2041–51.
Gurumurthi A, Westin JR, Subklewe M. The race is on: bispecifics vs CAR T-cells in B-cell lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2023;7(19):5713–6. https://doi.org/10.1182/bloodadvances.2022009066.
Strati P, Gregory T, Majhail NS, Jain N. Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy for hematologic malignancies: a practical review. JCO Oncol Pract. 2023;19:OP2200819.
Boardman AP, Salles G. CAR T-cell therapy in large B cell lymphoma. Hematol Oncol. 2023;41(Suppl 1):112–8.
Neelapu SS, Locke FL, Bartlett NL, Lekakis LJ, Miklos DB, Jacobson CA, et al. Axicabtagene ciloleucel CAR T-cell therapy in refractory large B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(26):2531–44.
Schuster SJ, Bishop MR, Tam CS, Waller EK, Borchmann P, McGuirk JP, et al. Tisagenlecleucel in adult relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(1):45–56.
Abramson JS, Palomba ML, Gordon LI, Lunning MA, Wang M, Arnason J, et al. Lisocabtagene maraleucel for patients with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphomas (TRANSCEND NHL 001): a multicentre seamless design study. Lancet. 2020;396(10254):839–52.
Neelapu SS, Jacobson CA, Ghobadi A, Miklos DB, Lekakis LJ, Oluwole OO, et al. Five-year follow-up of ZUMA-1 supports the curative potential of axicabtagene ciloleucel in refractory large B-cell lymphoma. Blood. 2023;141(19):2307–15.
Locke FL, Miklos DB, Jacobson CA, Perales MA, Kersten MJ, Oluwole OO, et al. Axicabtagene ciloleucel as second-line therapy for large B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2022;386(7):640–54.
Bishop MR, Dickinson M, Purtill D, Barba P, Santoro A, Hamad N, et al. Second-line tisagenlecleucel or standard care in aggressive B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2022;386(7):629–39.
Abramson JS, Solomon SR, Arnason J, Johnston PB, Glass B, Bachanova V, et al. Lisocabtagene maraleucel as second-line therapy for large B-cell lymphoma: primary analysis of the phase 3 TRANSFORM study. Blood. 2023;141(14):1675–84.
Westin JR, Oluwole OO, Kersten MJ, Miklos DB, Perales MA, Ghobadi A, et al. Survival with axicabtagene ciloleucel in large B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2023;389(2):148–57. This is the first trial in nearly 30 years to significantly improve overall survival in patients with second line LBCL.
Kamdar M, Solomon SR, Arnason J, Johnston PB, Glass B, Bachanova V, et al. Lisocabtagene maraleucel versus standard of care with salvage chemotherapy followed by autologous stem cell transplantation as second-line treatment in patients with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphoma (TRANSFORM): results from an interim analysis of an open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2022;399(10343):2294–308.
Sehgal A, Hoda D, Riedell PA, Ghosh N, Hamadani M, Hildebrandt GC, et al. Lisocabtagene maraleucel as second-line therapy in adults with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphoma who were not intended for haematopoietic stem cell transplantation (PILOT): an open-label, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2022;23(8):1066–77.
Neelapu SS, Dickinson M, Munoz J, Ulrickson ML, Thieblemont C, Oluwole OO, et al. Axicabtagene ciloleucel as first-line therapy in high-risk large B-cell lymphoma: the phase 2 ZUMA-12 trial. Nat Med. 2022;28(4):735–42. This is the first trial to use CAR T-cell therapy for patients in first line therapy of LBCL, a potentially historic landmark which has resulted in randomized trials in this space.
Bartlett NL, Wilson WH, Jung SH, Hsi ED, Maurer MJ, Pederson LD, et al. Dose-Adjusted EPOCH-R Compared with R-CHOP as frontline therapy for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: clinical outcomes of the Phase III Intergroup Trial Alliance/CALGB 50303. J Clin Oncol. 2019;37(21):1790–9.
Hilton LK, Ngu HS, Collinge B, Dreval K, Ben-Neriah S, Rushton CK, et al. Relapse timing is associated with distinct evolutionary dynamics in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2023;41:JCO2300570.
Wang Y, Farooq U, Link BK, Larson MC, King RL, Maurer MJ, et al. Late Relapses in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with immunochemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2019;37(21):1819–27.
Vercellino L, Di Blasi R, Kanoun S, Tessoulin B, Rossi C, D’Aveni-Piney M, et al. Predictive factors of early progression after CAR T-cell therapy in relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2020;4(22):5607–15.
Neelapu SS, Jacobson CA, Oluwole OO, Munoz J, Deol A, Miklos DB, et al. Outcomes of older patients in ZUMA-1, a pivotal study of axicabtagene ciloleucel in refractory large B-cell lymphoma. Blood. 2020;135(23):2106–9.
Westin JR, Locke FL, Dickinson M, Ghobadi A, Elsawy M, van Meerten T, et al. Safety and efficacy of axicabtagene ciloleucel versus standard of care in patients 65 years of age or older with relapsed/refractory large B-cell lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2023;29(10):1894–905.
Chihara D, Liao L, Tkacz J, Franco A, Lewing B, Kilgore KM, et al. Real-world evidence of CAR T-cell therapy in older patients with relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood. 2023;142:1055.
Bachy E, Le Gouill S, Di Blasi R, Sesques P, Manson G, Cartron G, et al. A real-world comparison of tisagenlecleucel and axicabtagene ciloleucel CAR T cells in relapsed or refractory diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Nat Med. 2022;28(10):2145–54.
Kwon M, Iacoboni G, Reguera JL, Corral LL, Morales RH, Ortiz-Maldonado V, et al. Axicabtagene ciloleucel compared to tisagenlecleucel for the treatment of aggressive B-cell lymphoma. Haematologica. 2023;108(1):110–21.
Efficace F, Cannella L, Sparano F, Giesinger JM, Vignetti M, Baron F, et al. Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy in hematologic malignancies and patient-reported outcomes: a sco** review. Hemasphere. 2022;6(12):e802.
Sureda A, Lugtenburg PJ, Kersten MJ, Subklewe M, Spanjaart A, Shah NN, et al. Cellular therapy in lymphoma. Hematol Oncol. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1002/hon.3200.
Elsawy M, Chavez JC, Avivi I, Larouche JF, Wannesson L, Cwynarski K, et al. Patient-reported outcomes in ZUMA-7, a phase 3 study of axicabtagene ciloleucel in second-line large B-cell lymphoma. Blood. 2022;140(21):2248–60.
Abramson JS, Johnston PB, Kamdar M, Ibrahimi S, Izutsu K, Arnason J, et al. Health-related quality of life with lisocabtagene maraleucel vs standard of care in relapsed or refractory LBCL. Blood Adv. 2022;6(23):5969–79.
Kambhampati S, Saumoy M, Schneider Y, Serrao S, Solaimani P, Budde LE, et al. Cost-effectiveness of second-line axicabtagene ciloleucel in relapsed refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood. 2022;140(19):2024–36.
Westin J, Jacobson CA, Chavez JC, Sureda A, Morschhauser F, Glaß B, Dickinson M, et al. ZUMA-23: A global, phase 3, randomized controlled study of axicabtagene ciloleucel versus standard of care as first-line therapy in patients with high-risk large B-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2023;41(16):TPS7578–TPS7578.
Dickinson MJ, Barba P, Jager U, Shah NN, Blaise D, Briones J, et al. A novel autologous CAR-T therapy, YTB323, with preserved T-cell stemness shows enhanced CAR T-cell efficacy in preclinical and early clinical development. Cancer Discov. 2023;13(9):1982–97. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-22-1276.
Perales MA, Anderson LD Jr, Jain T, Kenderian SS, Oluwole OO, Shah GL, et al. Role of CD19 chimeric antigen receptor T cells in second-line large B cell lymphoma: lessons from phase 3 trials. An Expert Panel Opinion from the American Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy. Transplant Cell Ther. 2022;28(9):546–59.
Cliff ERS, Kelkar AH, Russler-Germain DA, Tessema FA, Raymakers AJN, Feldman WB, et al. High cost of chimeric antigen receptor T-cells: challenges and solutions. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 2023;43:e397912.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Jason Westin has received research funding from Kite/Gilead, Novartis, BMS, Genentech, AstraZeneca, Janssen, Morphosys/Incyte, Precision Biosciences, and ADC Therapeutics and has received consulting funding from Kite/Gilead, Novartis, BMS, Janssen, AstraZeneca, Genentech, Morphosys/Incyte, ADC Therapeutics, Iksuda, Umoja, MonteRosa, and Merck. Anath Lionel has no conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lionel, A.C., Westin, J. Evolving Role of CAR T Cell Therapy in First- and Second-Line Treatment of Large B Cell Lymphoma. Curr Oncol Rep 25, 1387–1396 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11912-023-01466-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11912-023-01466-6