Abstract
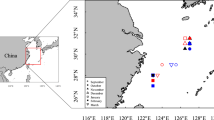
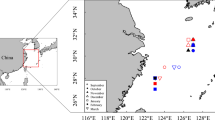
We applied solution-based ICP-MS method to quantify the trace-elemental signatures in statoliths of jumbo flying squid, Dosidius gigas, which were collected from the waters off northern and central Chile during the scientific surveys carried out by Chinese squid jigging vessels in 2007 and 2008. The age and spawning date of the squid were back-calculated based on daily increments in statoliths. Eight elemental ratios (Sr/Ca, Ba/Ca, Mg/Ca, Mn/Ca, Na/Ca, Fe/Ca, Cu/Ca and Zn/Ca) were analyzed. It was found that Sr is the second most abundant element next to Ca, followed by Na, Fe, Mg, Zn, Cu, Ba and Mn. There was no significant relationship between element/Ca and sea surface temperature (SST) and sea surface salinity (SSS), although weak negative or positive tendency was found. MANOVA analysis showed that multivariate elemental signatures did not differ among the cohorts spawned in spring, autumn and winter, and no significant difference was found between the northern and central sampling locations. Classification results showed that all individuals of each spawned cohorts were correctly classified. This study demonstrates that the elemental signatures in D. gigas statoliths are potentially a useful tool to improve our understanding of its population structure and habitat environment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arkhipkin, A., 1993. Age, growth, stock structure and migratory rate of pre-spawning short-finned squid Illex argentinus based on statolith ageing investigations. Fisheries Research, 16 (4): 313–338.
Arkhipkin, A. I., 2005. Statolith as ‘black boxes’ (life recorders) in squid. Marine Freshwater Research, 56: 573–583.
Arkhipkin, A. I., Campana, S. E., FitzGerald, J., and Thorrold, S. R., 2004. Spatial and temporal variation in elemental signatures of statoliths from the Patagonian longfin squid (Loligo gahi). Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 61: 1212–1224.
Argüelles, J., Lorrain, A., Cherel, Y., Graco, M., Tafur, R., Alegre, A., Espinoza, P., Taipe, A., Ayón, P., and Bertrand, A., 2012. Tracking habitat and resource use for the jumbo squid Dosidicus gigas: A stable isotope analysis in the Northern Humboldt Current System. Marine biology, 159 (9): 2105–2116.
Bettencourt, V., and Guerra, A., 2000. Growth increments and biomineralization process in cephalopod statoliths. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 248: 191–205.
Biemann, M. D., and Piatkowski, U., 2001. Amounts and composition of trace elements in the statoliths of loliginid squids: Reflection of environmental conditions? ICES CM, K: 5.
Campana, S. E., 1999. Chemistry and composition of fish otoliths: Pathways, mechanisms and applications. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 188: 263–297.
Chen, X. J., and Zhao, X. H., 2005. Catch distribution of jumbo flying squid and its relationship with SST in the offshore waters of Chile. Marine Fisheries, 27: 173–176 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Chen, X. J., Lu, H. J., Liu, B. L., and Chen, Y., 2011. Age, growth and population structure of jumbo flying squid, Dosidicus gigas, based on statolith microstructure off the Exclusive Economic Zone of Chilean waters. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom, 91 (1): 229–235.
Chen, X. J., Li, J. H., Liu, B. L., Chen, Y., Li, G., Fang, Z., and Tian, S. Q., 2013. Age, growth and population structure of jumbo flying squid, Dosidicus gigas, off the Costa Rica Dome. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom, 93 (2): 567–573.
Durholtz, M. D., Lipinski, M. R., Przybylowicz, W. J., and Mesjasz-Przybylowicz, J., 1997. Nuclear microprobe map** of statoliths of Chokka Squid Loligo vulgaris reynaudii d’Orbigny, 1845. Biology Bulletin, 193: 125–140.
Fowler, A. J., Campana, S. E., Jones, C. M., and Thorrold, S. R., 1995. Experimental assessment of the effect of temperature and salinity on elemental composition of otoliths using solution-based ICPMS. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 52: 1421–1430.
Gillanders, B. M., and Kingsford, M. J., 1996. Elements in otolith may elucidate the contribution of estuarine recruitment to sustaining coastal reef populations of a temperate reef fish. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 141: 13–20.
Hanlon, R. T., and Messenger, J. B., 1996. Cephalopod Behavior. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 232pp.
Hu, Z. M., Chen, X. J., Zhou, Y. Q., Qian, W. G., and Liu, B. L., 2011. Forecasting fishing ground of Dosidicus gigas based on habitat suitability index off Peru. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 5: 67–75 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Ibáñez, C. M., and Cubillos, L. A., 2007. Seasonal variation in the length structure and reproductive condition of the jumbo squid Dosidicus gigas (d’Orbigny, 1835) off central-south Chile. Scientia Marina, 71: 123–128.
Ikeda, Y., Arai, N., Kidokoro, H., and Sakamoto, W., 2003. Strontium:calcium ratios in statoliths of Japanese common squid Todarodes pacificus (Cephalopoda: Ommastrephidae) as indicators of migratory behavior. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 251: 169–179.
Ikeda, Y., Arai, N., and Sakamoto, W., 1995. Preliminary report on the PIXE analysis of the squid statoliths. International Journal of PIXE, 5: 159–162.
Ikeda, Y., Arai, N., Sakamoto, W., Kidokoro, H., Mitsuhashi, M., and Yoshida, K., 1999. Preliminary report on PIXE analysis for trace elements of Octopus dofleini statoliths. Fisheries Science, 65: 161–162.
Ikeda, Y., Arai, N., Sakamoto, W., Kidokoro, H., and Yoshida, K., 1996a. Relationship between statoliths and environmental variables in cephalopods. International Journal of PIXE, 6: 339–345.
Ikeda, Y., Arai, N., Sakamoto, W., Nateewathana, A., Murayama, T., Yatsu, A., and Yoshida, K., 1996b. PIXE analysis of trace elements in squid statoliths: Composition between Ommastrephidae and Loliginidae. International Journal of PIXE, 6: 537–542.
Ikeda, Y., Arai, N., Sakamoto, W., Kidokoro, H., Yatsu, A., Nateewathana, A., and Yoshida, K., 1997. Comparison on trace elements in squid statoliths of different species’ origin as available key for taxonomic and phylogenetic study. International Journal of PIXE, 7: 141–146.
Ikeda, Y., Okazaki, J., Sakurai, Y., and Sakamoto, W., 2002a. Periodic variation in Sr/Ca ratios in statoliths of the Japanese common squid Todarodes pacificus Steenstrup, 1880 (Cephalopoda: Ommastrephidae) maintained under constant water temperature. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 273: 161–170.
Ikeda, Y., Yatsu, A., Arai, N., and Sakamoto, W., 2002b. Concentration of statolith trace elements in the jumbo flying squid during El Niño and non-El Niño years in the eastern Pacific. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom, 82: 863–866.
Liu, B. L., Chen, X. J., Qian, W. G., Lu, H. J., and Li, S. L., 2010a. Preliminary study on reproductive biology of Dosidicus giagas in the high sea off Chile. Journal of Shanghai Ocean University, 19: 68–73 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu, B. L., Chen, X. J., Lu, H. J., Chen, Y., and Qian, W. G., 2010b. Fishery biology of the jumbo squid Dosidicus gigas off Exclusive Economic Zone of Chilean waters. Scientia Marina, 74: 687–695.
Ma, J., 2010. Statolith microstructure and microchemistry of the neon flying squid, Ommastrephes bartramii, in the Northwest Pacific Ocean. Master thesis. Shanghai Ocean University, 82pp (in Chinese).
Nigmatullin, Ch. M., Nesis, K. N., and Arkhipkin, A. I., 2001. A review of the biology of the jumbo squid Dosidicus gigas (Cephalopoda: Ommastrephidae). Fisheries Research, 54: 9–19.
Patterson, H. M., Thorrold, S. R., and Shenker, J. M., 1999. Analysis of otolith chemistry in Nassau grouper (Epinephelus striatus) from the Bahamas and Belize using soulution-based ICP-MS. Coral Reefs, 18: 171–178.
Qian, W. G., Chen, X. J., Zheng, B., and Liu, B. L., 2008. Study on the resource density distribution of Dosidicus gigas and marine environment in the high sea waters off Chile. Journal of Shanghai Ocean University, 17: 98–103 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Rocha, F., and Vega, M., 2003. Overview of cephalopod fisheries in Chilean waters. Fisheries Research, 60: 151–159.
Rodhouse, P. G., Robinson, K., Gajdatsy, S. B., Daly, H. I., and Ashmore, M. J. S., 1994. Growth, age structure and environmental history in the cephalopod Martialia hyadei (Teuthoidea: Ommastrephidae) at the Atlantic Polar Frontal Zone and on the Patagonian Shelf Edge. Antarctic Science, 6: 259–267.
Swart, P. K., Elderfield, H., and Greaves, M. J., 2002. A high-resolution calibration of Sr/Ca thermometry using the Caribbean coral Montastraea annularis. Geochemistry Geophysics Geosystems, 3: 1–11.
Swearer, S. E., Forrester, G. E., Steele, M. A., Brooks, A. J., and Lea, D. W., 2003. Spatio-temporal and interspecific variation in otolith trace-elemental fingerprints in a temperature estuarine fish assemblage. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 56: 1111–1123.
Thorrold, S. R., Jones, G. P., Hellberg, M. E., Burton, R. S., Swearer, S. E., Neigel, J. E., Morgan, S. G., and Warner, R. R., 2002. Quantifying larval retention and connectivity in marine populations with artificial and natural marks. Bulletin of Marine Science 70: 291–308.
Thorrold, S. R., and Shuttleworth, S., 2000. In situ analysis of trace elements and isotope ratios in fish otoliths using laser ablation sector field inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 57: 1232–1242.
Warner, R. R., Hamilton, S. L., Sheehy, M. S., Zeidberg, L. D., Brady, B. C., and Caselle, J. E., 2009. Geographic variation in natal and early larval trace-elemental signatures in the statoliths of the market squid Doryteuthis (formerly Loligo) opalescens. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 379: 109–121.
Yan, J., Xu, Q. H., Chen, X. J., Li, G., and Liu, B. L., 2012. Primary studies on the population genetic structure of Dosidicus gigas in the high seas of eastern Pacific Ocean. Journal of Fisheries of China, 35 (11): 1617–1623.
Yatsu, A., Mochioka, N., Morishita, K., and Toh, H., 1998. Strontium/calcium ratios in statoliths of the neon flying squid, Ommastrephes bartramii (Cephalopoda), in the North Pacific Ocean. Marine Biology, 131: 275–282.
Zacherl, D. C., Paradis, G. D., and Lea, D. W., 2003. Barium and strontium uptake into larval protoconchs and statoliths of the marine neogastropod Kelletia kelletii. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 67: 4091–4099.
Zumholz, K., 2005. The influence of environmental factors on the micro-chemical composition of cephalopod statoliths. PhD thesis. University of Kiel, Germany, 86pp.
Zumholz, K., Hansteen, T. H., Klügel, A., and Piatkowski, U., 2006. Food effects on statolith compositon of the common cuttlefish (Sepia officinalis). Marine Biology, 150: 237–244.
Zumholz, K., Hansteen, T. H., Piatkowski, U., and Croot, P. L., 2007a. Influence of temperature and salinity on the trace element incorporation into statoliths of the common cuttlefish (Sepia officinalis). Marine Biology, 151: 1321–1330.
Zumholz, K., Klügel, A., Hansteen, T. H., and Piatkowski, U., 2007b. Statolith microchemistry traces environmental history of the boreoatlantic armhook squid Gonatus fabricii. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 333: 195–204.
Zúñiga, M. J., Cubillos, L. A., and Ibáñez, C., 2008. A regular pattern of periodicity in the monthly catch of jumbo squid (Dosidicus gigas) along the Chilean coast (2002–2005). Ciencias Marinas, 34: 91–99.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, B., Chen, X., Fang, Z. et al. A preliminary analysis of trace-elemental signatures in statoliths of different spawning cohorts for Dosidicus gigas off EEZ waters of Chile. J. Ocean Univ. China 14, 1059–1067 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-015-2620-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-015-2620-2