Abstract
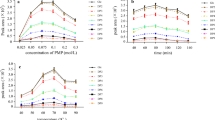
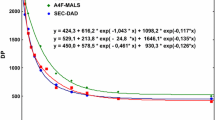
Characterization of the molecular properties of soluble microbial products (SMP) is critical for understanding the membrane filtration and fouling mechanisms in anaerobic and aerobic membrane bioreactors (AnMBR & MBR). In this study, the distributions of the absolute molecular weight and intrinsic viscosity of SMP polysaccharides from an AnMBR were effectively determined by a high performance size exclusion chromatography (HPSEC) that was coupled with the refractive index (RI), diode array UV (DAUV), right and low angle light scattering (LS), and viscometer (Vis) detectors. Based on the tetra-detector HPSEC determined absolute molecular weights and intrinsic viscosity, a universal calibration relationship for the SMP polysaccharides was developed and the molecular conformations, average molecular weights, and hydrodynamic sizes of the SMP polysaccharides were also explored. Two factors which can be derived from the tetra-detector HPSEC analysis were proposed for the characterization of the viscous and osmotic pressure properties of the SMP polysaccharides. In addition, it was also extrapolated how to analyze the resistance characteristics of the concentration polarization layers formed in membrane filtration based on the molecular properties determined by the tetra-detector HPSEC analysis.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lin H, Zhang M, Wang F, Meng F, Liao B Q, Hong H, Chen J, Gao W. A critical review of extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs) in membrane bioreactors: characteristics, roles in membrane fouling and control strategies. Journal of Membrane Science, 2014, 460(9): 110–125
Gao W J, Qu X, Leung K T, Liao B Q. Influence of temperature and temperature shock on sludge properties, cake layer structure, and membrane fouling in a submerged anaerobic membrane bioreactor. Journal of Membrane Science, 2012, (421–422): 131–144
Lyko S, Al-Halbouni D, Wintgens T, Janot A, Hollender J, Dott W, Melin T. Polymeric compounds in activated sludge supernatant— Characterisation and retention mechanisms at a full-scale municipal membrane bioreactor. Water Research, 2007, 41(17): 3894–3902
Shen Y X, Zhao W, **ao K, Huang X. A systematic insight into fouling propensity of soluble microbial products in membrane bioreactors based on hydrophobic interaction and size exclusion. Journal of Membrane Science, 2010, 346(1): 187–193
Shen Y X, **ao K, Liang P, Sun J, Sai S, Huang X. Characterization of soluble microbial products in 10 large-scale membrane bioreactors for municipal wastewater treatment in China. Journal of Membrane Science, 2012, 415: 336–345
Wu Z, Wang Q, Wang Z, Ma Y, Zhou Q, Yang D. Membrane fouling properties under different filtration modes in a submerged membrane bioreactor. Process Biochemistry, 2010, 45(10): 1699–1706
Zhu X, Wang Z, Wu Z. Characterization of membrane foulants in a full-scale membrane bioreactor for supermarket wastewater treatment. Process Biochemistry, 2011, 46(4): 1001–1009
Sun F Y, Wang X, Li X Y. Effect of biopolymer clusters on the fouling property of sludge from a membrane bioreactor (MBR) and its control by ozonation. Process Biochemistry, 2011, 46(1): 162–167
Yang Z, Juang Y C, Lee D J, Duan Y Y. Pore blockage of organic fouling layer with highly heterogeneous structure in membrane filtration: role of minor organic foulants. Journal of Membrane Science, 2012, 411–412: 30–34
Guo Q, Wang Q, Cui S W, Kang J, Hu X, **ng X, Yada R Y. Conformational properties of high molecular weight heteropolysaccharide isolated from seeds of Artemisia sphaerocephala Krasch. Food Hydrocolloids, 2013, 32(1): 155–161
Frølund B, Griebe T, Nielsen P H. Enzymatic activity in the activated-sludge floc matrix. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 1995, 43(4): 755–761
Bourven I, Simon S, Bhatia D, van Hullebusch E D, Guibaud G. Effect of various size exclusion chromatography (SEC) columns on the fingerprints of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) extracted from biological sludge. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2015, 49: 148–155
Hufnagel D. Anaerobic membrane bioreactor for high strength wastewater treatment: batch and continuous operation comparison. Journal of Water Reuse & Desalination, 2014, 5(2):95
Chen R. Application of Anaerobic Membrane Bioreactor for Brewery Wastewater Treatment. New Orleans, Louisiana: Weftec, 2014
Arabi S, Nakhla G. Impact of molecular weight distribution of soluble microbial products on fouling in membrane bioreactors. Separation and Purification Technology, 2010, 73(3): 391–396
Alasonati E, Slaveykova V I. Composition and molar mass characterisation of bacterial extracellular polymeric substances by using chemical, spectroscopic and fractionation techniques. Environmental Chemistry, 2011, 8(2): 155–162
Blumenkrantz N, Asboe-Hansen G. New method for quantitative determination of uronic acids. Analytical Biochemistry, 1973, 54(2): 484–489
DuBois M, Gilles K A, Hamilton J K, Rebers P A, Smith F. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Analytical Chemistry, 1956, 28(3): 350–356
Lowry O H, Rosebrough N J, Farr A L, Randall R J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1951, 193(1): 265–275
Grubisic Z, Rempp P, Benoit H. A universal calibration for gel permeation chromatography. Journal of Polymer Science. Part B: Polymer Letters, 1967, 5(9): 753–759
Teraoka I. Polymer Solutions: An Introduction to Physical Properties. London: John Wiley & Sons, 2002
Matsuoka S, Cowman M K. Equation of state for polymer solution. Polymer, 2002, 43(12): 3447–3453
Kwaambwa H M, Goodwin J W, Hughes R W, Reynolds P A. Viscosity, molecular weight and concentration relationships at 298 K of low molecular weight cis-polyisoprene in a good solvent. Colloids and Surfaces. A, Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2007, 294(1–3): 14–19
Striegel A M.Modern Size-exclusion Liquid Chromatography, 2nd ed. New York: John Wiley & Son, Inc., 2009
Pamies R, Hernández Cifre J G, del Carmen López Martínez M, García de la Torre J. Determination of intrinsic viscosities of macromolecules and nanoparticles. Comparison of single-point and dilution procedures. Colloid & Polymer Science, 2008, 286(11): 1223–1231
Johnson M, Kamm R. Scaling laws and the effects of concentration polarization on the permeability of hyalurronic acid. PhysicChemical Hydrodynamics, 1987, 9(34) 427–441
Wijmans J G, Nakao S, Van Den Berg J W A, Troelstra F R, Smolders C A. Hydrodynamic resistance of concentration polarization boundary layers in ultrafiltration. Journal of Membrane Science, 1985, 22(1): 117–135
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Ontario Centres of Excellence (CRSW- 11384-12), Canada Foundation for Innovation (CFI) (No. 28061), and GE Water and Process Technologies for the support on this research; Yi Liu for the preparation of the SMP samples; and Malvern specialist Ahmad Abu Romeh for his support on the tetra-detector HPSEC analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, Q., Chang, S. Tetra-detector size exclusion chromatography characterization of molecular and solution properties of soluble microbial polysaccharides from an anaerobic membrane bioreactor. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 11, 16 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-017-0922-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-017-0922-x