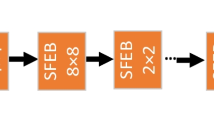
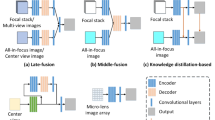
Abstract
Due to the remarkable ability to capture both spatial and angular information of the scene, light field imaging provides abundant cues and information. Over the last decade, various forms of data, such as the focal stack, all-in-focus image, depth map, sub-aperture image, center-view image, and micro-lens image array, have been exploited by different methods of light field salient object detection (SOD). In this study, we introduce a novel 3D–2D convolution hybrid network called HFSNet, which utilizes the focal stack as the only input to achieve SOD. The encoder network is constructed based on 3D convolution to extract and preserve the continuously changing focus cues within the focal stack. In order to reduce the computational burden of 3D convolution, we incorporate 3D max-pooling layers, channel reduction modules, and focal stack feature fusing modules to reduce the data dimension. The decoder network, on the other hand, is built on 2D convolution to generate coarse saliency maps, which are then refined using the refine module to obtain the final saliency map. We conduct experiments on five benchmark light field SOD datasets, and the results demonstrate that our method outperforms other models on DUTLF-V2 and DUTLF-FS, and achieves competitive outcomes on Lytro Illum, HFUT-Lytro, and LFSD.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Data and materials will be made available on request.
References
Borji, A., Cheng, M.M., Jiang, H., Li, J.: Salient object detection: a benchmark. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 24, 5706–5722 (2015)
Sun, W., Feng, X., et al.: Self-progress aggregate learning for weakly supervised salient object detection. Meas. Sci. Technol. 34, 065405 (2023)
Hong, S., You, T., et al.: Online tracking by learning discriminative saliency map with convolutional neural network. Proc. 32nd Int. Conf. Mach. Learn. 37, 597–606 (2015)
Chen, H.C., Jia, W.Y., et al.: Saliency-aware food image segmentation for personal dietary assessment using a wearable computer. Meas. Sci. Technol. 26, 025702 (2015)
Fu, K., Jiang, Y., et al.: Light field salient object detection: a review and benchmark. Comput. Vis. Media 8, 509–534 (2022)
Li, N., Ye, J., et al.: Saliency detection on light field. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 2806–2813 (2014)
Levoy, M., Hanrahan, P.: Light field rendering. In: Proceedings of 23rd annual conference computer graphics interactive techniques, pp. 31–42 (1996)
Ng, R., Levoy, M., et al.: Light field photography with a hand-held plenoptic camera. Stanford University (2005)
Zhang, J., Liu, Y., et al.: Light field saliency detection with deep convolutional networks. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 29, 4421–4434 (2020)
Tan, Z.P., Thurow, B.S.: Perspective on the development and application of light-field cameras in flow diagnostics. Meas. Sci. Technol. 32, 101001 (2021)
Wang, T.C., Zhu, J.Y., et al.: A 4d light-field dataset and CNN architectures for material recognition. In: Proceedings of 14th European conference computer vision, pp. 121–138 (2016)
Shin, C., Jeon. H,G., et al.: Epinet: a fully-convolutional neural network using epipolar geometry for depth from light field images. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 4748–4757 (2018)
Gul, M.K., Gunturk, B.K.: Spatial and angular resolution enhancement of light fields using convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 27, 2146–2159 (2018)
Piao, Y., Rong, Z., et al.: Deep light-field-driven saliency detection from a single view. In: Proceedings of 28th international joint conference on artificial intelligence, pp. 904–911 (2019)
Zhang, Q., Wang, S., et al.: A multi-task collaborative network for light field salient object detection. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 31, 1849–1861 (2021)
Zhang, M., Ji, W., et al.: LFNet: light field fusion network for salient object detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 29, 6276–6287 (2020)
Zhang, M., Li, J., et al.: Memory-oriented decoder for light field salient object detection. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 32, 896–906 (2019)
Piao, Y., Rong, Z., et al.: Exploit and replace: an asymmetrical two-stream architecture for versatile light field saliency detection. In: Proceedings of AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, pp. 11865–11873 (2020)
Wang, T., Piao, Y., et al.: Deep learning for light field saliency detection. In: IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp. 8838–8848 (2019)
Li, N., Sun, B., Yu, J.: A weighted sparse coding framework for saliency detection. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 5216–5223 (2015)
Zhang, J., Wang, M., et al.: Saliency detection with a deeper investigation of light field. In: Proceedings of 24th international joint conference artificial intelligence, pp. 2212–2218 (2015)
Zhang, J., Wang, M., et al.: Saliency detection on light field: a multi-cue approach. ACM Trans. Multimedia Comput. Commun. Appl. 13, 1–22 (2017)
Wang, A., Wang, M., et al.: A two-stage bayesian integration framework for salient object detection on light field. Neural Process Lett. 46, 1083–1094 (2017)
Piao, Y., Li, X., et al.: Saliency detection via depth-induced cellular automata on light field. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 29, 1879–1889 (2020)
Ji, S., Xu, W., et al.: 3D convolutional neural networks for human action recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 35, 221–231 (2013)
Tran, D., Bourdev, L., et al.: Learning spatiotemporal features with 3d convolutional networks. In: IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp. 4489–4497 (2015)
**e, S., Sun, C., et al.: Rethinking spatiotemporal feature learning: speed-accuracy trade-offs in video classification. In: European conference on computer vision, pp. 318–335 (2018)
Qiu, Z., Yao, T., Mei, T.: Learning spatio-temporal representation with pseudo-3d residual networks. In: IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp. 5533–5541 (2017)
Tran, D., Wang, H., et al.: A closer look at spatiotemporal convolutions for action recognition. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 6450–6459 (2018)
Dou, Q., Chen, H., et al.: Automatic detection of cerebral microbleeds from MR images via 3D convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. 35, 1182–1195 (2016)
Çiçek, Ö., Abdulkadir, A., et al.: 3D U-net: learning dense volumetric segmentation from sparse annotation. Med. Image Comput. Comput. Assist. Interv, pp. 424–432 (2016)
Min, K., Corso, J.J.: Tased-net: temporally-aggregating spatial encoder-decoder network for video saliency detection. In: IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp. 2394–2403 (2019)
Chen, Q., Liu, Z., et al.: RGB-D salient object detection via 3D convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, pp. 1063–1071 (2021)
He, K., Zhang, X., et al.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 770–778 (2016)
Carreira, J., Zisserman, A.: Quo vadis, action recognition? A new model and the kinetics dataset. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 6299–6308 (2017)
Qin, X., Zhang, Z., et al.: Basnet: boundary-aware salient object detection. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 7479–7489 (2019)
Chen, L.C., Papandreou, G., et al.: DeepLab: semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 40, 834–848 (2018)
Ioffe, S., Szegedy, C.: Batch normalization: accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In: Proceedings of 32nd international conference machine learning, pp. 448–456 (2015)
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Hinton, G.E.: Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM 60, 84–90 (2017)
Zhao, K., Gao, S., et al.: Optimizing the F-measure for threshold-free salient object detection. In: IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp. 8849–8857 (2019)
Achanta, R., Hemami, S., et al.: Frequency-tuned salient region detection. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 1597–1604 (2009)
Rahman, M.A., Wang, Y.: Optimizing Intersection-Over-Union in Deep Neural Networks for Image Segmentation. In: International symposium on visual computing, pp. 234–244 (2016)
Piao, Y., Rong, Z., et al.: DUT-LFSaliency: versatile dataset and light field-to-RGB saliency detection. ar**v: 2012.15124 (2020)
Perazzi, F., Krähenbühl, P., et al.: Saliency filters: contrast based filtering for salient region detection. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 733–740 (2012)
Fan, D.P., Cheng, M.M., et al.: Structure-measure: a new way to evaluate foreground maps. In: IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp. 4548–4557 (2017)
Fan, D.P., Gong, C., et al.: Enhanced-alignment measure for binary foreground map evaluation. In: Proceedings 27th international joint conference artificial intelligence, pp. 698–704 (2018)
Russakovsky, O., Deng, J., et al.: ImageNet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 115, 211–252 (2015)
Wei, J., Wang, S., Huang, Q.: F3Net: fusion, feedback and focus for salient object detection. Proc. AAAI Conf. on Artif. Intell. 34, 12321–12328 (2020)
Liu, J.J., Hou, Q., et al.: A simple pooling-based design for real-time salient object detection. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 3912–3921 (2019)
Qin, X., Zhang, Z., et al.: U2-Net: going deeper with nested U-structure for salient object detection. Pattern Recognit. 106, 107404 (2020)
Fan, D.P., Zhai, Y., et al.: BBS-Net: RGB-D Salient Object Detection with a Bifurcated Backbone Strategy Network. In: European conference on computer vision, pp. 275–292 (2020)
Zhang, M., Ren, W., et al.: Select, supplement and focus for RGB-D saliency detection. In: IEEE Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 3472–3481 (2020)
Zhang, J., Fan, D.P., et al.: Uncertainty inspired RGB-D saliency detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 44, 5761–5779 (2021)
Funding
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (62171178 and 61801161), the Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province (1908085QF282).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XW and GX contributed to the study design, implementation, results analysis and preparation of the final draft. YZ contributed to the design, conceptualization and preparation of the dataset. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., **ong, G. & Zhang, Y. Focal stack based light field salient object detection via 3D–2D convolution hybrid network. SIViP 18, 109–118 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-023-02700-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-023-02700-1