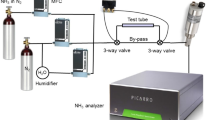
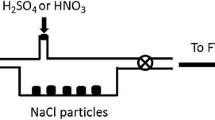
Abstract
Water plays a vital role in atmospheric heterogeneous chemistry by inducing particle surface speciation resulting in enhanced surface chemistry and reactivity. In this study, selected metal oxides (CdO, CuO, MnO2 and ZnO) were synthesized and characterized using UV–Vis spectroscopy for their λmax. The oxide particle sizes were found to fall within the 1–3 µm size range with satisfactory monodispersity. Particles were subjected to ambient (60–70%) and high (99%) relative humidity (%RH) levels at 28 °C—the average ambient temperature. Water adsorption of metal oxides in the presence of low-molecular-weight gas-phase organic compounds (formic acid, acetic acid, formaldehyde and acetaldehyde) was also evaluated. ATR-FTIR analyses were done by subjecting samples to dry, ambient and high % RH conditions in the presence and absence of volatilized organic compounds. Presence of infrared (IR) bands at 1600–1590 cm−1 and 3600–3100 cm−1 in sample IR spectra indicated water adsorption, the possible speciation of oxides into hydroxyl groups and the H bonding of water to hydroxyl groups, respectively. Surface roughness of dry and “wet” samples was also analyzed using atomic force microscopy (AFM) for supplementary surface characterization. Results show that increasing the %RH levels and presence of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) lead to increase in metal oxide water adsorption.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Albadleh H, Grassian V (2003) FTIR study of water adsorption on aluminum oxide surfaces. Langmuir 19:341–347. https://doi.org/10.1021/es00054a004
Al-Albadleh H, Al-Hosney H, Grassian V (2005) Oxide and carbonate surfaces as environmental interfaces: the importance of water in surface composition and surface reactivity. J Mol Catal A 228:47–54. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CC38872G
Andeani JK, Mohsenzadeh S (2013) Phytosynthesis of cadmium oxide nanoparticles from Achillea wilhelmsii flowers. J Chem. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/147613
Beasley M, Bartelink E, Taylor L, Miller R (2014) Comparison of transmission FTIR, ATR, and DRIFT spectra: implications for assessment of bone bioapatite diagenesis. J Archaeol Sci 46:16–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jas.2014.03.008
Chen J, Zhao C, Ma N, Yan P (2014) Aerosol hygroscopicity parameter derived from the light scattering enhancement factor measurements in the North China Plain. Atmos Chem Phys 14:8105–8118. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-14-8105-2014
Formenti P, Elbert W, Maenhaut W, Haywood J, Andreae MO (2003) Chemical composition of mineral dust aerosol during the saharan dust experiment (SHADE) airborne campaign in the Cape Verde region. J Geophys Res. https://doi.org/10.1029/2002JD002648
Fuzzi S, Baltensperger U, Carslaw K, Decesari S, Denier van der Gon H, Facchini MC, Fowler D, Koren I, Langford B, Lohmann U, Nemitz E, Pandis S, Riipinen I, Rudich Y, Schaap M, Slowik JG, Spracklen DV, Vignati E, Wild M, Williams M, Gilardoni S (2015) Particulate matter, air quality and climate: lessons learned and future needs. Atmos Chem Phys 15:8217–8299. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-15-8217-2015
Gankanda A, Cwiertny D, Grassian V (2016) Role of atmospheric CO2 and H2O Adsorption on ZnO and CuO nanoparticle aging: formation of new surface phases and the impact on nanoparticle dissolution. J Phys Chem C 120:19195–19203. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b05931
Ghorbani HR, Mehr FP, Pazoki H, Rahmani BM (2015) Synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles by precipitation method. Orient J Chem 31(2):1219–1221. https://doi.org/10.13005/ojc/310281
**g B, Tong S, Liu Q, Li K, Wang W, Zhang Y, Ge M (2016) Hygroscopic behavior of multicomponent organic aerosols and their internal mixtures with ammonium sulfate. Atmos Chem Phys 16:4101–4118. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-16-4101-2016
Joshi N, Romanias B, Riffault V, Thevenet F (2017) Investigating water adsorption onto natural mineral dust particles: linking DRIFTS experiments and BET theory. Aeol Res 27:35–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aeolia.2017.06.001
Kumar H, Sangwan M, Sangwan P (2013) Synthesis and characterization of MnO2 nanoparticles using co-precipitation technique. Int J Chem Chem Eng 3(3):155–160
Kumar A, Kumar D, Pandey G (2016) Characterization of hydrothermally synthesized CuO nanoparticles at different pH. J Technol Adv Sci Res 2(4):166–169. https://doi.org/10.14260/jtasr/2016/29
Lagashetty A (2016) Microwave-assisted synthesis and characterization of nanosized ZnO, CdO and ZnO–Cdo nanocomposite. J Nanosci Technol 2(2):97–99
Lassoued A, Dkhil B, Gadri A, Ammar S (2017) Control of the shape and size of iron oxide (α-Fe2O3) nanoparticles synthesized through the chemical precipitation method. Results Phys 7:3007–3015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2017.07.066
Li P, Qian H, Howard KW, Lyu X (2014) Anthropogenic pollution and variability of manganese in alluvial sediments of the Yellow River, Ningxia, northwest China. Environ Monit Asses 186(3):1385–1398. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-013-3461-3
Lough G, Schauer J, Park JS, Shafer M, DeMinter J, Weinstein JP (2005) Emissions of metals associated with motor vehicle roadways. Environ Sci Technol 39(3):826–836. https://doi.org/10.1021/es048715f
Lu PD, He T, Zhang YH (2008) Relative humidity anneal effect on hygroscopicity of aerosol particles studied by rapid-scan FTIR-ATR spectroscopy. Geophys Res Lett 35:L20812. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008GL035302
Ma Q, Liu Y, Liu C, He H (2012) Heterogeneous reaction of acetic acid on MgO, A-Al2O3 and CaCO3 and the effect on the hygroscopic behavior of these particles. Phys Chem Chem Phys 14:8403–8409. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2cp40510e
McNeill V (2017) Atmospheric aerosols: clouds, chemistry, and climate. Ann Rev Chem Biomol Eng 8:427–444. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-chembioeng-060816-101538
Morris H, Estillore A, Laskina O, Grassian V, Tivanski A (2016) Quantifying the hygroscopic growth of individual submicrometer particles with atomic force microscopy. Anal Chem 88(7):3647–3654. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.5b04349
Navea JG, Chen H, Huang M, Carmichel GR, Grassian VH (2010) A comparative evaluation of water uptake on several mineral dust sources. Environ Chem 7:162–170. https://doi.org/10.1071/EN09122
Oliveira R, Alburquerque DAC, Cruz Yamaji, Yamaji FM, Leite FL (2012) Measurement of the nanoscale roughness by atomic force microscopy: basic principles and applications. INTECH 7:147–159. https://doi.org/10.5772/37583
Phiwdang K, Suphankji S, Mekprasart W (2013) Synthesis of CuO nanoparticles by precipitation method using different precursors. Energy Proc 34:740–745. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2013.06.808
Poschl U (2005) Atmospheric aerosols: composition, transformation, climate and health effects. Angew Chem Int Ed 44:7520–7540. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200501122
Riipinen I, Pierce JR, Yli-Juuti T, Nieminen T, Häkkinen S, Ehn M, Junninen H, Lehtipalo K, Petäjä, Slowik J, Chang R, Shantz NC, Abbatt J, Leaitch WR, Kerminen VM, Worsnop DR, Pandis SN, Donahue NM, Kulmala M (2011) Organic condensation: a vital link connecting aerosol formation to cloud condensation nuclei (CCN). Atmos Chem Phys 11:3865–3878. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-11-3865-2011
Rubasinghege G, Grassian V (2013) Role(s) of adsorbed water in the surface chemistry of environmental surfaces. Chem Commun 49:3071. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CC38872G
Rubasinghege G, Baltrusaitis J, Grassian VH (2013) Heterogeneous uptake and adsorption of gas phase formic acid on oxide and clay particles: the roles of surface hydroxyl groups and adsorbed water in formic acid adsorption and the impact of formic acid adsorption on water uptake. J Phys Chem A 117:11316–11327. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp408169w
Schuttlefield J, Al-Hosney H, Zachariah A, Grassian VH (2007) Attenuated total reflection Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy to investigate water uptake and phase transitions in atmospherically relevant particles. Appl Spectrosc 61(3):283–292. https://doi.org/10.1366/000370207780220868
Seinfeld & Pandis (1998) Atmospheric chemistry and physics from air pollution to climate change. Wiley, New York
Somanathan T, Krishna VM, Saravan V, Kumar R, Kumar R (2016) MgO nanoparticles for effective uptake and release of doxorubicin drug: pH sensitive controlled drug release. J Nanosci Nanothecnol 16:9421–9431. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2016.12164
Sumner AL, Menke E, Dubowski Y, Newberg JT, Penner RM, Hemminger JC, Wingen LM, Brauers T, Finlayson-Pitts BJ (2004) The nature of water on surfaces of laboratory systems and implications for heterogeneous chemistry in the troposphere. Phys Chem Chem Phys 6:604–613. https://doi.org/10.1039/B308125G
Tamura H, Mita K, Tanaka A, Ito M (2001) Mechanism of hydroxylation of metal oxide surfaces. J Colloid Interface Sci 243:202–207. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcis.2001.7864
Tang M, Alexander JM, Kwon D, Estillore A, Laskina O, Young MA, Kleiber PD, Grassian VH (2016a) Optical and physicochemical properties of brown carbon aerosol: light scattering, FTIR extinction spectroscopy and hygroscopic growth. J Phys Chem 120(24):4155–4166. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpca.6b03425
Tang M, Larish WA, Fang Y, Gankamda A, Grassian VH (2016b) Heterogeneous reactions of acetic acid with oxide surfaces: effects of mineralogy and relative humidity. J Phys Chem A 120:5609–5616. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpca.6b05395
Tang M, Huang X, Lu K, Ge M, Li Y, Cheng P, Zhu T, Ding A, Zhang Y, Gligorovski S, Song W, Ding X, Bi X, Wang X (2017) Heterogeneous reactions of mineral dust aerosol: implications for tropospheric oxidation capacity. Atmos Chem Phys 17:11727–11777. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-17-11727-2017
Tong SR, Wu YW, Ge MF, Wang WG, Pu ZF (2010) Heterogenous chemistry of monocarboxylic acids on alpha-Al2O3 at different relative humidities. Atmos Chem Phys 10:7561–7574. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-10-7561-2010
Zamora I, Tabazadeh A, Golden DM, Jacobson MZ (2011) Hygroscopic growth of common organic aerosol solutes including humic substances, as derived from water activity measurements. J Geophys Res. https://doi.org/10.1029/2011JD016067
Zeng G, Kelley J, Kish JD, Liu Y (2014) Temperature-dependent deliquescent and efflorescent properties of methanesulfonate sodium by ATR-FTIR spectroscopy. J Phys Chem 118:583–591. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp405896y
Zhang R, Khalivoz AF, Pagels J, Zhang D, Xue H, McMurry P (2008) Variability in morphology, hygroscopicity, andoptical properties of soot aerosols during atmospheric processing. PNAS 105(30):10291–10296. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0804860105
Acknowledgements
This work was supported and funded by the Natural Sciences Research Institute (Project Code: CHE-17-1-05) of the University of the Philippines Diliman Campus. Analytical Services Laboratory, Dr. Leon M. Payawan’s research group and Dr. Portia Mahal G. Sabido’s research group at UP Diliman are also acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Babela, D.L.D.T., Lamorena, R.B. Effect of humidity and organic vapors on water absorption of metal oxides. Chem. Pap. 74, 217–227 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-019-00870-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-019-00870-2