Abstract
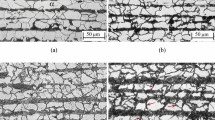
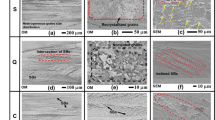
In this work, the microstructure, and mechanical properties of cold-rolled low-density multi-principal-element Fe-30Mn-10Al-1.57C-2.3Cr-0.3Si-0.6Ti (wt.%) specimens were systematically investigated by annealing under different conditions. The microstructural evolution and strengthening mechanism were also examined. Results from x-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD) analyses confirmed that carbides were composed of TiC and κ-carbides. As the annealing temperature increased, both the volume fraction of κ-carbides and yield strength (YS) of the alloys decreased. TEM images indicated a pile-up of dislocations around carbides and boundary of twins. The increase in annealing temperature to 450 °C led to best mechanical properties of specimens with σ0.2% = 1270.28 MPa, Rm = 1318.67 MPa, and ε = 19.47%. Moreover, YS decreased by 9.28% and TE increased by 192.78%. Notably, the density of the as-obtained alloy reached 6.58 g/cm3, a value 15.6% lower than that of conventional steel. In sum, these findings are promising for future applications of low-density alloys.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The raw/processed data required to reproduce these findings cannot be shared owing to the ongoing nature of our current project.
References
M.Y.K. Hashimoto, K. Fujimura, T. Matsui, and K. Izumiya, Global CO2 Recycling-Novel Materials and Prospect for Prevent of Global Warming and Abundant Energy Supply, Mater. Sci. Eng. A A, 1999, 267, p 200–206.
K. Kaygusuz, Energy and Environmental Issues Relating to Greenhouse Gas Emissions for Sustainable Development in Turkey, Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev., 2009, 13(1), p 253–270.
M. Ritzkowski and R. Stegmann, Controlling Greenhouse Gas Emissions Through Landfill In Situ Aeration, Int. J. Greenh. Gas. Control, 2007, 1(3), p 281–288.
G. Frommeyer and U. Brüx, Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of High-Strength Fe-Mn-AI-C Light-Weight TRIPLEX Steels, Steels Automot. Appl., 2006, 77, p 9–10.
S.S. Sohn, B.J. Lee, S. Lee, N.J. Kim, and J.H. Kwak, Effect of Annealing Temperature on Microstructural Modification and Tensile Properties in 0.35C-3.5Mn-5.8Al Lightweight Steel, Acta Mater., 2013, 61(13), p 5050–5066.
K.G. Chin, H.J. Lee, J.H. Kwak, J.Y. Kang, and B.J. Lee, Thermodynamic Calculation on the Stability of (Fe, Mn)3AlC Carbide in High Aluminum Steels, J. Alloys Compd., 2010, 505(1), p 217–223.
H.R. Ogden, R.I. Jaffee, and F.C. Holden, Structure and Properties of Ti-C Alloys, J. Metals, 1955, 203, p 73–80.
H. Kim, D.W. Suh, and N.J. Kim, Fe-Al-Mn-C Lightweight Structural Alloys: A Review on the Microstructures and Mechanical Properties, Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater., 2013, 14(1), p 014205.
J. Moon, S.J. Park, J.H. Jang, T.H. Lee, C.H. Lee, H.U. Hong, H.N. Han, J. Lee, B.H. Lee, and C. Lee, Investigations of the Microstructure Evolution and Tensile Deformation Behavior of Austenitic Fe-Mn-Al-C Lightweight Steels and the Effect of Mo Addition, Acta Mater., 2018, 147, p 226–235.
F. Wang, S. Wang, B. Chen, W. Ma, Q. **g, X. Zhang, M. Ma, Q. Wang, and R. Liu, Effect of Ti Addition on the Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Novel Al-Rich Low-Density Multi-Principal-Element Alloys, J. Alloys Compd., 2022, 891, p 162028.
F. Yang, R. Song, Y. Li, T. Sun, and K. Wang, Tensile Deformation of Low Density Duplex Fe-Mn-Al-C Steel, Mater. Des., 2015, 76, p 32–39.
J. Herrmann, G. Inden, and G. Sauthoff, Deformation Behaviour of Iron-Rich Iron-Aluminum Alloys at Low Temperatures, Acta Mater., 2003, 51(10), p 2847–2857.
C. Castan, F. Montheillet, and A. Perlade, Dynamic Recrystallization Mechanisms of an Fe-8% Al Low Density Steel Under Hot Rolling Conditions, Scripta Mater., 2013, 68(6), p 360–364.
R. Rana, C. Liu, and R.K. Ray, Low-Density Low-Carbon Fe-Al Ferritic Steels, Scripta Mater., 2013, 68(6), p 354–359.
A. Zargaran, H.S. Kim, J.H. Kwak, and N.J. Kim, Effects of Nb and C Additions on the Microstructure and Tensile Properties of Lightweight Ferritic Fe-8Al-5Mn Alloy, Scripta Mater., 2014, 89, p 37–40.
S. Chen, R. Rana, A. Haldar, and R.K. Ray, Current State of Fe-Mn-Al-C Low Density Steels, Prog. Mater. Sci., 2017, 89, p 345–391.
T. Sakai, A. Belyakov, R. Kaibyshev, H. Miura, and J.J. Jonas, Dynamic and Post-Dynamic Recrystallization Under Hot, Cold and Severe Plastic Deformation Conditions, Prog. Mater Sci., 2014, 60, p 130–207.
K. Sato, K. Tagawa, and Y. Inoue, Modulated Structure and Magnetic Properties of Age-Hardenable Fe-Mn-Al-C alloys, Metall. Trans. A, 1990, 21, p 5–11.
W. Song, W. Zhang, J. von Appen, R. Dronskowski, and W. Bleck, κ-Phase Formation in Fe-Mn-Al-C Austenitic Steels, Steel Res. Int., 2015, 86(10), p 1161–1169.
G.R. Speich, V.A. Demares, and R.L. Miller, Formation of Austenite During Intercritical Annealing of Dual-Phase Steels, Metall. Mater. Trans. A., 1981, 12, p 1419–1428.
S. Dutta, V. Ra**ikanth, A.K. Panda, A. Mitra, S. Chatterjee, and R.K. Roy, Effect of Annealing Treatment on Mechanical and Magnetic Softening Behaviors of Cold Rolled Interstitial-Free Steel, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2019, 28(4), p 2228–2236.
S. Dutta, A.K. Panda, S. Chatterjee, and R.K. Roy, Effect of Annealing Treatment on Magnetic Texture of Cold Rolled ULC Steel, Mater. Lett., 2020, 276, p 128211.
I. Gutierrez-Urrutia and D. Raabe, Multistage Strain Hardening Through Dislocation Substructure and Twinning in a High Strength and Ductile Weight-Reduced Fe-Mn-Al-C Steel, Acta Mater., 2012, 60(16), p 5791–5802.
Z.H. Cai, H. Ding, R.D.K. Misra, and H. Kong, Unique Serrated Flow Dependence of Critical Stress in a Hot-Rolled Fe-Mn-Al-C Steel, Scripta. Mater., 2014, 71, p 5–8.
Z. Dapeng, L. Yong, L. Feng, W. Yuren, Z. Liujie, and D. Yuhai, ODS Ferritic Steel Engineered with Bimodal Grain Size for High Strength and Ductility, Mater. Lett., 2011, 65(11), p 1672–1674.
Z.H. Li, J.K. Ren, C. Wang, X. Wang, R.D. Misra, and G.D. Wang, Design of a Cold-Rolled Novel Advanced High-Strength Steel: An Analysis of Microstructural Evolution and Mechanical Properties, Mater. Charact., 2020, 163, p 110265.
M. Liu, X. Li, Y. Zhang, C. Song, and Q. Zhai, Multiphase Precipitation and Its Strengthening Mechanism in a V-Containing Austenite-Based Low Density Steel, Intermetallics, 2021, 134, p 107179.
B.J. Lee, J.S. Song, W.J. Moon, and S.I. Hong, Modifications of Partial-Dislocation-Induced Defects and Strength/Ductility Enhancement in Metastable High Entropy Alloys Through Nitrogen Do**, Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 2021, 803, p 140684.
X. Ma, B. Langelier, B. Gault, and S. Subramanian, Effect of Nb Addition to Ti-Bearing Super Martensitic Stainless Steel on Control of Austenite Grain Size and Strengthening, Metall. Mater. Trans. A., 2017, 48(5), p 2460–2471.
M.C. Ha, J.M. Koo, J.K. Lee, S.W. Hwang, and K.T. Park, Tensile Deformation of a Low Density Fe-27Mn-12Al-0.8C Duplex Steel in Association with Ordered Phases at Ambient Temperature, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, 586, p 276–283.
J. Lee, H. Kim, S.J. Park, J. Moon, and H.N. Han, Correlation Between Macroscale Tensile Properties and Small-Scale Intrinsic Mechanical Behavior of Mo-Added Fe-Mn-Al-C Lightweight Steels, Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 2019, 768, p 138460.
I. Gutierrez-Urrutia and D. Raabe, Influence of Al Content and Precipitation State on the Mechanical Behavior of Austenitic High-Mn Low-Density Steels, Scripta. Mater., 2013, 68(6), p 343–347.
R.B. Figueiredo and T.G. Langdon, Deformation Mechanisms in Ultrafine-Grained Metals with an Emphasis on the Hall-Petch Relationship and Strain Rate Sensitivity, J. Market. Res., 2021, 14, p 137–159.
L. Zhang and Y. Shibuta, Inverse Hall-Petch Relationship of High-Entropy Alloy by Atomistic Simulation, Mater. Lett., 2020, 274, p 128024.
Y. Chong, G. Deng, S. Gao, J. Yi, A. Shibata, and N. Tsuji, Yielding Nature and Hall-Petch Relationships in Ti-6Al-4V Alloy with Fully Equiaxed and Bimodal Microstructures, Scripta. Mater., 2019, 172, p 77–82.
M.Y. Seok, I.C. Choi, J. Moon, S. Kim, U. Ramamurty, and J.I. Jang, Estimation of the Hall-Petch Strengthening Coefficient of Steels Through Nanoindentation, Scripta. Mater., 2014, 87, p 49–52.
M. Sauzay, B. Fournier, M. Mottot, A. Pineau and I. Monnet, Cyclic Softening of Martensitic Steels at High Temperature—Experiments and Physically Based Modelling, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, 483484, p 410414.
T. Ungár, A.D. Stoica, G. Tichy, and X.L. Wang, Orientation-Dependent Evolution of the Dislocation Density in Grain Populations with Different Crystallographic Orientations Relative to the Tensile Axis in a Polycrystalline Aggregate of Stainless Steel, Acta Mater., 2014, 66, p 251–261.
S. Lee, Y. Estrin, and B.C. De Cooman, Constitutive Modeling of the Mechanical Properties of V-Added Medium Manganese TRIP Steel, Metall. Mater. Trans. A., 2013, 44(7), p 3136–3146.
C.H. Nathan, Mechanical and Materials for Design, McGrow-Hill Book Company, New York, 1984.
H. Wen, T.D. Top**, D. Isheim, D.N. Seidman, and E.J. Lavernia, Strengthening Mechanisms in a High-Strength Bulk Nanostructured Cu-Zn-Al Alloy Processed via Cryomilling and Spark Plasma Sintering, Acta Mater., 2013, 61(8), p 2769–2782.
D. Lee, J.K. Kim, S. Lee, K. Lee, and B.C. De Cooman, Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Ti and Mo Micro-Alloyed Medium Mn Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2017, 706, p 1–14.
K. Ma, H. Wen, T. Hu, T.D. Top**, D. Isheim, D.N. Seidman, E.J. Lavernia, and J.M. Schoenung, Mechanical Behavior and Strengthening Mechanisms in Ultrafine Grain Precipitation-Strengthened Aluminum Alloy, Acta Mater., 2014, 62, p p141-155.
C.W. Kim, M. Terner, J.H. Lee, H.U. Hong, J. Moon, S.J. Park, J.H. Jang, C.H. Lee, B.H. Lee, and Y.J. Lee, Partitioning of C into κ-Carbides by Si Addition and Its Effect on the Initial Deformation Mechanism of Fe-Mn-Al-C Lightweight Steels, J. Alloys Compd., 2019, 775, p p554-564.
M.D. Mulholland and D.N. Seidman, Nanoscale Co-Precipitation and Mechanical Properties of a High-Strength Low-Carbon Steel, Acta Mater., 2011, 59(5), p 1881–1897.
L. Bartlett, R.A. Howell, A. Schulta, D. VanAken, and K. Peaslee, A Review of the Physical and Mechanical Properties of a Cast High Strength and Lightweight Fe-Mn-Al-C Steel, Proc. Mater. Sci. Technol. Conf. Exhib., 2010, 3, p 1941–1953.
M. Liu, X. Li, Y. Zhang et al., Multiphase Precipitation and Its Strengthening Mechanism in a V-Containing Austenite-Based Low-Density Steel, Intermetallics, 2021, 134, p 107179.
T. Gladman, The Physical Metallurgy of Microalloyed Steels, (2002)
Y. Li, Y. Lu, W. Li, M. Khedr, H. Liu, and X. **, Hierarchical Microstructure Design of a Bimodal Grained Twinning-Induced Plasticity Steel with Excellent Cryogenic Mechanical Properties, Acta Mater., 2018, 158, p 79–94.
H. Song, J. Yoo, S.-H. Kim, S.S. Sohn, M. Koo, N.J. Kim, and S. Lee, Novel Ultra-High-Strength Cu-Containing Medium-Mn Duplex Lightweight Steels, Acta Mater., 2017, 135, p 215–225.
Z.G. Liu, X.H. Gao, M. **ong, P. Li, R.D. Misra, D.Y. Rao, and Y.C. Wang, Role of Hot Rolling Procedure and Solution Treatment Process on Microstructure, Strength and Cryogenic Toughness of High Manganese Austenitic Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 2021, 807, p 140881.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National major research instrument development project (Grant No. 52127808). The authors would like to thank Dr. B.H. Chen, Dr. P.F. Ji, and Dr. B. Li for help and guidance with writing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, F., An, Z.L., Qian, Z.Z. et al. Effect of Annealing on Microstructure and Mechanical Behavior of Cold Deformed Low-Density Multi-principal-Element High-Strength Alloys. J. of Materi Eng and Perform (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-023-08465-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-023-08465-5