Abstract
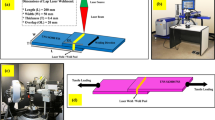
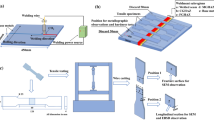
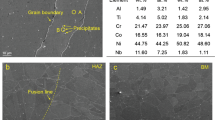
In this study, the microstructural evolutions, phase equilibrium, mechanical properties and fracture mechanism of hot-rolled and post-weld solution-treated Fe-12.5Mn-9.8Al-1.0C(wt.%) low-density steel welded joints were investigated. Optical microscopy (OM), scanning electron microscope (SEM), eelectron backscatter diffraction (EBSD) and x-ray diffraction (XRD) were used to analyze microstructure and phases of the weld metal. Tensile test and microhardness test were inspected to determine the mechanical properties. Tensile fracture morphology was also determined by SEM. The results illustrated that welded joint was composed of austenite and annealing twins. Compared with the hot-rolled experimental steel, the strength and hardness of the post-weld solution-treated steel were reduced, but the elongation was increased. Especially, when the solution temperature was 950 °C, the elongation increased to 10.6%, which improved the plasticity and the quality of the welded joint.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.A. Howell and D.C. Van Aken, A Literature Review of Age Hardening Fe-Mn-Al-C Alloys, Iron Steel Tech, 2009, 6, p 193–212.
H. Kim, D.W. Suh and N.J. Kim, Fe-Al-Mn-C Lightweight Structural Alloys: a Review on the Microstructures and Mechanical Properties, Sci. Tech. Adv. Mater., 2013, 14, p 1–11.
S.D. Woo and N.J. Kim, Viewpoint Set 53: Low Density Steels, Scripta. Mater., 2013, 68, p 337–442.
R. Rana, Special Topic: Low Density Steels, JOM, 2014, 66, p 1730–1876.
Bausch M, Frommeyer G, Hofmann H, Balichev E, Soler M, Didier M, et al. Ultra high-strength and ductile Fe-Mn-Al-C light-weight steels. Final Report RFCS Grant No RFSR-CT-2006–00027. (2009)
G. Frommeyer and U. Brüx, Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of High-Strength Fe-Mn-Al-C Light-Weight Triplex Steels, Steel Res. Int., 2006, 77, p 627–633.
I.S. Kalashnikov, O. Acselrad and L.C. Pereira, Chemical Composition Optimization for Austenitic Steels of the Fe-Mn-Al-C System, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2000, 9, p 597–602.
Y. Sutou, N. Kamiya, R. Umino, I. Ohnuma and K. Ishida, High-Strength Fe-20Mn-Al-C-Based Alloys with Low Density, ISIJ Int., 2010, 50, p 893–899.
D. Raabe, H. Springer, I. Gutierrez-Urrutia, F. Roters, M. Bausch, J.B. Seol et al., Alloy Design, Combinatorial Synthesis, and Microstructure-Property Relations for Low-Density Fe-Mn-Al-C Austenitic Steels, JOM, 2014, 66, p 1845–1855.
X.F. Zhang, Z.W. Kan, Y. Yang et al., Investigation of the Effect of Electrolytic Hydrogen Charging on Tensile-Ductility Loss in Different Al-Added Low Density Steels, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2020, 795, 140027.
J.S. Ku, N.J. Ho, S.C. Tjong et al., Properties of Electron-Beam-Welded and Laser-Welded Austenitic Fe-28Mn-5Al-1C Alloy[J], J. Mater. Sci., 1993, 28(10), p 2808–2814.
Sebeck K, Toppler I, Rogers M, Limmer K, Cheeseman B,Howell R, High Mn, high Al steels for thick plate Armor applications. In: 2018 NDIA GVSET symposium. pp. 7–9 Aug 2018
M. Sabzi and S.M. Dezfuli, Post Weld Heat Treatment of Hypereutectoid Hadfield Steel: Characterization and Control of Microstructure, Phase Equilibrium, Mechanical Properties and Fracture Mode of Welding Joint, J. Manuf. Process., 2018, 34, p 313–328.
S.H. Mousavi Anijdan and M. Sabzi, The Effect of Heat Treatment Process Parameters on Mechanical Properties, Precipitation, Fatigue Life, and Fracture Mode of an Austenitic Mn Hadfield Steel[J], J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2018, 27(10), p 5246–5253.
M. Sabzi and M. Farzam, Hadfield Manganese Austenitic Steel: a Review of Manufacturing Processes and Properties, Mater. Res. Expr., 2019, 6(10), p 10652.
L. Xu, S. Wei, F. **ao, H. Zhou, G. Zhang and J. Li, Effects of Carbides on Abrasive Wear Properties and Failure Behaviors of High Speed Steels with Different Alloy Element Content, Wear, 2017, 376, p 968–974.
AWS B21 Standard Welding Procedure Specification, Shielded Metal Arc Welding of Carbon Steel. AWS Int. 1, 1–16 (2005)
I. Gutierrez-Urrutia, S. Zaefferer and D. Raabe, The Effect of Grain Size and Grainorientation on Deformation Twinning in a Fe-22 wt.% Mn-0.6 wt.% C TWIP Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2010, 527, p 3552–3560.
N. Kumar, M. Mukherjee and A. Bandyopadhyay, Study on Laser Welding of Austenitic Stainless Steel by Varying Incident Angle of Pulsed Laser Beam, Opt. Laser Technol., 2017, 94, p 296–309.
L.H. Xu, Z.L. Tian, Y. Peng et al., Comparison of MIG Weld-ing and Laser-MIG Welding of High Strength Aluminum Alloy, Trans. China Weld. Inst., 2007, 28(2), p 38–42.
Z.F. Zhou and W.Y. Zhang, Welding metallurgy and metal weld-ability, Mechanical Industry Press, Bei**g, 1988.
X. Zhang, G. Mi, S. Li, X. Hu, C. Wang and Y. Zhang, Study of Microstructural Inhomogeneity and its Effects on Mechanical Properties of Multi-layer Laser Welded Joint, Int J Adv Manufact Technol., 2017, 94(5–8), p 2163–2174.
C. Zheng, Q. Liu, S. Zheng, X. Chong, Y. Jiang and J. Feng, Effect of Solution Treatment on Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Welded Joints of Fe-29Mn-9Al-0.9C Low-Density Steel, J Micromechan Mol Phys., 2020, 5(02), p 2050006.
Z. Mi, D. Tang, H. Jiang, Y. Dai and S. Li, Effects of Annealing Temperature on the Microstructure and Properties of the 25Mn-3Si-3Al TWIP Steel, Int J Minerals Metall Mater., 2009, 16(2), p 154–158.
J. Pang, Z. Zhou, Z. Zhao, D. Tang, J. Liang and Q. He, Tensile Behavior and Deformation Mechanism of Fe-Mn-Al-C Low Density Steel with High Strength and High Plasticity, Metals, 2019, 9(8), p 897.
G. Qizhi, Y. Wanli and B. Yongjun, Study of Crystal Defects in Natural Diamond, Diam. Relat. Mater., 1993, 2(9), p 1239–1242.
J. Cao, J.C. Yang and W.G. Zhu, Effect of Pulse Current on the Microstructure of Tungsten Electrode in Tensile Process, Mater. Sci. Forum, 2015, 817, p 104–108.
A.K. Lakshminarayanan, V. Balasubramanian and K. Elangovan, Effect of Welding Processes on Tensile Properties of AA6061 Aluminium Alloy Joints, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2009, 40(3–4), p 286–296.
H.R. Jafarian, M. Sabzi, S.H.M. Anijdan et al., The Influence of Austenitization Temperature on Microstructural Developments, Mechanical Properties, Fracture Mode and Wear Mechanism of Hadfield High Manganese Steel, J. Market. Res., 2021, 10, p 819–831.
T.R. Tabrizi, M. Sabzi, S.H.M. Anijdan et al., Comparing the Effect of Continuous and Pulsed Current in the GTAW Process of AISI 316L Stainless Steel Welded Joint: Microstructural Evolution, Phase Equilibrium, Mechanical Properties and Fracture Mode, J. Market. Res., 2021, 15, p 199–212.
M.H. Razmpoosh, M. Shamanian and M. Esmailzadeh, The Microstructural Evolution and Mechanical Properties of Resistance Spot Welded Fe-31Mn-3Al-3Si TWIP Steel, Mater. Des., 2015, 67, p 571–576.
W. Peng, X. Gao, X. Guo, H. Lu, G. Li, X. **ao and H. Dong, Effect of Microstructure Evolution in Austenite Zone on Mechanical Properties of Fe-10Mn-5.5 Al-0.25 C Steel, Mater Des., 2020, 196, p 109163.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the National Natural Science Fund (No. 51674004), and Anhui Provincial Natural Science Foundation (No. 2108085ME143), and Anhui Provincial Universities Natural Science Research Project (No. KJ2021ZD0045).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mei, X., Ya-xiong, W., **ao-feng, Z. et al. The Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Welded Joints of Hot-Rolled and Post-Weld Solution-Treated Fe-12.5Mn-9.8Al-1.0C Low-Density Steel. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 32, 4892–4901 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-07455-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-07455-3