Abstract
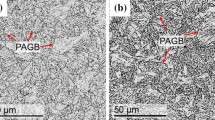
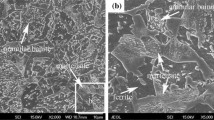
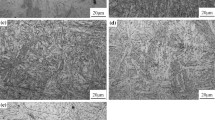
The effect of molybdenum content (1.25, 2.25, 3.0 wt.%) on the microstructure, mechanical properties, and thermal stability of 4Cr5Mo2V steel has been investigated. The increase of Mo content promotes the transition of M23C6 to M6C and inhibits the nucleation and growth of M23C6, as supported by the transmission electron microscope observation presented in this paper. The result shows that the mechanical properties and the thermal stability at 620 °C are both strongly dependent on the Mo content. The yield/tensile strengths at room temperature of 1.25, 2.25, and 3.0% Mo steels are 1028/1287, 1080/1347, and 1114/1402 MPa; meanwhile, the elongation is 23, 26, and 27%, respectively. And the yield/tensile strengths at 620 °C of the 1.25, 2.25, and 3.0% Mo steels are 285/661, 379/714 and 335/690 MPa; meanwhile, the elongation is 23, 20, and 22%, respectively. The M6C-type nano-carbides in the three steels enhance the tensile strength through the Orowan bypass strengthening mechanism, providing increments of tensile strength of 145 MPa (1.25 Mo), 167 MPa (2.25 Mo), and 182 MPa (3.0 Mo), respectively. It is obvious that the coarsening kinetics of solute atoms in three steels is controlled by volume diffusion during the tempering at 620 °C. The Avrami exponent n of the 1.25, 2.25, and 3.0% Mo steels at 620 °C is 0.42, 0.41, and 0.37, respectively. The calculations were in consistent with the finding that the average precipitation rate and coarsening rate of carbides in 3.0 Mo steel are the lowest.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y.L. Wang, K.X. Song, Y.M. Zhang and G.X. Wang, Microstructure Evolution and Fracture Mechanism of H13 Steel During High Temperature Tensile Deformation, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2019, 746, p 127–133.
B. Wang, X.F. Zhao, W.Z. Li, M. Qin and J.F. Gu, Effect of Nitrided-Layer Microstructure Control on Wear Behavior of AISI H13 Hot Work Die Steel, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2018, 431, p 39–43.
B. Podgornik, G. Pus, B. Zuzek, V. Leskovsek and M. Godec, Heat Treatment Optimization and Properties Correlation for H11-Type Hot-Work Tool Steel, Metall. Mater. Trans. A., 2018, 49, p 555–562.
D.H. Kim, H.C. Lee, B.M. Kim and K.H. Kim, Estimation of Die Service Life Against Plastic Deformation and Wear During Hot Forging Processes, J. Mater. Process. Tech., 2005, 166, p 372–380.
Q. Zhou, X. Wu, N. Shi, J. Li and M. Na, Microstructure Evolution and Kinetic Analysis of DM Hot-Work Die Steels During Tempering, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2011, 528, p 5696–5700.
Y. Wang, K. Song and Y. Zhang, High-Temperature Softening Mechanism and Kinetic of 4Cr5MoSiV1 Steel During Tempering, Mater. Res. Express, 2019, 6(9), p 069513.
N. Du, H. Liu, P. Fu, H. Liu and D. Li, Microstructural Stability and Softening Resistance of a Novel Hot-Work Die Steel, Curr. Comput.-Aided Drug Des., 2020, 10, p 238.
J. Wang, Z. Xu and X. Lu, Effect of the Quenching and Tempering Temperatures on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of H13 Steel, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2020, 29, p 1–3.
A. Inoue and T. Masumoto, Carbide Reactions (M3C→M7C3→M23C6→M6C) During Tempering of Rapidly Solidified High Carbon Cr-W and Cr-Mo Steels, Metall. Trans. A, 1980, 11, p 739–747.
X.B. Hu, M. Zhang and X.C. Wu, Simulations of Coarsening Behavior for m23c6 Carbides in AISI h13 Steel, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2006, 22, p 153–158.
J. Zhu, G.T. Lin, Z.H. Zhang and J.X. **e, The Martensitic Crystallography and Strengthening Mechanisms of Ultra-High Strength Rare Earth Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2020, 797, p 140139.
A. Liu, L. Wang, L. Pan and X. Cheng, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of a Novel High-Density Steel Having High Tungsten Content, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2021, 824, p 141797.
R. Uemori, R. Chijiiwa, H. Tamehiro and H. Morikawa, AP-FIM Study on the Effect of Mo Addition on Microstructure in Ti-Nb Steel, Appl. Surf. Sci., 1994, 76, p 255–260.
W.B. Lee, S.G. Hong, C.G. Park, K.H. Kim and S.H. Park, Influence of Mo on Precipitation Hardening in Hot Rolled HSLA Steels Containing Nb, Scr. Mater., 2000, 43, p 319–324.
B. Kim, C. Celada, D. San Martín, T. Sourmail and P.E.J. Rivera-Díaz-del-Castillo, The Effect of Silicon on the Nano-Precipitation of Cementite, Acta Mater., 2013, 61, p 6983.
G. Miyamoto, J.C. Oh, K. Hono, T. Furuhara and T. Maki, Effect of Partitioning of Mn-Si on the Growth Kinetics of Cementite in Tempered Fe–0.6 Mass% C Martensite, Acta Mater., 2007, 55, p 5027.
D. Rojas, J. Garcia, O. Prat, G. Sauthoff and A.R. Kaysser-Pyzalla, 9%Cr Heat Resistant Steels: Alloy Design, Microstructure Evolution and Creep Response at 650 °C, Mater. Sci. Eng., 2011, 528, p 5164–5176.
D. Wu, F. Wang and J. Cheng, Effects of Nb and Tempering Time on Carbide Precipitations Behavior and Mechanical Properties of Cr-Mo-V Steel for Brake Discs, Steel Res. Int., 2018, 89, p 1700491.
T. Siwecki, J. Eliasson, R. Lagneborg and B. Hutchinson, Vanadium Microalloyed Bainitic Hot Strip Steels, ISIJ Int., 2010, 50, p 760–767.
Z. Wang, W. Hui, Z. Chen, Y. Zhang and X. Zhao, Effect of Vanadium on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Bainitic Forging Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng., 2020, 771, p 138653.
J. Sun, S. Wei and S. Lu, Influence of Vanadium Content on the Precipitation Evolution and Mechanical Properties of High-Strength Fe-Cr-Ni-Mo Weld Metal, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2020, 772, p 138739-1-138739-S10.
R. Wan, S. Feng, L. Zhang and A. Shan, Development and Study of High-Strength Low-Mo Fire-Resistant Steel, Mater. Des., 2012, 36, p 227–232.
S. Jiang, W. Hui, W. Yuan, X. Liu and Z.P. Lu, Ultrastrong Steel via Minimal Lattice Misfit and High-Density Nanoprecipitation, Sci. Found. China, 2017, 544, p 460.
Z. Wang, H. Zhang, C. Guo, W.B. Liu, Z.G. Yang, X.J. Sun, Z.Y. Zhang and F.C. Jiang, Effect of Molybdenum Addition on the Precipitation of Carbides in the Austenite Matrix of Titanium Micro-Alloyed Steels, J. Mater. Sci., 2016, 51, p 4996–5007.
W.B. Lee, S.G. Hong, C.G. Park, K.H. Kim and S.H. Park, Carbide Precipitation and High-Temperature Strength of Hot-Rolled High-Strength, Low-Alloy Steels Containing Nb and Mo, Metall. Mater. Trans. A., 2002, 33, p 1689–1698.
K. Zhang, M. Zhang, Z. Guo, N. Chen and Y. Rong, A New Effect of Retained Austenite on Ductility Enhancement in High-Strength Quenching–Partitioning–Tempering Martensitic Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2011, 528, p 8486–8491.
Y. Wang, K. Song and Y. Zhang, High-Temperature Softening Mechanism and Kinetic of 4Cr5MoSiV1 Steel During Tempering, Mater. Res. Express, 2019, 6, p 096513.
R.C. Thomson and M.K. Miller, Carbide Precipitation in Martensite During the Early Stages of Tempering Cr and Mo-Containing Low Alloy Steels, Acta Mater., 1998, 46, p 2203–2213.
L. Jiang, R. Marceau, B. Guan, T. Dorin and N. Stanford, The Effect of Molybdenum on Clustering and Precipitation Behaviour of Strip-Cast Steels Containing Niobium, Materialia, 2019, 8, p 100462–100462.
Z. Wang, H. Zhao, L. Chen, G. Wu and M. Wang, Evolution and its Stability of M23(C, N) 6 Carbonitride in Martensite Ferritic Steel During Long-Term Thermal Aging, Mater. Charact., 2019, 152, p 36–43.
Z. Wang, L. Hui, S. Qin, W. Liu and Z. Wang, Nano-Precipitates Evolution and Their Effects on Mechanical Properties of 17–4 Precipitation-Hardening Stainless Steel, Acta Mater., 2018, 156, p 158–171.
B.B. Zhang, F.K. Yan, M.J. Zhao, N.R. Tao and K. Lu, Combined Strengthening from Nanotwins and Nanoprecipitates in an Iron-Based Superalloy, Acta Mater., 2018, 151, p 310–320.
Z.J. Zhang, J.S. Zhang, Y. Lian, M.Y. Ma, C. Zhao, H.Y. Ye, G.J. Li, C. Zhang and J.F. Huang, Effects of Vanadium Content on the Carbides Transformation and Strengthening Mechanism of MPS700V Hot-Work Die Steel at Room and Elevated Temperatures, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2021, 813, p 141091.
H.Y. Yue, H. Peng, Y.J. Su, X.P. Wang and Y.Y. Chen, Microstructure and High-Temperature Tensile Property of TiAl Alloy Produced by Selective Electron Beam Melting, Rare Met., 2021, 6, p 1–10.
F. Krumphals, B. Reggiani, L. Donati, T. Wlanis and C. Sommitsch, Deformation Behaviour of a Ferritic Hot-Work Tool Steel with Respect to the Microstructure, Comput. Mater. Sci., 2012, 52, p 40–45.
M. Madivala, A. Schwedt, S.L. Wong, F. Roters, U. Prahl and W. Bleck, Temperature Dependent Strain Hardening and Fracture Behavior of TWIP Steel, Int. J. Plast., 2018, 80, p 103.
B. Mintz, S. Yue and J. Jonas, Hot Ductility of Steels and its Relationship to the Problem of Transverse Cracking During Continuous Casting, Int. Mater. Rev., 1991, 36, p 187–217.
I.M. Lifshitz and V. Slyozov, The Kinetics of Precipitation from Supersaturated Solid Solutions, J. Phys. Chem. Solids, 1961, 19, p 35–50.
C. Wagner, Theorie der Alterung von Niederschlägen Durch Umlösen, Zeitschrift für Elektrochemie, Berichte der Bunsengesellschaft für Physikalische, Chemie, 2015, 65, p 581–591.
S. **ang, R.M. Wu, W. Li, T. Hu and S. Huang, Improved Red Hardness and Toughness of Hot Work Die Steel through Tungsten Alloying, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2021, 30, p 7.
R.M. Wu, W. Li, M. Chen, S. Huang and T. Hu, Improved Mechanical Properties by Nanosize Tungsten-Molybdenum Carbides in Tungsten Containing Hot Work Die Steels, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2021, 812, p 141140.
X. Hu, L. Li and X. Wu, Coarsening Behavior of M23C6 Carbides After Ageing Or Thermal Fatigue in AISI H13 Steel with Niobium, Int. J. Fatigue, 2006, 28, p 175–182.
D. Nadezhda and K. Rustam, On the Precipitation Sequence in a 10%Cr Steel under Tempering, ISIJ Int., 2011, 51, p 826–831.
Acknowledgment
This research has been supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China during the 13th Five-year Plan Period (Grant No. SQ2020YFF04012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, T., Wu, R., Li, F. et al. Effect of Mo-Related Precipitation Behavior on the Strengthening and Thermal Stability of 4Cr5Mo2V Die Steel. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 31, 10213–10224 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-07029-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-07029-3