Abstract
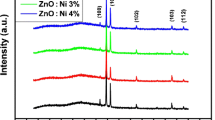
Indium-doped ZnO thin films were prepared using the spray pyrolysis technique, and their electrical properties were investigated. The films were characterized using different techniques, including x-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy, energy-dispersive x-ray analysis, UV–Vis spectroscopy, and Hall measurements. The XRD pattern confirmed that all films had a polycrystalline hexagonal wurtzite crystal structure. An undoped ZnO film showed a preferred crystalline orientation along the (002) peak, while for In-doped ZnO thin films, the preferred orientation changed from the (002) peak to the (101) peak. The surface morphology of the ZnO film changed from a hexagonal nanorod-like structure to a nanorod structure after indium do**. The presence of zinc, oxygen, and indium elements was confirmed by an energy-dispersive spectrometer. Optical studies showed transmittance of 80% for the deposited films, and it decreased with In do**. The optical band gap increased with indium concentration. Hall effect measurements revealed that all the films showed n-type conductivity. The films deposited at 2% In content were found to have relatively low resistivity of 0.937 Ω cm.
Graphical Abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Smaali, S. Abdelli, A. Lafane, J. Mavlonov, S. Lenzner, M. Richter, O. Kechouane, and K. Nemraoui, Ellmer, Pulsed Laser Deposited Transparent and Conductive V-doped ZnO Films. Thin Solid Films 700, 137892 (2020).
Y. Su, C. Chiou, V. Marinova, S. Lin, N. Bozhinov, and B. Blagoev, Atomic Layer Deposition Prepared Al-doped ZnO for Liquid Crystal Displays Applications. Opt. Quantum Electron. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-018-1469-1.
A. Sharmin, S. Tabassum, M. Bashar, and Z. Mahmood, Depositions and Characterization of Sol–gel Processed Al-doped ZnO (AZO) as Transparent Conducting Oxide (TCO) for Solar Cell Application. J. Theor. Appl. Phys. 13, 123 (2019).
J. Beckford, M. Behera, K. Yarbrough, B. Obasogie, S. Pradhan, and M. Bahoura, Gallium Doped Zinc Oxide Thin Films as Transparent Conducting Oxide for Thin-Film Heaters. AIP Adv. 11, 075208 (2021).
F. He, Y. Wang, H. Yuan, Z. Lin, J. Su, and J. Zhang, Solution Processed In2O3/IGO Heterojunction Thin Film Transistors with High Carrier Concentration. Ceram. Int. 47, 35029 (2021).
V.N. Krasil’nikov, I.V. Baklanova, V.P. Zhukov, ОI. Gyrdasova, ТV. Dyachkova, and АP. Tyutyunnik, Thermally Stimulated Infrared Shift of Cadmium Oxide Optical Absorption Band Edge. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 124, 105605 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2020.105605.
D.T. Peaks, Effect of Concentration, Aging, and Annealing on Sol Gel ZnO and Al-doped ZnO Thin Films. Int. J. Mech. Mater. Eng. 15, 2 (2020).
G.L. Tan, D. Tang, D. Dastan, A. Jafari, Z. Shi, and Q. Chu, Structures, Morphological Control, and Antibacterial Performance of Tungsten Oxide Thin Films. Ceram. Int. 47, 17153 (2021).
J. Li, C. Mu and X. Li, Structure and Physical Properties Evolution of ITO Film During Amorphous-Crystalline Transition Using a Highly Effective Annealing Technique. Ceram. Int. 45, 16214 (2019).
U. Rehman, M. Kanwal, K. Mahmood, A. Ashfaq, A. Ali, and S. Tahir, Improving the Thermoelectric Properties of Zinc Tin Oxide Thin Films by Varying Post Growth Annealing Duration. Ceram. Int. 47, 32371 (2021).
M. Zhang, Y. Tang, X. Tian, H. Wang, J. Wang, and Q. Zhang, Magnetron co-Sputtering Optimized Aluminum-doped Zinc Oxide (AZO) Film for High-Response Formaldehyde Sensing. J. Alloys Compd. 880, 160510 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.160510.
Y. Vijayakumar, P. Nagaraju, V. Yaragani, S. Parne, N. Awwad, and M. Ramana Reddy, Nanostructured Al and Fe co-doped ZnO Thin Films for Enhanced Ammonia Detection. Phys B. Condens. Matter. 58, 411976 (2020).
S. Swathi, E. Sunil Babu, R. Yuvakkumar, G. Ravi, A. Chinnathambi, S. Ali Alharbi, and D. Velauthapillai, Branched and Unbranched ZnO Nanorods Grown via Chemical Vapor Deposition Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting Application. Ceram. Int. 47, 9785 (2021).
S. Roguai and A. Djelloul, A Structural and Optical Properties of Cu-Doped ZnO Films Prepared by Spray Pyrolysis. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 126, 1 (2020).
Y. Pepe, M. Yildirim, A. Karatay, A. Ates, H. Unver, and A. Elmali, The Effect of Do** and Annealing on the Nonlinear Absorption Characteristics in Hydrothermally Grown Al Doped ZnO Thin Films. Opt. Mater. 98, 109495 (2019).
F. Baig, A. Asif, M. Waseem Ashraf, and H. Muhammad Fahad, Tailoring of Optical, Hydrophobic, and Anti-icing Properties of Ca–Mg co-doped ZnO Thin Films via sol–gel Method. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 97, 706 (2021).
A. Mostafa and E. Mwafy, Synthesis of ZnO and Au-ZnO core/shell Nano-catalysts by Pulsed Laser Ablation in Different Liquid Media. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 9, 3241 (2020).
V. Kumar, S.K. Singh, H. Sharma, S. Kumar, M.K. Banerjee, and A. Vij, Investigation of Structural and Optical Properties of ZnO Thin Films of Different Thickness Grown by Pulse Laser Deposition Method. Phys. B Phys. Condens. Matter 552, 221 (2019).
Y. Wang, J. Song, J. Zhang, G. Zheng, X. Duan, X. **e, B. Han, X. Meng, F. Yang, G. Wang, Y. Zhao, and J. Li, Effect of Substrate Temperature on F and Al co-doped ZnO Films Deposited Byradio Frequency Magnetron Sputtering. Sol. Energy 194, 471 (2019).
D. Mahesh and M.S. Kumar, Synergetic Effects of Aluminium and Indium Dopants in the Physical Properties of ZnO Thin Films via Spray Pyrolysis. Superlattices Microstruct. 142, 106511 (2020).
A. Lopez-Suarez, D. Acosta, C. Magana, and F. Hernandez, Optical, Structural and Electrical Properties of ZnO Thin Films Doped with Mn. J. Mate. Sci. Mater. Electron. 31, 7389 (2020).
M. Aleksandrova, Polymeric Seed Layer as a Simple Approach for Nanostructuring of Ga-doped ZnO Films for Flexible Piezoelectric Energy Harvesting. Microelectron. Eng. 233, 111434 (2020).
A. Ambedkar, M. Singh, V. Kumar, B. Pal Singh, A. Kumar, and Y. Gautam, Structural, Optical and Thermoelectric Properties of Al-doped ZnO Thin Films Prepared by Spray Pyrolysis. Surf. Interfaces 19, 100504 (2020).
A. Alsaad, A. Ahmad, I. Qattan, Q. Al-Bataineh, and Z. Albataineh, Structural, Optoelectrical, Linear, and Nonlinear Optical Characterizations of Dip-synthesized Undoped ZnO and Group-III Elements (B, al, ga, and in)-doped ZnO Thin Films. Curr. Comput.-Aided Drug Des. 10, 252 (2020).
L.-H. Wong and Y.-S. Lai, Substrate Temperature Dependence of Material, Optical and Electrical Properties of Boron Doped ZnO Thin Films. Opt. Mater. 115, 111052 (2021).
L. Dintle, P. Luhanga, M. Cand, and C. Muiva, Compositional Dependence of Optical and Electrical Properties of Indium Doped Zinc Oxide (IZO) Thin Films Deposited by Chemical Spray Pyrolysis. Phys. E: Low Dimension Syst. Nanostruct. 99, 91 (2018).
P. Dhamodharan, J. Chen, and C. Manoharan, Fabrication of In-doped ZnO Thin Films by Spray Pyrolysis as Photoanode in DSSCs. Surf. Interfaces 23, 100965 (2021).
N. Kumar, A. Haider Chowdhury, B. Bahrami, M. Raza Khan, and M. Kumar, Origin of Enhanced Carrier Mobility and Electrical Conductivity in Seed Layer Assisted Sputtered Grown Al-doped ZnO Thin Films. Thin Solid Films 700, 13716 (2020).
A.P. Rambu, D. Sirbu, A.V. Sandu, G. Prodan, and V. Nica, Influence of In-Do** on Electro-Optical Properties of ZnO Films. Bull. Mater. Sci. 36, 231 (2013).
G. Malik, S. Mourya, J. Jaiswal, and R. Chandra, Effect of Annealing Parameters on Optoelectronic Properties of Highly Ordered ZnO Thin Films. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 100, 200 (2019).
D. Ali, M.Z. Butt, C. Coughlan, D. Caffrey, I.V. Shvets, and K. Fleischer, Nitrogen Grain-Boundary Passivation of In-doped ZnO Transparent Conducting Oxide. Phys. Rev. Materials 2, 043402 (2018).
Y. Fang, J.R. Dilworth, M. Pepper, and P.P. Edwards, Investigations of the Optical and Electronic Effects of Silicon and Indium co-do** on ZnO Thin Films Deposited by Spray Pyrolysis. Zeitschrift fur Naturforschung B 75, 23 (2020).
P. Doni, W. Joseph, K. Hariprasad, V. Ganesh, A. Elhosiny, H. Algarni, and I. Yahi, Enhancement of Optoelectronic Properties of ZnO Thin Films by Al Do** for Photodetector Applications. Superlattices Microstruct. 151, 106790 (2021).
D. Bao, H. Gu, and A. Kuang, Sol Gel Derived c-axis Orientated ZnO Films. Thin Solid Films 312, 37 (1998).
S. Shinde, P. Shinde, C. Bhosale, and K. Rajundoped, Optoelectronic Properties of Sprayed Transparent and Conducting Indium Doped Zinc Oxide Thin Films. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. (2008). https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/41/10/105109.
P. Velusamy, R. Ramesh Babu, K. Ramamurthi, and M. Dahlem, Highly Transparent Conducting Cerium Incorporated CdO Thin Films Deposited by a Spray Pyrolytic Technique. RSC Adv. 5, 102741 (2015).
S. Dev, P. Kumar, A. Rani, A. Agarwal, and R. Dhar, Development of Indium Doped ZnO Thin Films for Highly Sensitive Acetylene (C2H2) Gas Sensing. Superlattices Microstruct. 145, 106638 (2020).
K. Radhi Devi, G. Selvan, M. Karunakaran, I.L. Poul Raj, V. Ganesh, and S. Al Faify, Enhanced Room Temperature Ammonia Gas Sensing Properties of Strontium Doped ZnO Thin Films by Cost-Effective SILAR Method. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 119, 105117 (2020).
A. Goktas, I. Mutlu, and Y. Yamada, Influence of Fe-do** on the Structural, Optical, and Magnetic Properties of ZnO Thin Films Prepared by Sol–gel Method. Superlattices Microstruct. 57, 139 (2013).
M. Saleem, S. Siddiqi, S. Atiq, M. Anwar, I. Hussain, and S. Alam, Carriers-Mediated Ferromagnetic Enhancement in Al-doped Zn-MnO Dilute Magnetic Semiconductors. Mater. Char. 62, 1102 (2011).
P. Raghavendra, J. Bhat, and N. Deshpande, Enhancement of Photoluminescence in Sr Doped ZnO Thin Films Prepared by Spray Pyrolysis. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 68, 262 (2017).
M. Rajendra Prasad, M. Haris, and M. Sridharan, Investigation on Structural, Morphological, Optical and Ammonia Sensing Properties Indium Doped Nano Crystalline ZnO Thin Films Synthesized by Spray Pyrolysis Technique. Sens. Imaging (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11220-018-0211-1.
S. Bharath, K. Bangera, and G. Shivakumar, Enhanced Gas Sensing Properties of Indium Doped ZnO Thin Films. Superlattices Microstruct. 124, 72 (2018).
S. Pati, P. Banerji, and S. Majumder, Properties of Indium Doped Nanocrystalline ZnO Thin Films and their Enhanced Gas Sensing Performance. RSC Adv. 5, 61230 (2015).
Y. Benkhetta, A. Attaf, H. Saidi, R. Messemeche, A. Bouhdjer, H. Bendjedidi, I.B. Kherkhachi, and A. Rahil, Controlling of c-axis Position of ZnO Nano-Crystalline Films Deposited at Various Substrate Temperature by Ultrasonic Spray Method. Surf. Interfaces 21, 100698 (2020).
R. Vinodkumar, K.J. Lethy, D. Beena, A.P. Detty, I. Navas, U.V. Nayar, V.P. Mahadevan Pillai, V. Ganesan, and V.R. Reddy, Effect of ITO Buffer Layers on the Structural, Optical and Electrical Properties of ZnO Multilayer Thin Films Prepared by Pulsed Laser Deposition Technique. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells. 94, 68 (2010).
N. Zohra, I. Saima, R. Rida, R. Saira, and N. Shahzad, Effect of Cu Do** on the Structural, Magnetic and Optical Properties of ZnO Thin Films. Appl. Phys. A 124, 468 (2018).
Y. Kim and J.-Y. Leem, Effects of Do** Concentration on the Structural and the Optical Properties of Sol-gel-derived In-doped ZnO Thin Films Grown on Muscovite Mica Substrates. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 66, 1516 (2015). https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.66.1516.
R. Biswal, A. Maldonado, J. Vega-Pérez, D.R. Acosta, and M. De La Luz Olvera, Indium Doped Zinc Oxide Thin Films Deposited by Ultrasonic Chemical Spray Technique, Starting from Zinc Acetylacetonate and Indium Chloride. Materials 7, 5038 (2014). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma7075038.
D. Mahesh and M. Santhosh Kumar, An investigation on the In-Do** of ZnO Thin Films by Spray Pyrolysis. AIP Conf. Proc. 1942, 080049 (2018).
B. Sahoo, D. Behera, S.K. Pradhan, D.K. Mishra, S.K. Sahoo, R.R. Nayak, and K.P.C. Sekhar, Analysis of Structural, Optical and Electrical Properties of Nano-particulate Indium Doped Zinc Oxide Thin Films. Mater. Res. Express 6, 1150a6 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab4cbd.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kathwate, L.H., Mote, V.D. Optical and Electrical Properties of In-doped ZnO Films via the Spray Pyrolysis Technique for Optoelectronics Device Applications. J. Electron. Mater. 51, 6894–6902 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-022-09918-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-022-09918-8