Abstract
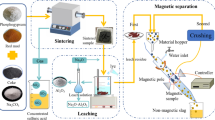
Spent pot-lining (SPL) and red mud (RM) are the two major solid wastes of the aluminum industry. In this study, an innovative method has been proposed for co-treatment of SPL and RM to reuse carbon and recover metal (iron, aluminum and sodium) by a reductive roasting-leaching-magnetic separation process (RRLMS process). Moreover, the transformation behaviors of fluoride, cyanide and sulfur present in these residues were studied. The effects of parameters such as temperature, CaO/SiO2 molar ratio, addition amount of SPL, Na2O/Al2O3 molar ratio and roasting time on the result of the process were investigated. Under optimum conditions, the recovery extents of Al2O3 and Na2O were 83.12 and 91.80 pct, respectively. The corresponding leaching extent and loss of F upon roasting process were 16.03 and 35.27 pct, respectively, and only 29.02 pct of ST in the roasted product was leached. Furthermore, reduction extent of 78.65 pct and a metallization extent of 62.83 pct for iron minerals were achieved. The SPL-RM mixture after treatment was rendered non-hazardous. Finally, wet magnetic separation at 1.2 A current (magnetic field strength of approximately 130 mT) provided 30.83 wt pct concentrate yield with 59.09 wt pct total iron concentration and iron recovery extent of 65.25 pct from the leached residue.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. Flores, F. Fraiz, R. A. Lopes Junior, and B.M. Covcevich: J. Mater. Res. Technol., 2019, vol. 8, pp. 33–40.
J. **ao, J. Yuan, Z. Tian,, K.Yang, Z. Yao, and B. Yu: Ultrason. Sonochem., 2018, vol. 40, pp. 21-29
X. M. Li, W. D. Yin, Z. Fang, Q.H. Liu, Y. R. Cui, J.X. Zhao, and H. Jia: Metall. Mater.Trans. B, 2019, vol. 50, pp. 914.
S. B. Sleap, B. D. Turner, and S. W. Sloan: J. Environ. Chem. Eng., 2015, vol. 4, pp. 2580-2587.
U.S. Geological Survey: Mineral Commodity Summaries 2019: U.S. Geological Survey, 2019, p. 21.
U. Ntuk, S. Tait, E. T.White, and K. M. Steel: Hydrometallurgy, 2015, vol. 155, pp. 79-87.
J. Yuan, J. **ao, F. Li, B. Wang, Z. Yao, and B. Yu: Ultrason. Sonochem., 2018, vol.41, pp. 608-618.
D.F. Lisbona, C. Somerfield, and K.M. Steel: Hydrometallurgy, 2013, vols. 134-135, pp. 132-43.
N. Li, G. **e, Z. X. Wang, Y. Q. Hou, and R. X. Li: Adv. Mater. Res., 2014, vols. 881-883, pp. 1660-64.
Z. N. Shi,, L. I. Wei, W. X. Hu, B. J. Ren, B. L.Gao, and Z. W. Wang: Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 2012, vol. 22, pp. 222-227.
G Ospina and M. I. Hassan: JOM, 2017, vol. 69, pp. 1-7.
S. Liu, J. Zeng,and Y. Wang: Metall. Mater.Trans. B, 2017, vol 48, pp. 2223.
M. Taneez, C. Hurel: Environ Sci Pollut Res, 2019, vol. 26, pp. 22106–22125.
Z. Liu and H. Li: Hydrometallurgy, 2015, vol.155, pp. 29-43.
K. Jayasankar, P. K. Ray, A. K. Chaubey, A. Padhi, B. K. Satapathy, and P. S. Mukherjee: Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 2012, vol.19, pp. 679-684.
M. Gräfe, G. Power, C. Klauber: Hydrometallurgy, 2011, vol.108, pp. 60-79.
Y. Liu, R. Naidu:Waste Management,2014, vol.134, pp. 2662-2673.
Kasliwal, P. S. T Sai: Hydrometallurgy,1999, vol.53, pp. 73-87.
S. J. Couperthwaite and G. J. Millar: Miner. Eng., 2016, vol. 99, pp. 8-18.
F. M. Kaußen and B. Friedrich: Hydrometallurgy, 2018, vol. 176, pp. 49–61.
F. H. Lu, T. F. **ao, and J. Lin: Hydrometallurgy, 2018, vol.175, pp. 124-132.
W. Liu, S. Sun, L. Zhang, and J. Yang: Miner. Eng., 2012, vol.39, pp. 213-218.
T. Chun, D. Zhu, J. Pan. And H Zhen: Metall and Materi Trans B, 2014, vol. 45, pp. 827.
M. Samouhos, M. Taxiarchou, G. Pilatos, P. E. Tsakiridis, E. Devlin, and M. Pissas: Miner. Eng., 2017, vol.105, pp. 36-43.
A. He and J. Zeng: Mater. Des., 2017, vol.115, pp.433-440.
Y. Qu, H.Li, W. Tian, X.Wang, and, X. Jia: Miner. Eng., 2015, vol.81, pp.1-4.
Y. Qu, B. Lian, B. Mo, and C. Liu: Hydrometallurgy,2013, vol.136, pp. 71-77.
F. Vakilchap, S. M. Mousavi, and S. A. Shojaosadati: Bioresour. Technol, 2016, vol.218, pp. 991-998.
X. B. Li, W. **ao, and W. Liu: Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 2009, vol.19, pp.1342-1347.
W. C. Liu, J. Yang, and B. **ao: J. Hazard. Mater., 2009, vol.161, pp.474-478.
Z. Liu, H. Li, M. Huang, D. Jia, and N. Zhang: Hydrometallurgy, 2017, vol.167, pp.92-100.
S. Agrawal, V. Rayapudi, N. Dhawan: Miner. Eng., 2019, vol.132, pp.202-210.
S. Gostu, B. Mishra, and G.P. Martins: Light Metals, The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series, 2017, pp. 67–73.
M. Weaver, R. David, and G. Carkin. Application: US 2011/040988 A1, U.S. Patent and Trademark Office, Washington, DC, 2011.
W. Li and X. Chen: Light Metals, 2016, vol.179, pp.1064-1069.
Y. Liu and R.Naidu:Waste Manage, 2014, vol.34, pp. 2662-2673.
F. H. Lu, T. F. **ao, and J. Lin: Hydrometallurgy, 2017, vol. 174, pp. 105-115.
Z. Xu, J. Hwang, R. Greenlund, X. Huang, J. Luo, and S. Anschuetz: J. Miner. Mater. Charact. Eng, 2003,vol.2, pp. 2557-2564.
N. I. Bento, P. S. Santos, T. E. De Souza,, L. C. Oliveira, and C. S. Castro, J. Hazard. Mater., 2016, vol.314, pp. 304-311.
D. Dodoo-Arhin, D. S. Konadu, E. Annan, F. P. Buabeng, A. Yaya, and B. Agyei-Tuffour: Am. J. Mater. Sci., 2013,vol. 3, pp.110-119.
C.E. Bamberger, G.M. Begun, and D.E. Heatherly: React. Solids, 1987, vol. 3(1–2), pp. 165–70.
C.E. Bamberger: React. Solids, 1986, vol. 2(3), pp. 277–82.
A. Donald and N.Y. Holt, and Niagara Falls: U.S. Patent No. 2,128,819, U.S. Patent Office, Washington, DC, 1937.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51664010 and 51664008), Science and Technology Foundation of Guizhou Province ([2018]0002), Guizhou Novel Process Engineering Research Center of Process industry, China [KY(2017)021], and High-level Talents Foundation of Guizhou Institute of Technology (XJGC20181010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Manuscript submitted December 19, 2019.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, F., Su, X., Huang, F. et al. Co-Treatment of Spent Pot-Lining and Red Mud for Carbon Reutilization and Recovery of Iron, Aluminum and Sodium by Reductive Roasting Process. Metall Mater Trans B 51, 1564–1575 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-020-01882-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-020-01882-0