Abstract
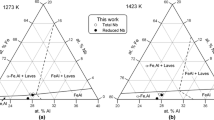
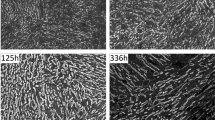
A new Fe-Cr-Al (FCA) alloy system has been developed with good oxidation resistance and creep strength at high temperature. The alloy system is a candidate for use in future fossil-fueled power plants. The creep strength of these alloys at 973 K (700 °C) was found to be comparable with traditional 9 pct Cr ferritic–martensitic steels. A few FCA alloys with general composition of Fe-30Cr-3Al-.2Si-xNb (x = 0, 1, or 2) with a ferrite matrix and Fe2Nb-type Laves precipitates were prepared. The detailed microstructural characterization of samples, before and after creep rupture testing, indicated precipitation of the Laves phase within the matrix, Laves phase at the grain boundaries, and a 0.5 to 1.5 μm wide precipitate-free zone (PFZ) parallel to all the grain boundaries. In these alloys, the areal fraction of grain boundary Laves phase and the width of the PFZ controlled the cavitation nucleation and eventual grain boundary ductile failure. A phenomenological model was used to compare the creep strain rates controlled by the effects of the particles on the dislocations within the grain and at grain boundaries. (The research sponsored by US-DOE, Office of Fossil Energy, the Crosscutting Research Program).














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Enviornmental_Protection_Agency, EPA 430-R-16-002, Washington, DC, April 2016.
F. Abe, Sci and Tech of Adv Mat, 2008, 9, 013002.
P. Auerkari, S. Holmström, J. Veivo and J. Salonen, Int. J. Pressure Vessels Pip., 2007, 84, 69-74.
H. Hirata and K. Ogawa, Welding International, 2005, 19, 118-124.
H. Hirata and K. Ogawa, Welding International, 2005, 19, 109-7.
K. Laha, K.S. Chandravathi, P. Parameswaran, and K. BhanuSankaraRao, Metall Mater Trans A, 2008, 40A, 386-397.
S. Tsukamoto, M. Tabuch, T. Shirane and F. Abe, Trends in Welding Research, 2009, pp. 296–302.
Y. Yamamoto, X. Yu, S.S. Babu, and B. Shassere: Proceeding of the 10th Liège Conference on Materials for Advanced Power Engineering, 2014.
F. Abe, Metall Mater Trans A, 2005, 36A, 321-332.
M. Shibuya, Y. Toda, K. Sawada, H. Kushima and K. Kimura, Mat Sci and Eng: A, 2011, 528, 5387-5393.
B. Kuhn, C. A. Jimenez, L. Niewolak, T. Hüttel, T. Beck, H. Hattendorf, L. Singheiser and W. J. Quadakkers, Mat Sci and Eng: A, 2011, 528, 5888-5899.
Y. Yamamoto, B.A. Pint, B. Shassere, and P.S.S. Babu: Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL), Oak Ridge, TN, 2016.
Y.-T. Chiu and C.-K. Lin, Journal of Power Sources, 2012, 198, 149-157.
F. Abe, T.-U. Kern and R. Viswanathan, Woodhead Publishing, 2008.
ASTM_E8/E8M-16a, 2016.
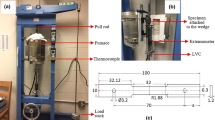
ASTM_E139-11, 2016.
R. L. Coble, Journal Name: J of App Phy; 1963, 34, 1679-1682.
I. Lifshitz, Soviet Physics JETP, 1963, 17, 909-920.
D. Williams and B. Carter: Springer Science-Business Media, New York, 2009.
T. F. Kelly and M. K. Miller, Review of Scientific Instruments, 2007, 78, 031101.
G. Li, N. Zhao, T. Liu, J. Li, C. He, C. Shi, E. Liu and J. Sha, Mat Sci and Eng: A, 2014, 617, 219-227.
N. Pourkia, M. Emamy, H. Farhangi and S. H. S. Ebrahimi, Mat Sci and Eng: A, 2010, 527, 5318-5325.
B.L. Wu, G.Y. Sha, Y.N. Wang, Y.D. Zhang, and C. Esling: in Materials science forum, Trans Tech Publ, 2007, pp. 917–22.
F. Stein, G. Sauthoff and M. Palm, J of Phase Equilibria, 2002, 23, 480-494.
A. Khvan and B. Hallstedt, Calphad, 2012, 39, 62-69.
T. D. Nguyen, K. Sawada, H. Kushima, M. Tabuchi and K. Kimura, Mat Sci and Eng: A, 2014, 591, 130-135.
J. A. Wert, E. Parker and V. Zackay, Metall Mater Trans A, 1979, 10, 1313-1322.
M. F. Ashby, Acta Metall Mater, 1966, 14, 679-&.
K. Maruyama, K. Sawada and J. Koike, Isij Int, 2001, 41, 641-653.
M. Taneike, F. Abe and K. Sawada, Nature, 2003, 424, 294-296.
J.E. Bird, A.K. Mukherjee, and J.E. Dorn: California Univ., Berkeley, Lawrence Radiation Lab., 1969.
M. F. Ashby, Acta Metall Mater, 1972, 20, 887-897.
T. G. Langdon and F. A. Mohamed, J of Mat Sci, 1978, 13, 1282-1290.
F. A. Mohamed and T. G. Langdon, Metall Mater Trans A, 1974, 5, 2339-2345.
B. A. Shassere, Y. Yamamoto and S. S. Babu, Metall Mater Trans A, 2016, 47, 2188-2200.
J. Wadsworth, O.A. Ruano, and O.D. Sherby: in Minerals, Metal and Materials Society Annual Meeting, San Diego, Calif, 1999.
T. G. Langdon, Philosophical Magazine, 2006, 22, 689-700.
H. Lüthy, R. A. White and O. D. Sherby, Mater Sci Eng, 1979, 39, 211-216.
R. C. Gifkins, Metall Trans A, 1976, 7, 1225-1232.
L.-B. Niu, A. Katsuta, M. Kobayashi and H. Takaku, Isij Int, 2003, 43, 251-255.
X. J. Wu and A. K. Koul, Metall Mater Trans A, 1995, 26, 905-14.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. **nghua Yu and Thomas Muth at Oak Ridge National Laboratory for their comments on this manuscript. Research sponsored by the Crosscutting Research Program, Office of Fossil Energy, U.S. Department of Energy. A portion of this research was conducted at the Center for Nanophase Materials Sciences, which is a DOE Office of Science User Facility.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This manuscript has been authored by UT-Battelle, LLC under Contract No. DE-AC05-00OR22725 with the U.S. Department of Energy. The United States Government retains and the publisher, by accepting the article for publication, acknowledges that the United States Government retains a non-exclusive, paid-up, irrevocable, world-wide license to publish or reproduce the published form of this manuscript, or allow others to do so, for United States Government purposes. The Department of Energy will provide public access to these results of federally sponsored research in accordance with the DOE Public Access Plan (http://energy.gov/downloads/doe-public-access-plan).
Manuscript submitted April 11, 2017.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shassere, B., Yamamoto, Y., Poplawsky, J. et al. Heterogeneous Creep Deformations and Correlation to Microstructures in Fe-30Cr-3Al Alloys Strengthened by an Fe2Nb Laves Phase. Metall Mater Trans A 48, 4598–4614 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-017-4274-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-017-4274-8