Abstract
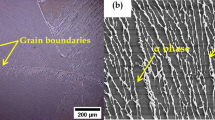
To provide insight into the mechanical behavior and microstructural evolution of bulk ultrafine-grained (UFG) Ti-6Al-4V alloys, we produced Ti-6Al-4V alloy sheets with grain size smaller than 300 nm through severe warm rolling of three different starting microstructures (i.e., lamellar, equiaxed, and hybrid, that is half equiaxed plus half lamellar microstructures) with various reduction ratios (i.e., 60, 70, 80, and 90 pct) at 873 K (600 °C). Accordingly, the tensile behavior, microhardness, grain size, and dislocation density of the UFG Ti-6Al-4V alloys with different starting microstructures and reduction ratios were comparatively analyzed. Our results show that, following the continuous enhancement of tensile strength and hardness as the rolling reduction ratio increased from 0 to 70 pct, there was a saturation state in which the values of strength and hardness remained constant as the reduction ratio further increased from 70 to 90 pct for all the alloy samples with different starting microstructures. In terms of microstructural evolution, although grain size decreased and dislocation density increased continuously as the rolling reduction ratio increased from 0 to 70 pct, grain size and dislocation density did not change significantly when the reduction ratio further increased from 70 to 90 pct. Our results suggest that, whereas the starting microstructure influences the early stages of grain refinement and mechanical performance, this influence diminishes as the rolling reduction ratio is increased beyond a critical value. This behavior was rationalized on the basis of the limits of grain boundary and dislocation strengthening during severe warm rolling.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Lütjering, J.C. Williams: Titanium, 2nd ed., Springer, Berlin, 2007.
Zherebtsov SV, Salishchev GA, Galeyev RM, Valiakhmetov OR, Mironov SY, Semiatin SL. Scr Mater, 2004, vol. 51, pp. 1147-51.
Zhang Y, Sato YS, Kokawa H, Park SHC, Hirano S. Mater Sci Eng A, 2008, vol. 485, pp. 448-55.
Zherebtsov S, Salishchev G, Łojkowski W. Mater Sci Eng A, 2009, vol. 515, pp. 43-8.
Semenova IP, Raab GI, Golubovskiy ER, Valiev RR. J Mater Sci, 2013, vol. 48, pp. 4806-12.
Kim Y, Kim E-P, Song Y-B, Lee SH, Kwon Y-S. J Alloy Compd, 2014, vol. 603, pp. 207-12.
Sergueeva AV, Stolyarov VV, Valiev RZ, Mukherjee AK. Scr Mater, 2000, vol. 43, pp. 819-24.
Semenova IP, Raab GI, Saitova LR, Valiev RZ. Mater Sci Eng A, 2004, vol. 387–389, pp. 805-8.
Chao Q, Hodgson P, Beladi H. Metall Mater Trans A, 2014, vol. 45, pp. 2659-71.
Murty SVSN, Nayan N, Kumar P, Narayanan PR, Sharma SC, George KM. Mater Sci Eng A, 2014, vol. 589, pp. 174-81.
Li Z, Fu L, Fu B, Shan A. Mater Sci Eng A, 2012, vol. 558, pp. 309-18.
Li Z, Fu L, Fu B, Yang X, Shan A. J Nanosci Nanotechno, 2014, vol. 14, pp. 7740-4.
Dragomir IC, Li DS, Castello-Branco GA, Garmestani H, Snyder RL, Ribarik G, et al. Mater Charact, 2005, vol. 55, pp. 66-74.
Ribarik G, Ungar T, Gubicza J. J Appl Crystallogr, 2001, vol. 34, pp. 669-76.
Dragomir IC, Ungar T. J Appl Crystallogr, 2002, vol. 35, pp. 556-64.
Z. Li, B. Zheng, Y. Wang, T. Top**, Y. Zhou, R. Valiev, et al.: J Mater Sci, 2014, vol. pp. 6656–66.
Ungár T. Mater Sci Eng A, 2001, vol. 309–310, pp. 14-22.
W.F. Smith, J. Hashemi: Foundations of Materials Science and Engineering, 4th ed., McGraw-Hill, New York, 2006.
Milner JL, Abu-Farha F, Bunget C, Kurfess T, Hammond VH. Mater Sci Eng A, 2013, vol. 561, pp. 109-17.
M.A. Krivoglaz: X-ray and Neutron Diffraction in Nonideal Crystals, Springer, Berlin, 1996.
Dederichs PH. Phys Rev B, 1971, vol. 4, pp. 1041-50.
Bailey JE, Hirsch PB. Philos Mag, 1960, vol. 5, pp. 485-97.
Li Z, Chen D, Wang H, Lavernia EJ, Shan A. J Mater Res, 2014, vol. 29, pp. 2514-24.
Ding R, Guo ZX. Mater Sci Eng A, 2004, vol. 365, pp. 172-9.
Lee YT, Peters M, Welsch G. Metall Trans A, 1991, vol. 22, pp. 709-14.
Hall EO. Proc Phys Soc B, 1951, vol. 64, pp. 747-53.
Lin Y, Wen H, Li Y, Wen B, Liu W, Lavernia E. Metall Mater Trans B, 2014, vol. 45, pp. 795-810.
Lin Y, Xu B, Feng Y, Lavernia EJ. J Alloy Compd, 2014, vol. 596, pp. 79-85.
Acknowledgments
The authors (ZL, YS and AS) would like to acknowledge support from the Shanghai Committee of Science and Technology (13DZ1942800). The financial support (ZL and EJL) from the US National Science Foundation (NSF DMR-1210437) is also gratefully appreciated. Furthermore, the author (ZL) would like to thank the financial support from the China Scholarship Council (No. 201306230030).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Manuscript submitted April 9, 2015.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Sun, Y., Lavernia, E.J. et al. Mechanical Behavior of Ultrafine-Grained Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Produced by Severe Warm Rolling: The Influence of Starting Microstructure and Reduction Ratio. Metall Mater Trans A 46, 5047–5057 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-015-3080-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-015-3080-4