Abstract
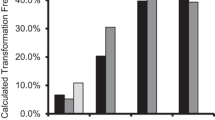
In Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated plant transformation, the promoter chosen to drive a selectable marker gene has an effect on transformation frequency. The objective of this work was to compare the effect on soybean transformation of different promoter and regulator combinations driving a selectable marker gene using mature seeds as explants. Two commonly used promoters, double cauliflower mosaic virus 35S (CaMV 35S) and nopaline synthase (NOS), and one regulator, tobacco etch virus (TEV) translational enhancer, were tested. Four different promoter/enhancer combinations were constructed to drive a bialaphos resistance gene (bar) and used for multiple independent transformation experiments. Herbicide application and PCR analysis were used to confirm the inheritance of the bar gene in the T 1 generation. Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) was used to estimate transgene copy number in T 1 transgenic events. The average transformation frequency from combining NOS with the TEV enhancer (3.5% across 12 replications) was significantly higher than the frequencies obtained from the double CaMV 35S without an enhancer (1.6% across 16 replications), double CaMV 35S with an enhancer (1.4% across 8 replications), and NOS without an enhancer (1.0% across 12 replications). The bar transcript levels in T 1 transgenic leaf tissue did not correlate with transformation frequencies achieved by the different constructs. No significant differences were identified between constructs in the average transgene copy number across events. These data show that a selectable marker system comprised of the bar gene regulated by the NOS promoter in combination with the TEV enhancer is preferred in Agrobacterium-mediated soybean transformation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
An G, Costa MA, Ha S-B (1990) Nopaline synthase promoter is wound inducible and auxin inducible. Plant Cell 2:225–233
An G, Costa MA, Mitra A, Ha SB, Márton L (1988) Organ-specific and developmental regulation of the nopaline synthase promoter in transgenic tobacco plants. Plant Physiol 88:547–552
Assad-García N, Ochoa-Alejo N, García-Hernández E, Herrera-Estrella L, Simpson J (1992) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of tomatillo (Physalis ixocarpa) and tissue specific and developmental expression of the CaMV 35S promoter in transgenic tomatillo plants. Plant Cell Rep 11:558–562
Battraw MJ, Hall TC (1990) Histochemical analysis of CaMV 35S promoter-β-glucuronidase gene expression in transgenic rice plants. Plant Mol Biol 15:527–538
Becker D, Kemper E, Schell J, Masterson R (1992) New plant binary vectors with selectable markers located proximal to the left T-DNA border. Plant Mol Biol 20:1195–1197
Bhattacharyya S, Dey N, Maiti IB (2002) Analysis of cis-sequence of subgenomic transcript promoter from the figwort mosaic virus and comparison of promoter activity with the cauliflower mosaic virus promoters in monocot and dicot cells. Virus Res 90:47–62
Carrington JC, Freed DD (1990) Cap-independent enhancement of translation by a plant potyvirus 5′ nontranslated region. J Virol 64:1590–1597
Chen SY (2004) High-efficiency Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of soybean. Acta Bot Sin 46:610–617
Depicker A, Stachel S, Dhaese P, Zambryski P, Goodman HM (1982) Nopaline synthase: transcript map** and DNA sequence. JMol Appl Genet 1:561–573
Di R, Purcell V, Collins GB, Ghabril SA (1996) Production of transgenic soybean lines expressing the bean pod mottle virus coat protein precursor gene. Plant Cell Rep 15:746–750
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1987) A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem Bull 19:11–15
Edwards K, Johnstone C, Thompson C (1991) A simple and rapid method for the preparation for plant genomic DNA for PCR analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 19:1349
Gallie DR, Tanguay RL, Leathers V (1995) The tobacco etch viral 5′ leader and poly(a) tail are functionally synergistic regulators of translation. Gene 165:223–238
Głowacka K, Kromdijk J, Leonelli L, Niyogi KK, Clemente TE, Long SP (2016) An evaluation of new and established methods to determine T-DNA copy number and homozygosity in transgenic plants. Plant Cell Environ 39:908–917
Hajduikiewicz P, Svab Z, Maliga P (1994) The small versatile pPZP family of Agrobacterium binary vectors for plant transformation. Plant Mol Biol 25:989–994
Harpster MH, Townsend JA, Jones JDG, Bedbrook J, Dunsmuir P (1988) Relative strengths of the 35S cauliflower mosaic virus, 1′, 2′, and nopaline synthase promoters in transformed tobacco sugarbeet and oilseed rape callus tissue. Mol Gen Genet 212:182–190
Hobbs SLA, Kpodar P, DeLong CMO (1990) The effect of T-DNA copy number, position and methylation on reporter gene expression in tobacco transformants. Plant Mol Biol 15:851–864
Hiei Y, Ohta S, Komari T, Kumashiro T (1994) Efficient transformation of rice (Oryza sativa L.) mediated by Agrobacterium and sequence analysis of the boundaries of the T-DNA. The Plant J 6:271-282
Hood EE, Helmer GL, Fraley RT, Chilton MD (1986) The hypervirulence of Agrobacterium tumefaciens A281 is encoded in a region of pTiBo542 outside of T-DNA. J Bacteriol 168:1291–1301
Hu R, Fan C, Li H, Zhang Q, Fu YF (2009) Evaluation of putative reference genes for gene expression normalization in soybean by quantitative real-time RT-PCR. BMC Mol Biol 10:93–105
Ingham DJ, Beer S, Money S, Hansen G (2001) Quantitative real-time PCR assay for determining transgene copy number in transformed plants. BioTechniques 31:132–141
Jian B, Liu B, Bi Y, Hou W, Wu C, Han T (2008) Validation of internal control for gene expression study in soybean by quantitative real-time PCR. BMC Mol Biol 9:59–73
Joersbo M, Mikkelsen JD, Brunstedt J (2000) Relationship between promoter strength and transformation frequencies using mannose selection for the production of transgenic sugar beet. Mol Breed 6:207–213
Lemmetyinen J, Keinonen-Mettälä K, Lännenpää M, Von Weissenberg K, Sopanen T (1998) Activity of the CaMV 35S promoter in various parts of transgenic early flowering birch clones. Plant Cell Rep 18:243–248
Li Z, Jayasankar S, Gray DJ (2001) Expression of a bifunctional green fluorescent protein (GFP) fusion marker under than control of three constitutive promoters and enhanced derivatives in transgenic grape (Vitis vinifera). Plant Sci 160:877–887
Liu SC, Zhang GC, Yang LF, Mii M, Gai JY, Zhu YL (2014) Bialaphos-resistant transgenic soybeans produced by the Agrobacterium-mediated cotyledonary-node method. J Agric Sci Technol 16:175–190
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408
Luth D, Warnberg K, Wang K (2015) Soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merr.]. In: Agrobacterium Protocols (3rd edition). K. Wang (ed). Springer, USA, pp 275–284
Mason G, Provero P, Vaira AM, Accotto GP (2002) Estimating the number of integrations in transformed plants by quantitative real-time PCR. BMC Biotechnol 2:20
Mason HS, Dewald D, Mullet JE (1993) Identification of a methyl jasmonate-responsive domain in the vspB promoter. Plant Cell 5:241–251
Nakamura H, Hakata M, Amano K, Miyao A, Toki N, Kajikawa M, Pang J, Higashi N, Ando S, Toki S, Fujita M, Enju A, Seki M, Nakazawa M, Ichikawa T, Shinozaki K, Matsui M, Nagamura Y, Hirochika H, Ichikawa H (2007) A genome-wide gain-of function analysis of rice genes using the FOX-hunting system. Plant Mol Biol 65:357–371
Odell JT, Nagy F, Chua NH (1985) Identification of DNA sequences required for activity of the cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter. Nature 313:810–812
Olhoft PM, Flagel LE, Donovan CM, Somers DA (2003) Efficient soybean transformation using hygromycin B selection in the cotyledonary-node method. Planta 216:723–725
Pauk J, Stefanov SS, Fekete S, Bögre L, Karsai I, Fehér A, Dudits D (1995) A study of different (CaMV 35S and mas) promoter activities and risk assessment of field use in transgenic rapeseed plants. Euphytica 85:411–416
Paz M, Martinez JC, Kalvig A, Fonger T, Wang K (2006) Improved cotyledonary node method using an alternative explant derived from mature seed for efficient Agrobacterium-mediated soybean transformation. Plant Cell Rep 25:206–213
Paz MM, Shou H, Guo Z, Zhang Z, Banerjee AK, Wang K (2004) Assessment of conditions affecting Agrobacterium-mediated soybean transformation using the cotyledonary node explant. Euphytica 136:167–179
Sanders PR, Winter JA, Barnason AR, Rogers SG, Fraley RT (1987) Comparison of cauliflower mosaic virus 35S and nopaline synthase promoters in transgenic plants. Nucleic Acids Res 15:1543–1558
Schledzewski K, Mendel RR (1994) Quantitative transient gene expression: comparison of the promoters for maize polyubiquitin1, rice actin1, maize-derived emu and CaMV 35S in cells of barley, maize, and tobacco. Transgenic Res 3:249–255
Schmutz J, Cannon SB, Schlueter J, Ma J, Mitros T, Nelson W, Hyten DL, Song Q, Thelen JJ, Cheng J, Xu D, Hellsten U, May GD, Yu Y, Sakurai T, Umezawa T, Bhattacharyya MK, Sandhu D, Valliyodan B, Lindquist E, Peto M, Grant D, Shu S, Goodstein D, Barry K, Futrell-Griggs M, Abernathy B, Du J, Tian Z, Zhu L, Gill N, Joshi T, Libault M, Sethuraman A, Zhang X-C, Shinozaki K, Nguyen HT, Wing RA, Cregan P, Specht J, Grimwood J, Rokhsar D, Stacey G, Shoemaker RC, Jackson SA (2010) Genome sequence of the palaeopolyploid soybean. Nature 463:178–183
Stefanov I, Fekete S, Bögre L, Pauk J, Fehér A, Dudits D (1994) Differential activity of the mannopine synthase and the CaMV 35S promoters during development of transgenic rapeseed plants. Plant Sci 95:175–186
Thompson CJ, Movva NR, Tizard R, Crameri R, Davies JE, Lauwereys M, Botterman J (1987) Characterization of the herbicide-resistance gene bar from Streptomyces hygroscopicus. EMBO J 6:2519–2523
White J, Chang SY, Bibb MJ (1990) A cassette containing the bar gene of Streptomyces hygroscopicus: a selectable markers for plant transformation. Nucleic Acids Res 18:1062
Wise A, Liu Z, Binns AN (2006a) Three methods for the introduction of foreign DNA into Agrobacterium. In: Wang K (ed) Agrobacterium Protocols, 2nd edn. Humana Press Inc, USA, pp 43–53
Wise A, Liu Z, Binns AN (2006b) Nucleic acid extraction from Agrobacterium strains. In: Wang K (ed) Agrobacterium protocols, 2nd edn. Humana Press Inc, USA, pp 67–76
Xue R-G, **e H-F, Zhang B (2006) A multi-needle-assisted transformation of soybean cotyledonary node cells. Biotechnol Lett 28:1551-1557
Yang X-F, Yu X-Q, Zhou Z, Ma W-J, Tang G-X (2016) A high-efficiency Agrobacterium tumefaciens mediated transformation system using cotyledonary node as explants in soybean (Glycine max L.) Acta Physiol Plant 38:60
Zhang F, Chen C, Ge H, Liu J, Luo Y, Liu K, Chen L, Xu K, Zhang Y, Tan G, Li C (2014) Efficient soybean regeneration and Agrobacterium-mediated transformation using a whole cotyledonary node as an explant. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 61:620–625
Zhou J, Yang Y, Wang X, Yu F, Yu C, Chen J, Cheng Y, Yan C, Chen J (2013) Enhanced transgene expression in rice following selection controlled by weak promoters. BMC Biotechnol 13:29
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Chichun Yang and Qing Ji for their assistance in constructing pTF101.2, pTF101.3, and pTF101.4. Graduate research (by A.T.) was supported by the US Department of Agriculture (USDA) National Institute of Food and Agriculture (NIFA) grant (proposal number 2012-03598 to K.W.). Additional support was provided by the USDA-NIFA Hatch Project (No. IOW05162) and by State of Iowa funds (K.W., K.L., D.L.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Editor: David R. Duncan
Electronic supplementary material
Figure S1
Comparison of T-DNA copy number estimation in T 1 generation by qPCR and ddPCR. The T-DNA copy numbers determined by ddPCR were plotted against those estimated by SYBR-qPCR. A total of 10 plants with one to 31 copies of T-DNA were included in the analysis. A strong linear correlation was found: slope was 0.85 and the correlation coefficient (r) was 0.95. (PPTX 37 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Testroet, A., Lee, K., Luth, D. et al. Comparison of transformation frequency using the bar gene regulated by the CaMV 35S or NOS promoter in Agrobacterium-mediated soybean (Glycine max L.) transformation. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Plant 53, 188–199 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11627-017-9810-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11627-017-9810-0