Abstract
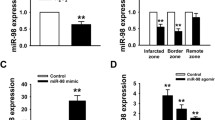
The mechanisms for cardiomyocyte death in cardiovascular diseases are incompletely understood. The aim of this study is to reveal the function of miR-381 in myocardium infarction (MI)-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis. We established mouse model of MI and cellular models of apoptosis induced by oxidative stress (H2O2 and hypoxia/reoxygenation (H/R)). The expression of miR-381 in these models was assessed by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR); we employed approaches including cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8) assay and flow cytometry to evaluate the cell viability and apoptosis. Notch signaling was determined by western blot analysis of key signaling components including Notch1 intracellular domain (ICD), Jag1, and Hes1. The predicted binding of miR-381 to Jag1 3′ untranslated region (UTR) was validated by luciferase assay. Following MI, miR-381 expression was upregulated time dependently in the border zone of ischemic area but not in the non-ischemic area. MiR-381 expression was also upregulated in cardiomyocytes treated with H2O2 and H/R. Overexpression of miR-381 exacerbated H2O2- and H/R-induced apoptosis of cardiomyocytes; in contrast, inhibition of miR-381 attenuated apoptosis in these conditions. Importantly, in vivo delivery of miR-381 antagomir significantly reduced infarction size. Moreover, miR-381 negatively regulates the cardioprotective Notch signaling in vivo and in vitro, which might be an effect of targeted inhibition of Jag1 by itself. These data indicate an essential role of miR-381/Jag1 pathway in regulating Notch signaling-mediated cardioprotective effect in cardiomyocytes. Our study also provides a potential therapeutic target for cardiovascular diseases.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Rand MD, Lake RJ (1999) Notch signaling: cell fate control and signal integration in development. Science 284:770–776
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297
Barwari T, Joshi A, Mayr M (2016) MicroRNAs in cardiovascular disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 68:2577–2584
Bernardo BC, Nguyen SS, Winbanks CE, Gao XM, Boey EJ, Tham YK, Kiriazis H, Ooi JY, Porrello ER, Igoor S, Thomas CJ, Gregorevic P, Lin RC, Du XJ, McMullen JR (2014) Therapeutic silencing of miR-652 restores heart function and attenuates adverse remodeling in a setting of established pathological hypertrophy. FASEB J 28:5097–5110
Brou C, Logeat F, Gupta N, Bessia C, LeBail O, Doedens JR, Cumano A, Roux P, Black RA, Israel A (2000) A novel proteolytic cleavage involved in Notch signaling: the role of the disintegrin-metalloprotease TACE. Mol Cell 5:207–216
Cao Q, Liu F, Ji K, Liu N, He Y, Zhang W, Wang L (2017) MicroRNA-381 inhibits the metastasis of gastric cancer by targeting TMEM16A expression. J Exp Clin Cancer Res : CR 36(29):29
Castaldi A, Zaglia T, Di Mauro V, Carullo P, Viggiani G, Borile G, Di Stefano B, Schiattarella GG, Gualazzi MG, Elia L, Stirparo GG, Colorito ML, Pironti G, Kunderfranco P, Esposito G, Bang ML, Mongillo M, Condorelli G, Catalucci D (2014) MicroRNA-133 modulates the beta1-adrenergic receptor transduction cascade. Circ Res 115:273–283
Chen C, Jia KY, Zhang HL, Fu J (2016) MiR-195 enhances cardiomyocyte apoptosis induced by hypoxia/reoxygenation injury via downregulating c-myb. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 20:3410–3416
Chi YC, Shi CL, Zhou M, Liu Y, Zhang G, Hou SA (2017) Selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor NS-398 attenuates myocardial fibrosis in mice after myocardial infarction via Snail signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 21:5805–5812
Greco S, Perfetti A, Fasanaro P, Cardani R, Capogrossi MC, Meola G, Martelli F (2012) Deregulated microRNAs in myotonic dystrophy type 2. PLoS One 7:e39732
Gude NA, Emmanuel G, Wu W, Cottage CT, Fischer K, Quijada P, Muraski JA, Alvarez R, Rubio M, Schaefer E, Sussman MA (2008) Activation of Notch-mediated protective signaling in the myocardium. Circ Res 102:1025–1035
He X, Wei Y, Wang Y, Liu L, Wang W, Li N (2016) MiR-381 functions as a tumor suppressor in colorectal cancer by targeting Twist1. OncoTargets Ther 9:1231–1239
Hori M, Nishida K (2009) Oxidative stress and left ventricular remodelling after myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Res 81:457–464
**g R, Zhou Z, Kuang F, Huang L, Li C (2017) microRNA-99a reduces lipopolysaccharide-induced oxidative injury by activating Notch pathway in H9c2 cells. Int Heart J 58:422–427
Kageyama R, Ohtsuka T (1999) The Notch-Hes pathway in mammalian neural development. Cell Res 9:179–188
Katz MG, Fargnoli AS, Kendle AP, Hajjar RJ, Bridges CR (2016) The role of microRNAs in cardiac development and regenerative capacity. Am J Phys Heart Circ Phys 310:H528–H541
Meng X, Ji Y, Wan Z, Zhao B, Feng C, Zhao J, Li H, Song Y (2017) Inhibition of miR-363 protects cardiomyocytes against hypoxia-induced apoptosis through regulation of Notch signaling. Biomed Pharmacother 90:509–516
Mortality GBD, Causes of Death C (2016) Global, regional, and national life expectancy, all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of death, 1980–2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet 388:1459–1544
Nabeebaccus A, Zhang M, Shah AM (2011) NADPH oxidases and cardiac remodelling. Heart Fail Rev 16:5–12
Oswald F, Tauber B, Dobner T, Bourteele S, Kostezka U, Adler G, Liptay S, Schmid RM (2001) p300 acts as a transcriptional coactivator for mammalian Notch-1. Mol Cell Biol 21:7761–7774
Pei H, Yu Q, Xue Q, Guo Y, Sun L, Hong Z, Han H, Gao E, Qu Y, Tao L (2013) Notch1 cardioprotection in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion involves reduction of oxidative/nitrative stress. Basic Res Cardiol 108:373
Rothschild SI, Tschan MP, Jaggi R, Fey MF, Gugger M, Gautschi O (2012) MicroRNA-381 represses ID1 and is deregulated in lung adenocarcinoma. J Thorac Oncol 7:1069–1077
Rotini A, Martinez-Sarra E, Pozzo E, Sampaolesi M (2017) Interactions between microRNAs and long non-coding RNAs in cardiac development and repair. Pharmacol Res 127:58–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2017.05.029
Song T, Yao Y, Wang T, Huang H, **a H (2017) Tanshinone IIA ameliorates apoptosis of myocardiocytes by up-regulation of miR-133 and suppression of Caspase-9. Eur J Pharmacol 815:343–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2017.08.041
Su X, Liang H, Wang H, Chen G, Jiang H, Wu Q, Liu T, Liu Q, Yu T, Gu Y, Yang B, Shan H (2017) Over-expression of microRNA-1 causes arrhythmia by disturbing intracellular trafficking system. Sci Rep 7:46259
Sun C, Liu H, Guo J, Yu Y, Yang D, He F, Du Z (2017a) MicroRNA-98 negatively regulates myocardial infarction-induced apoptosis by down-regulating Fas and caspase-3. Sci Rep 7:7460
Sun T, Dong YH, Du W, Shi CY, Wang K, Tariq MA, Wang JX, Li PF (2017b) The role of microRNAs in myocardial infarction: from molecular mechanism to clinical application. Int J Mol Sci 18
Wang L, Song G, Liu M, Chen B, Chen Y, Shen Y, Zhu J, Zhou X (2016) MicroRNA-375 overexpression influences P19 cell proliferation, apoptosis and differentiation through the Notch signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med 37:47–55
Weber K, Rostert N, Bauersachs S, Wess G (2015) Serum microRNA profiles in cats with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Mol Cell Biochem 402:171–180
Xu Z, Alloush J, Beck E, Weisleder N (2014) A murine model of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury through ligation of the left anterior descending artery. J Vis Exp : JoVE. https://doi.org/10.3791/51329
Xue Y, Xu W, Zhao W, Wang W, Zhang D, Wu P (2017) miR-381 inhibited breast cancer cells proliferation, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and metastasis by targeting CXCR4. Biomed Pharmacother 86:426–433
Yan S, Jiao K (2016) Functions of miRNAs during mammalian heart development. Int J Mol Sci 17
Yang B, Lin H, **ao J, Lu Y, Luo X, Li B, Zhang Y, Xu C, Bai Y, Wang H, Chen G, Wang Z (2007) The muscle-specific microRNA miR-1 regulates cardiac arrhythmogenic potential by targeting GJA1 and KCNJ2. Nat Med 13:486–491
Yang X, Ruan H, Hu X, Cao A, Song L (2017) miR-381-3p suppresses the proliferation of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells by directly targeting FGFR2. Am J Cancer Res 7:913–922
Yang Y, Del Re DP, Nakano N, Sciarretta S, Zhai P, Park J, Sayed D, Shirakabe A, Matsushima S, Park Y, Tian B, Abdellatif M, Sadoshima J (2015) miR-206 mediates YAP-induced cardiac hypertrophy and survival. Circ Res 117:891–904
Zhao Y, Ponnusamy M, Dong Y, Zhang L, Wang K, Li P (2017) Effects of miRNAs on myocardial apoptosis by modulating mitochondria related proteins. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 44:431–440
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The study was performed in compliance with the guidelines approved by an institute animal care committee.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Editor: Tetsuji Okamoto
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, L., Zhang, H., Dong, W. et al. MiR-381 negatively regulates cardiomyocyte survival by suppressing Notch signaling. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 54, 610–619 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-018-0277-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-018-0277-z