Abstract
Objective
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is an aggressive hematological malignancy characterized by abnormal myeloid blast expansion. Recent studies have demonstrated that circular RNAs play a role in AML pathogenesis. In this study, we aimed to investigate the clinical significance of circ_0012152 in AML and elucidate its underlying molecular mechanism in the pathogenesis of this condition.
Methods
Circ_0012152 expression was detected by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction in samples obtained from 247 patients with AML and 40 healthy controls. A systematic analysis of clinical characteristics and prognostic factors was also conducted. Cell growth was assessed using the Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay, and apoptosis and cell cycle progression were evaluated by flow cytometry. Moreover, RNA pull-down was performed to identify target microRNAs, and transcriptome RNA sequencing and bioinformatics analyses were utilized to identify downstream mRNA targets.
Results
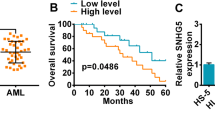
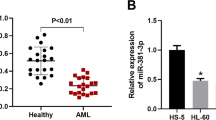
Circ_0012152 was significantly upregulated in samples from patients with AML and served as an independent adverse prognostic factor for overall survival (OS) (hazard ratio: 2.357; 95% confidence interval 1.258–4.415). The circ_0012152 knockdown reduced cell growth, increased apoptosis, and inhibited cell cycle progression in AML cell lines. RNA pull-down and sequencing identified miR-652-3p as a target microRNA of circ_0012152. Cell growth inhibition by circ_0012152 knockdown was significantly relieved by miR-652-3p inhibitors. We suggested that miR-652-3p targeted SOX4, as the decrease in SOX4 expression resulting from circ_0012152 knockdown was upregulated by miR-652-3p inhibitors in AML cells.
Conclusion
Circ_0012152 is an independent poor prognostic factor for OS in AML, and it promotes AML cell growth by upregulating SOX4 through miR-652-3p.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papaemmanuil E, Gerstung M, Bullinger L, et al. Genomic Classification and Prognosis in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. N Engl J Med, 2016,374(23):2209–2221
Burnett A, Stone R. AML: New Drugs but New Challenges. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk, 2020,20(6):341–350
Thol F, Ganser A. Treatment of Relapsed Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Curr Treat Options Oncol, 2020,21(8):66
Cummins KD, Gill S. Will CAR T-cell therapy have a role in AML? Promises and pitfalls. Seminars in hematol, 2019,56(2):155–163
Fennell KA, Bell CC, Dawson MA. Epigenetic therapies in acute myeloid leukemia: where to from here? Blood, 2019,134(22):1891–1901
Kumar S, Gonzalez EA, Rameshwar P, et al. Non-Coding RNAs as Mediators of Epigenetic Changes in Malignancies. Cancers (Basel), 2020,12(12):3657
Jeck WR, Sorrentino JA, Wang K, et al. Circular RNAs are abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats. RNA, 2013,19(2):141–157
Verduci L, Strano S, Yarden Y, et al. The circRNA-microRNA code: emerging implications for cancer diagnosis and treatment. Mol Oncol, 2019,13(4):669–680
Li A, Wang WC, McAlister V, et al. Circular RNA in colorectal cancer. J Cell Mol Med, 2021, 25(8):3667–3679
Lei B, Tian Z, Fan W, et al. Circular RNA: a novel biomarker and therapeutic target for human cancers. Int J Med Sci, 2019,16(2):292–301
Fu L, Tang D, Sun A, et al. Recent progress in study of circRNAs and its role in leukemia. J Leukoc Biol, 2021,109(4):731–739
Ding Y, Dong Y, Lu H, et al. Circular RNA profile of acute myeloid leukemia indicates circular RNA annexin A2 as a potential biomarker and therapeutic target for acute myeloid leukemia. Am J Transl Res, 2020,12(5):1683–1699
Hu Q, Gu Y, Chen S, et al. Hsa_circ_0079480 promotes tumor progression in acute myeloid leukemia via miR-654-3p/HDGF axis. Aging (Albany NY), 2020,13(1):1120–1131
Zhou X, Zhan L, Huang K, et al. The functions and clinical significance of circRNAs in hematological malignancies. J Hematol Oncol, 2020,13(1):138
Li W, Zhong C, Jiao J, et al. Characterization of hsa_circ_0004277 as a New Biomarker for Acute Myeloid Leukemia via Circular RNA Profile and Bioinformatics Analysis. Int J Mol Sci, 2017,18(3):597
Rybak-Wolf A, Stottmeister C, Glažar P, et al. Circular RNAs in the Mammalian Brain Are Highly Abundant, Conserved, and Dynamically Expressed. Mol Cell, 2015,58(5):870–885
Kristensen LS, Hansen TB, Venø MT, et al. Circular RNAs in cancer: opportunities and challenges in the field. Oncogene, 2018,37(5):555–565
Li Z, Huang C, Bao C, et al. Exon–intron circular RNAs regulate transcription in the nucleus. Nat Struct Mol Biol, 2015,22(3):256–264
Guo S, Li B, Chen Y, et al. Hsa_circ_0012152 and Hsa_circ_0001857 Accurately Discriminate Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia From Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Front Oncol, 2020,10(1655):1–13
Shang Z, Ming X, Wu J, et al. Downregulation of circ_0012152 inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia cells through the miR-625-5p/SOX12 axis. Hematol Oncol, 2021,39(4):539–548
Liu X, Liu X, Cai M, et al. CircRNF220, not its linear cognate gene RNF220, regulates cell growth and is associated with relapse in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia. Mol Cancer, 2021,20(1):139
Zhang Z, Lin S, Yin J, et al. CircRNF220 plays a pathogenic role to facilitate cell progression of AML in vitro by sponging miR-330-5p to induce upregulation of SOX4. Histol Histopathol, 2022,37(10):1019–1030
Bataller A, Garrido A, Guijarro F, et al. European LeukemiaNet 2017 risk stratification for acute myeloid leukemia: validation in a risk-adapted protocol. Blood Adv, 2022,6(4):1193–1206
De Kouchkovsky I, Abdul-Hay M. Acute myeloid leukemia: a comprehensive review and 2016 update. Blood Cancer J, 2016,6(7):e441
Levis M. FLT3 mutations in acute myeloid leukemia: what is the best approach in 2013? Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program, 2013,2013:220–226
Nicolet BP, Engels S, Aglialoro F, et al. Circular RNA expression in human hematopoietic cells is widespread and cell-type specific. Nucleic Acids Res, 2018,46(16):8168–8180
Zhang F, Jiang J, Qian H, et al. Exosomal circRNA: emerging insights into cancer progression and clinical application potential. J Hematol Oncol, 2023,16(1):67
Zhou B, Mo Z, Lai G, et al. Targeting tumor exosomal circular RNA cSERPINE2 suppresses breast cancer progression by modulating MALT1-NF-κB-IL-6 axis of tumor-associated macrophages. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2023,42(1):48
Sun X, Dongol S, Qiu C, et al. miR-652 Promotes Tumor Proliferation and Metastasis by Targeting RORA in Endometrial Cancer. Mol Cancer Res, 2018,16(12):1927–1939
Chao Y, Yang C, **ong W, et al. miR-652 Inhibits the Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion of Osteosarcoma Cells by Targeting HOXA9 and Regulating the PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway. J Oncol, 2022,2022:4809312
Jiang Q, Lu X, Huang P, et al. Expression of miR-652-3p and Effect on Apoptosis and Drug Sensitivity in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Biomed Res Int, 2018,2018:5724686
Zhang J, **ao C, Feng Z, et al. SOX4 promotes the growth and metastasis of breast cancer. Cancer Cell Int, 2020,20:468
Lu JW, Hsieh MS, Hou HA, et al. Overexpression of SOX4 correlates with poor prognosis of acute myeloid leukemia and is leukemogenic in zebrafish. Blood Cancer J, 2017,7(8):e593
Gruszka AM, Valli D, Alcalay M. Wnt Signaling in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cells, 2019, 8(11):1403
Tickenbrock L, Schwäble J, Wiedehage M, et al. Flt3 tandem duplication mutations cooperate with Wnt signaling in leukemic signal transduction. Blood, 2005,105(9):3699–3706
Moreno CS. SOX4: The unappreciated oncogene. Semin Cancer Biol 2020,67(Pt 1):57–64
Qu Y, Wang Y, Wang P, et al. Overexpression of long noncoding RNA HOXA-AS2 predicts an adverse prognosis and promotes tumorigenesis via SOX4/PI3K/AKT pathway in acute myeloid leukemia. Cell Biol Int, 2020,44(8):1745–1759
Mehta GA, Parker JS, Silva GO, et al. Amplification of SOX4 promotes PI3K/Akt signaling in human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat, 2017,162(3):439–450
Ramezani-Rad P, Geng H, Hurtz C, et al. SOX4 enables oncogenic survival signals in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood, 2013,121(1):148–155
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
This research was supported by grants from the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (No. LY20H080001), and Medical and Health Science and Technology Projects of Zhejiang Province (No. 2021KY997, No. 2022KY306, No. 2022KY316, No. 2023KY263).
Supplementary data
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Li, Bx., Niu, Tt. et al. Circ_0012152 Accelerates Acute Myeloid Leukemia Progression through the miR-652-3p/SOX4 Axis. CURR MED SCI 44, 611–622 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-024-2878-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-024-2878-y