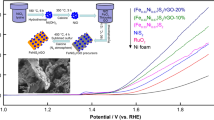
Abstract
Electrochemical water splitting is essential for enabling the storage of renewable electricity through the chemical bonds of hydrogen, while the efficiency of water splitting is low because of the sluggish kinetics of oxygen evolution reaction (OER) in the anode. Herein, we demonstrate that the electrocatalytic water splitting efficiency could be significantly improved by constructing 2D reduced graphene oxide (RGO) supported NiP/Fe4P nanosheets as OER electrocatalysts through a facile wet chemical and subsequent in situ phosphating method. Impressively, using NiP/Fe4P/RGO composites, which are prone to displaying largely exposed surface active area and remarkably improved electrical conductivity to boost the electron transfer. As a consequence, the electrochemical measurements reveal that the NiP/Fe4P/RGO composites could enable water oxidation at an overpotential of 268 mV with a nominal current density of 10 mA cm−2, along with outstanding long-term electrochemical stability. This work presents an advanced electrocatalyst with both high electrocatalytic OER activity and durability, which will allow us to produce hydrogen at low voltages in scale-up potential with the assistance of cost-effective electrocatalysts.
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xu H, Shang H, Wang C, Du Y (2020) Ultrafine Pt-based nanowires for advanced catalysis. Adv Funct Mater 30:2000793
Xu H, Shang H, Wang C, Du Y (2020) Low-dimensional metallic nanomaterials for advanced electrocatalysis. Adv Funct Mater 30:2006317
Zhao M, **a Y (2020) Crystal-phase and surface-structure engineering of ruthenium nanocrystals. Nat Rev Mater 5:440–459
Luo Y, Tang L, Khan U, Yu Q, Cheng HM, Zou X et al (2019) Morphology and surface chemistry engineering toward pH-universal catalysts for hydrogen evolution at high current density. Nat Commun 10:269
Feng G, An L, Li B, Zuo Y, Song J, Ning F et al (2019) Atomically ordered non-precious Co3Ta intermetallic nanoparticles as high-performance catalysts for hydrazine electrooxidation. Nat Commun 10:4514
Bao Y, Feng L Formic acid electro-oxidation catalyzed by PdNi/graphene aerogel. Acta Phys -Chim Sin. https://doi.org/10.3866/PKU.WHXB202008031
Li D, Liu H, Feng L (2020) A review on advanced FeNi-based catalysts for water splitting reaction. Energy Fuel 34:13491–13522
Yang L, Liu Z, Zhu S, Feng L, **ng W (2021) Ni-based layered double hydroxide catalysts for oxygen evolution reaction. Mater Today Phys 16:100292
Stoerzinger KA, Favaro M, Ross PN, Yano J, Liu Z, Hussain Z et al (2018) Probing the surface of platinum during the hydrogen evolution reaction in alkaline electrolyte. J Phys Chem B 122:864–870
Tiwari JN, Sultan S, Myung CW, Yoon T, Li N, Ha M et al (2018) Multicomponent electrocatalyst with ultralow Pt loading and high hydrogen evolution activity. Nat Energy 3:773–782
Hegde C, Sun X, Dinh KN, Huang A, Ren H, Li B et al (2020) Cu- and Fe-codoped Ni porous networks as an active electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution in alkaline medium. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12:2380–2389
Li Y, Sun Y, Qin Y, Zhang W, Wang L, Luo M et al (2020) Recent advances on water-splitting electrocatalysis mediated by noble-metal-based nanostructured materials. Adv Energy Mater 10:1903120
Zhang B, Zhu C, Wu Z, Stavitski E, Lui YH, Kim TH et al (2020) Integrating Rh species with NiFe-layered double hydroxide for overall water splitting. Nano Lett 20:136–144
Xu H, Zhao Y, Wang Q, He G, Chen H (2022) Supports promote single-atom catalysts toward advanced electrocatalysis. Coord Chem Rev 451:214261
Sarno M, Ponticorvo E, Scarpa D (2020) Active and stable graphene supporting trimetallic alloy-based electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution by seawater splitting. Electrochem Commun 111:106647
Chen D, Lu R, Pu Z, Zhu J, Li H-W, Liu F et al (2020) Ru-doped 3D flower-like bimetallic phosphide with a climbing effect on overall water splitting. Appl Catal B Environ 279:119396
Hu P, Jia Z, Che H, Zhou W, Liu N, Li F et al (2019) Engineering hybrid CoMoS4/Ni3S2 nanostructures as efficient bifunctional electrocatalyst for overall water splitting. J Power Sources 416:95–103
Xu Q, Jiang H, Zhang H, Hu Y, Li C (2019) Heterogeneous interface engineered atomic configuration on ultrathin Ni(OH)2/Ni3S2 nanoforests for efficient water splitting. Appl Catal B Environ 242:60–66
Liu Y, Jiang S, Li S, Zhou L, Li Z, Li J et al (2019) Interface engineering of (Ni, Fe)S2@MoS2 heterostructures for synergetic electrochemical water splitting. Appl Catal B Environ 247:107–114
Kuang P, He M, Zou H, Yu J, Fan K (2019) 0D/3D MoS2-NiS2/N-doped graphene foam composite for efficient overall water splitting. Appl Catal B Environ 254:15–25
Li A, Ooka H, Bonnet N, Hayashi T, Sun Y, Jiang Q et al (2019) Stable potential windows for long-term electrocatalysis by manganese oxides under acidic conditions. Angew Chem Int Ed 58:5054–5058
Wang B, Tang C, Wang HF, Chen X, Cao R, Zhang Q (2019) A nanosized CoNi hydroxide@hydroxysulfide core-shell heterostructure for enhanced oxygen evolution. Adv Mater 31:1805658
Begum H, Ahmed MS, Jeon S (2019) δ-MnO2 nanoflowers on sulfonated graphene sheets for stable oxygen reduction and hydrogen evolution reaction. Electrochim Acta 296:235–242
Xu N, Nie Q, Luo L, Yao C, Gong Q, Liu Y et al (2019) Controllable hortensia-like MnO2 synergized with carbon nanotubes as an efficient electrocatalyst for long-term metal-air batteries. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11:578–587
Wang Z, **ao B, Lin Z, Shen S, Xu A, Du Z et al (2021) In-situ surface decoration of RuO2 nanoparticles by laser ablation for improved oxygen evolution reaction activity in both acid and alkali solutions. J Energy Chem 54:510–518
Cui X, Ren P, Ma C, Zhao J, Chen R, Chen S et al (2020) Robust interface Ru centers for high-performance acidic oxygen evolution. Adv Mater 32:e1908126
Yao Q, Huang B, Zhang N, Sun M, Shao Q, Huang X (2019) Channel-rich RuCu nanosheets for pH-universal overall water splitting electrocatalysis. Angew Chem Int Ed 58:13983–13988
Hu Y, Luo X, Wu G, Chao T, Li Z, Qu Y et al (2019) Engineering the atomic layer of RuO2 on PdO nanosheets boosts oxygen evolution catalysis. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11:42298–42304
Tian L, Li Z, Wang P, Zhai X, Wang X, Li T (2021) Carbon quantum dots for advanced electrocatalysis. J Energy Chem 55:279–294
Tian L, Qiu G, Shen Y, Wang X, Wang J, Wang P et al (2019) Carbon quantum dots modulated NiMoP hollow nanopetals as efficient electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution. Ind Eng Chem Res 58:14098–14105
Tian L, Wang J, Wang K, Wo H, Wang X, Zhuang W et al (2019) Carbon-quantum-dots-embedded MnO2 nanoflower as an efficient electrocatalyst for oxygen evolution in alkaline media. Carbon. 143:457–466
Tian L, Zhai X, Wang X, Pang X, Li J, Li Z (2020) Morphology and phase transformation of α-MnO2/MnOOH modulated by N-CDs for efficient electrocatalytic oxygen evolution reaction in alkaline medium. Electrochim Acta 337:135823
Xu H, Shang H, Wang C, ** L, Chen C, Wang C et al (2020) Three-dimensional open CoMoOx/CoMoSx/CoSx nanobox electrocatalysts for efficient oxygen evolution reaction. Appl Catal B Environ 265:118605
Xu H, Shang H, Di J, Du Y (2019) Geometric and electronic engineering of Mn-doped Cu(OH)2 hexagonal nanorings for superior oxygen evolution reaction electrocatalysis. Inorg Chem 58:15433–15442
Li Z, Feng H, Song M, He C, Zhuang W, Tian L (2021) Advances in CoP electrocatalysts for water splitting. Mater Today Energy 20:100698
Tian L, Zhai X, Wang X, Li J, Li Z (2020) Advances in manganese-based oxides for oxygen evolution reaction. J Mater Chem A 8:14400–14414
Xu H, Shang H, Wang C, Du Y (2020) Surface and interface engineering of noble-metal-free electrocatalysts for efficient overall water splitting. Coord Chem Rev 418:213374
Xu H, Shang H, ** L, Chen C, Wang C, Du Y (2019) Boosting electrocatalytic oxygen evolution over Prussian blue analog/transition metal dichalcogenide nanoboxes by photo-induced electron transfer. J Mater Chem A 7:26905–26910
Li Z, Song M, Zhu W, Zhuang W, Du X, Tian L (2021) MOF-derived hollow heterostructures for advanced electrocatalysis. Coord Chem Rev 439:213946
Wu S, Liu J, Liang D, Sun H, Ye Y, Tian Z et al (2016) Photo-excited in situ loading of Pt clusters onto rGO immobilized SnO2 with excellent catalytic performance toward methanol oxidation. Nano Energy 26:699–707
Kannan R, Kim AR, Nahm KS, Lee HK, Yoo DJ (2014) Synchronized synthesis of Pd@C-RGO carbocatalyst for improved anode and cathode performance for direct ethylene glycol fuel cell. Chem Commun 50:14623–14626
Cao E, Chen Z, Wu H, Yu P, Wang Y, **ao F et al (2020) Boron-induced electronic-structure reformation of CoP nanoparticles drives enhanced pH-universal hydrogen evolution. Angew Chem Int Ed 59:4154–4160
Wang X, Fei Y, Li W, Yi L, Feng B, Pan Y et al (2020) Gold-incorporated cobalt phosphide nanoparticles on nitrogen-doped carbon for enhanced hydrogen evolution electrocatalysis. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12:16548–16556
Yan L, Cao L, Dai P, Gu X, Liu D, Li L et al (2017) Metal-organic frameworks derived nanotube of nickel-cobalt bimetal phosphides as highly efficient electrocatalysts for overall water splitting. Adv Funct Mater 27:1703455
Saadi FH, Carim AI, Drisdell WS, Gul S, Baricuatro JH, Yano J et al (2017) Operando spectroscopic analysis of CoP films electrocatalyzing the hydrogen-evolution reaction. J Am Chem Soc 139:12927–12930
Zhang G, Wang G, Liu Y, Liu H, Qu J, Li J (2016) Highly active and stable catalysts of phytic acid-derivative transition metal phosphides for full water splitting. J Am Chem Soc 138:14686–14693
Liang H, Gandi AN, Anjum DH, Wang X, Schwingenschlogl U, Alshareef HN (2016) Plasma-assisted synthesis of NiCoP for efficient overall water splitting. Nano Lett 16:7718–7725
Mendoza-Garcia A, Zhu H, Yu Y, Li Q, Zhou L, Su D et al (2015) Controlled anisotropic growth of Co-Fe-P from Co-Fe-O nanoparticles. Angew Chem 54:9642–9645
Li P, Zeng HC (2017) Advanced oxygen evolution catalysis by bimetallic Ni-Fe phosphide nanoparticles encapsulated in nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulphur tri-doped porous carbon. Chem Commun 53:6025–6028
Wang W, Liu Y, Li J, Luo J, Fu L, Chen S (2018) NiFe LDH nanodots anchored on 3D macro/mesoporous carbon as a high-performance ORR/OER bifunctional electrocatalyst. J Mater Chem A 6:14299–14306
Zhong H, Liu T, Zhang S, Li D, Tang P, Alonso-Vante N et al (2019) Template-free synthesis of three-dimensional NiFe-LDH hollow microsphere with enhanced OER performance in alkaline media. J Energy Chem 33:130–137
Liu B, Cao B, Cheng Y, **g P, Zhao J, Gao R et al (2020) Ultrafine CoP/Co2P nanorods encapsulated in janus/twins-type honeycomb 3D nitrogen-doped carbon nanosheets for efficient hydrogen evolution. iScience 23:101264
Kim H, Kim J, Ahn SH (2019) Monitoring oxygen-vacancy ratio in NiFe-based electrocatalysts during oxygen evolution reaction in alkaline electrolyte. J Ind Eng Chem 72:273–280
Liang H, Gandi AN, **a C, Hedhili MN, Anjum DH, Schwingenschlögl U et al (2017) Amorphous NiFe-OH/NiFeP electrocatalyst fabricated at low temperature for water oxidation applications. ACS Energy Lett 2:1035–1042
Kumar P, Murthy AP, Bezerra LS, Martini BK, Maia G, Madhavan J (2021) Carbon supported nickel phosphide as efficient electrocatalyst for hydrogen and oxygen evolution reactions. Int J Hydrog Energy 46:622–632
Li BQ, Zhang SY, Tang C, Cui X, Zhang Q (2017) Anionic regulated NiFe (Oxy)sulfide electrocatalysts for water oxidation. Small. 13:1700610
Funding
This work was financed by Xuzhou science and technology plan project of China (KC21294), The Natural Science Foundation of the Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions of China (19KJB150019), Youth Science and Technology Talents Enrollment Project of the Jiangsu Association of Science and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 156 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhuang, W., Li, Z., Song, M. et al. Synergistic improvement in electron transport and active sites exposure over RGO supported NiP/Fe4P for oxygen evolution reaction. Ionics 28, 1359–1366 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-021-04396-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-021-04396-0