Abstract
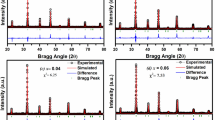
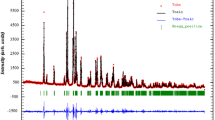
Solid solution of general formula Bi2V1−xTix/2Nbx/2O5.5−δ (0.1 ≤ x ≤ 0.25) were synthesized and characterized by XRD, SEM, FTIR spectroscopy, and AC impedance spectroscopy. The detail XRD analysis reveals coexistence of two phases, i.e., β-orthorhombic and tetragonal at room temperature in these compounds. For lower x (˂ 0.15), β-orthorhombic phase dominates while at higher do** concentration tetragonal phase dominates with the optimum concentration of tetragonal phase for x = 0.15 composition. FTIR studies are in conformity with the observation of XRD results. SEM studies show decrease in average grain size with increase in dopants’ concentration. The impedance spectroscopy data were fitted with suitable equivalent circuit and circuit parameters were obtained. A correlation among crystal structure, surface morphology, and ionic conductivity was found. At low and intermediate temperature regime, highest conductivity was obtained for x = 0.15 and at high temperature region, it was for x = 0.1. The measured conductivity values are higher as compared to single doped Ti/Nb and parent compounds.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boivin JC, Pirovano C, Nowogrocki G, Mairesse G, Labrune P, Lagrange G (1998) Electrode–electrolyte BIMEVOX system for moderate temperature oxygen separation. Solid State Ionics 113–115:639–651
Löfberg A, Boujmiai S, Capoen E, Steil MC, Pirovano C, Vannier RN, Mairesse G, Bordes-Richard E (2004) Oxygen permeation versus catalytic properties of bismuth-based oxide ion conductors used for propene oxidation in a catalytic dense membrane reactor. Catal Today 91–92:79–83
Al-Areqi NAS, Al-Kamali ASN, Ghaleb KAS, Al-Alas A, Al-Mureish K (2014) Influence of phase stabilization and perovskite vanadate oxygen vacancies of the BINIVOX catalyst on photocatalytic degradation of azo dye under visible light irradiation. Radiat Eff Defect Solids 169(2):117–128
Kumar S, Sahare PD (2013) Photocatalytic activity of bismuth vanadate for the degradation of organic compounds. Nano 08(1):1350007
Trzciński K, Borowska-Centkowska A, Sawczak M, Lisowska-Oleksiak A (2015) Photoelectrochemical properties of BIMEVOX (ME = Cu, Zn, Mn) electrodes in contact with aqueous electrolyte. Solid State Ionics 271:63–68
Pasciak G, Prociow K, Mielcarek W, Gornicka B, Mazurek B (2001) Solid electrolytes for gas sensors and fuel cells applications. J Eur Ceram Soc 21:1867–1870
Khaerudini DS, Guan G, Zhang P, Hao X, Abudula A (2014) Prospects of oxide ionic conductivity bismuth vanadate-based solid electrolytes. Rev Chem Eng 30:539–551
Vannier RN, Pernot E, Anne M, Isnard O, Nowogrocki G, Mairesse G (2003) Bi4V2O11 polymorph crystal structures related to their electrical properties. Solid State Ionics 157:147–153
Abraham F, Boivin JC, Mairesse G, Nowogrocki G (1990) The BIMEVOX series: a new family of high performances oxide ion conductors. Solid State Ionics 40(41):934–937
Krok F, Abrahams I, Zadrozna A, Małys M, Bogusz W, Nelstrop JAG, Bush AJ (1999) Electrical conductivity and structure correlation in BIZNVOX. Solid State Ionics 119:139–144
Lee CK, West AR (1996) Thermal behavior and polymorphism of BIMEVOX oxide ion conductors including the new materials: Bi4V2O11: M; M = La, Y, Mg, B. Solid State Ionics 86-88:235–239
Krok F, Abrahams I, Malys M, Bogusz W, Dygas JR, Nelstrop JAG, Bush AJ (2000) Structural and electrical consequences of high dopant levels in the BIMGVOX system. Solid State Ionics 136–137:119–125
Lazure S, Vernochet C, Vannier RN, Nowogrocki G, Mairesse G (1996) Composition dependence of oxide anion conduction in the BIMEVOX family. Solid State Ionics 90:117–123
Paydar MH, Hadian AM, Fafilek G (2004) Ionic conductivity and crystal structure relationships in Ti/Cu substituted Bi4V2O11. J Mater Sci 39:1357–1361
Emel’yanova YV, Tsygankova EN, Petrova SA, Buyanova ES, Zhukovskii VM (2007) Synthesis, structure, and conduction of solid solutions BIMEVOX (Me = Cu, Ti). Russ J Electrochem 47:737–741
Buyanova ES, Petrova SA, Borodina YV E’y NA, Zakharov RG, Zhukovskii VM (2009) Crystal structure and conduction of BICUTIVOX. Russ J Inorg Chem 54:864–872
Tripathy D, Pandey A (2018) Structural and impedance studies of TiIV and NbV co-doped bismuth vanadate system. J Alloys Compd 737:136–143
Alga M, Ammar A, Essalim R, Tanouti B, outzourhit A, Mauvy F, Decort R (2005) Study on structural, thermal, sintering and conductivity of Cu-Co doubly substituted Bi4V2O11. Ionics 11:81–86
Alga M, Ammar A, Tanouti B, Outzourhit A, Mauvy F, Decourt R (2005) Effect of niobium do** on structural, thermal, sintering and electrical properties of Bi4V1.8Cu0.2O10.7. J Solid State Chem 178:2873–2879
Buyanova ES, Morozova MV, Emelyanova YV, Barikina YA, Petrova SA, Zaharov RG (2015) Synthesis, structure, and properties of BIFENBVOX. Ionics 21:2815–2823
Kant R, Singh K, Pandey OP (2009) Microstructural and electrical behavior of Bi4V2-xCuxO11-δ (0 ≤x≤0.4). Ceram Int 35:221–227
Al-Alas A, Beg S, Al-Areqi NAS (2012) Investigation of phase stability and oxide ion performance in new perovskite-type bismuth vanadate. Mater Chem Phys 136:15–20
Kant R, Singh K, Pandey OP (2009) Ionic conductivity and structural properties of MnO-doped Bi4V2O11 system. Ionics 15:567–570
Sooryanarayana K, Guru Row TN, Varma KBR (1999) Structural phase transitions in Bi2V1-xGexO5.5-x/2 (x = 0.2, 0.4, and 0.6) single crystals: x-ray crystallographic study. Mater Res Bull 34(3):425–432
Muller C, Anne M, Bacmann M (1998) Lattice vibrations and order-disorder transition in the oxide anion conductor BICOVOX.15: a neutron thermo diffractometry study. Solid State Ionics 111:27–36
Match! – phase identification from powder diffract – version 3, crystal impact, H. Putz, K. Brandenburg GbR, Kreuzherrenstr. 102, 53227 Bonn, Germany, http://www.crystalimpact.com/match
Bondarenko AS, Ragoish GA (2005) In: Pomerantsev AL (ed) Progress in chemometrics research. Nova Science Publishers, New York, pp 89–102 http://www.abc.chemistry.bsu.by/vi/analyser/
Yan J, Greenblatt M (1995) Ionic conductivities of Bi4V2–x MxO11–x/2 (M = Ti, Zr, Sn, Pb) solid solutions. Solid State Ionics 81:225–233
Khaerudini DS, Guan G, Zhang P, Abudula A (2016) Oxide ion conductors based on niobium-doped bismuth vanadate: conductivity and phase transition features. Ionics 22:93–97
Alga M, Ammar A, Essalim R, Tanouti B, Mauvy F, Decourt R (2005) Synthesis, sintering and electrical properties of P-doped Bi4V2O11 ceramics. Solid State Sci 7:1173–1179
Zaki HM, Mansour SF (2006) X-ray and IR analysis of Cu-Si ferrite. J Phys Chem Solids 67:1643–1648
Martin MC, Mecartney ML (2003) Grain boundary ionic conductivity of yttrium stabilized zirconia as a function of silica content and grain size. Solid State Ionics 161:67–79
Bowman WJ, Zhu J, Sharma R, Crozier PA (2015) Electrical conductivity and grain boundary composition of Gd-doped and Gd/Pr co-doped ceria. Solid State Ionics 272:9–17
Kežionis A, Bogusz W, Krok F, Dygas J, Orliukas A, Abrahams I, Gebicki W (1999) Relaxation dispersion of ionic conductivity of BICOVOX. Solid State Ionics 119:145–150
Beg S, Al-Areqi NAS, Al-Alas A, Hafeez S (2009) Influence of dopant concentration on the phase transition and ionic conductivity in BIHFVOX system. Physica B 404:2072–2079
Heitjans P, Indris S (2003) Diffusion and ionic conduction in nanocrystalline ceramics. J Phys Condens Matter 15:R1257–R1289
Tilley RJD (2016) Perovskites: structure-property relationships. John Willey and Sons, Ltd, Chichester, pp 157–175
Abrahams I, Krok F, Malys M, Wrobel W (2005) Phase transition studies in BIMEVOX solid electrolytes using AC impedance spectroscopy. Solid State Ionics 176:2053–2058
Zainullina VM, Zhukovskii VM, Buyanova ES, Emel’yanova YV (2007) Electronic structure and chemical bonding in oxygen conductors β-Bi4V2O11 and ϒ-Bi4V2O11. Russ J Inorg Chem 52:225–232
Joubert O, Jouanneaux A, Ganne M, Vannier RN, Mairesse G (1994) Solid phase synthesis and characterization of new BIMEVOX series: Bi4V2–x MxO11 (M= SbV, NbV). Solid State Ionics 73:309–318
Buyanova ES, Morozova MV, Emel’yanova YV, Petrova SA, Zakharovb RG, Zhukovskii VM (2013) Synthesis, structure, and conductivity of BINBVOX ceramics. Russ J Inorg Chem 58:259–264
Abrahams I, Krok F, Malys M, Bush AJ (2001) Defect structure and ionic conductivity as a function of thermal history in BIMGVOX solid electrolytes. J Mater Sci 36:1099–1104
Beg S, Al-Areqi NAS, Hafeez S, Al-Alas A (2015) Improved structural and electrical properties of nickel and aluminum co-doped Bi4V2O11 solid electrolyte. Ionics 21:421–428
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to DST, New Delhi for providing FIST facility in the Physics department vide sanction order number SB/52/CMP-093/2013 for XRD and impedance studies. FTIR facility of SAIC, Tezpur University is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tripathy, D., Saikia, A. & Pandey, A. Effect of simultaneous Ti and Nb do** on structure and ionic conductivity of Bi2V1−xTix/2Nbx/2O5.5−δ (0.1 ≤ x ≤ 0.25) ceramics. Ionics 25, 2221–2230 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-018-2622-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-018-2622-3