Abstract
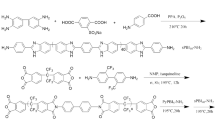
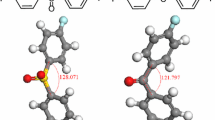
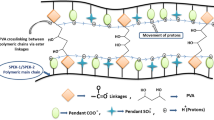
Sulfonated polybenzimidazole-polyimide block copolymers are synthesized through condensation polymerization at high temperature. The length of the polyimide chain is varied to give a series of block copolymers with various block lengths. The as-synthesized block polymers are used to prepare the corresponding membranes through the solvent evaporation method. The structure of the block copolymers is characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR). Their mechanical strength, thermal behavior, water uptake, swelling ratio, and proton conductivity, as well as oxidative stability are also investigated. All the block copolymers exhibit good thermal stability, dimensional stability, mechanical strength, and proton conductivity. Compared to the random sulfonated polyimide-containing benzimidazole membranes with the same degree of sulfonation, the membranes prepared from the block copolymers show higher proton conductivities. The proton conductivities of the block copolymer membranes range from 6.2 × 10−4 to 1.1 × 10−2 S cm−1 at 105 °C. The block copolymer membrane doped with phosphoric acid exhibits proton conductivity higher than 0.2 S cm−1 at 160 °C, indicating its potential applications in proton exchange membrane fuel cells operated under high temperature and low humidity conditions.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Steele BCH, Heinzel A (2001) Materials for fuel-cell technologies. Nature 414(6861):345–352. https://doi.org/10.1038/35104620
Hickner MA, Ghassemi H, Kim YS, Einsla BR, McGrath JE et al (2004) Alternative polymer systems for proton exchange membranes (PEMs). Chem Rev 104(10):4587–4611. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr020711a
Fontananova E, Cucunato V, Curcio E, Trotta F, Biasizzo M, Drioli E, Barbieri G (2012) Influence of the preparation conditions on the properties of polymeric and hybrid cation exchange membranes. Electrochim Acta 66:164–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2012.01.074
Amirinejad M, Madaeni SS, Lee K-S, Ko U, Rafiee E, Lee JS (2012) Sulfonated poly(arylene ether)/heteropolyacids nanocomposite membranes for proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Electrochim Acta 62:227–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2011.12.025
Prater K (1990) The renaissance of the solid polymer fuel-cell. J Power Sources 29(1-2):239–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-7753(90)80023-7
Mistri EA, Mohanty AK, Banerjee S, Komber H, Voit B (2013) Naphthalene dianhydride based semifluorinated sulfonated copoly(ether imide)s: synthesis, characterization and proton exchange properties. J Membr Sci 441:168–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2013.03.015
Suzuki K, Iizuka Y, Tanaka M, Kawakami H et al (2012) Phosphoric acid-doped sulfonated polyimide and polybenzimidazole blend membranes: high proton transport at wide temperatures under low humidity conditions due to new proton transport pathways. J Mater Chem 22(45):23767–23772. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2jm34529c
Lee HF, Wang PH, Huang YC, Su WH, Gopal R, Lee CC, Holdcroft S, Huang WY et al (2014) Synthesis and proton conductivity of sulfonated, multi-phenylated poly(arylene ether)s. J Polym Sci Polym Chem 52(18):2579–2587. https://doi.org/10.1002/pola.27273
Chae KJ, Kim KY, Choi MJ, Yang E, Kim IS, Ren X, Lee M et al (2014) Sulfonated polyether ether ketone (SPEEK)-based composite proton exchange membrane reinforced with nanofibers for microbial electrolysis cells. Chem Eng J 254:393–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.05.145
Salarizadeh P, Javanbakht M, Pourmahdian S (2015) Fabrication and physico-chemical properties of iron titanate nanoparticles based sulfonated poly (ether ether ketone) membrane for proton exchange membrane fuel cell application. Solid State Ionics 281:12–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2015.08.014
Yao HY, Shi KX, Song NN et al (2016) Polymer electrolyte membranes based on cross-linked highly sulfonated co-polyimides. Polymer 103:171–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2016.09.049
Geng L, He Y, Liu D, Lü C (2012) New organic-inorganic hybrid membranes based on sulfonated polyimide/aminopropyltriethoxysilane do** with sulfonated mesoporous silica for direct methanol fuel cells. J Appl Polym Sci 123(5):3164–3172. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.34978
Shabanikia A, Javanbakht M, Amoli HS, Hooshyari K, Enhessari M (2015) Novel nanocomposite membranes based on polybenzimidazole and Fe2TiO5 nanoparticles for proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Ionics 21(8):2227–2236. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-015-1392-4
Ugur MH, Kayaman-Apohan N, Avci D et al (2015) Phosphoric acid functional UV-cured proton conducting polymer membranes for fuel cells. Ionics 21(11):3097–3107. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-015-1495-y
Tan N, **ao G, Yan D, Sun G (2010) Preparation and properties of polybenzimidazoles with sulfophenylsulfonyl pendant groups for proton exchange membranes. J Membr Sci 353(1-2):51–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2010.02.029
Cho H, Hur E, Henkensmeier D, Jeong G, Cho E, Kim HJ, Jang JH, Lee KY, Hjuler HA, Li Q, Jensen JO, Cleemann LN (2014) Meta-PBI/methylated PBI-OO blend membranes for acid doped HT PEMFC. Eur Polym J 58:135–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2014.06.019
Yin Y, Wang J, Yang X, Du Q, Fang J, Jiao K et al (2014) Modeling of high temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells with novel sulfonated polybenzimidazole membranes. Int J Hydrog Energy 39(25):13671–13680. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2014.04.019
Kim SK (2016) Polybenzimidazole and phosphonic acid groups-functionalized polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane composite electrolyte for high temperature proton exchange membrane. J Nanomater. https://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/2954147
Chen C-Y, Lai W-H, Chen Y-K, Su SS et al (2014) Characteristic studies of a PBI/H3PO4 high temperature membrane PEMFC under simulated reformate gases. Int J Hydrog Energy 39(25):13757–13762. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2014.02.090
van de Ven E, Chairuna A, Merle G et al (2013) Ionic liquid doped polybenzimidazole membranes for high temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cell applications. J Power Sources 222:202–209
Roy A, Yu X, Dunn S, McGrath JE et al (2009) Influence of microstructure and chemical composition on proton exchange membrane properties of sulfonated-fluorinated, hydrophilic-hydrophobic multiblock copolymers. J Membr Sci 327(1-2):118–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2008.11.016
Genies C, Mercier R, Sillion B, Petiaud R, Cornet N, Gebel G, Pineri M et al (2001) Stability study of sulfonated phthalic and naphthalenic polyimide structures in aqueous medium. Polymer 42(12):5097–5105. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-3861(00)00645-5
Pan HY, Zhang YY, Pu HT et al (2014) Organic-inorganic hybrid proton exchange membrane based on polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes and sulfonated polyimides containing benzimidazole. J Power Sources 263:195–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2014.04.055
Si J, Lu S, Xu X, Peng S, **u R, **ang Y et al (2014) A gemini quaternary ammonium poly (ether ether ketone) anion-exchange membrane for alkaline fuel cell: design, synthesis, and properties. ChemSusChem 7(12):3389–3395. https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.201402664
Chen GF, Pei XL, Wei HB et al (2015) Synthesis and characterization of sulfonated block copolyimides derived from 4,4 '-sulfide-bis(naphthalic anhydride) for proton exchange membranes. J Appl Polym Sci 132(8):41501–41508. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.41501
Mondal S, Soam S, Kundu PP (2015) Reduction of methanol crossover and improved electrical efficiency in direct methanol fuel cell by the formation of a thin layer on Nafion 117 membrane: effect of dip-coating of a blend of sulphonated PVdF-co-HFP and PBI. J Membr Sci 474:140–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2014.09.023
Mauritz KA, Moore RB (2004) State of understanding of nafion. Chem Rev 104(10):4535–4585. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr0207123
**a Z, Ying L, Fang J, Du YY, Zhang WM, Guo X, Yin J (2017) Preparation of covalently cross-linked sulfonated polybenzimidazole membranes for vanadium redox flow battery applications. J Membr Sci 525:229–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2016.10.050
Cai Y, Yue Z, Xu S (2017) A novel polybenzimidazole composite modified by sulfonated graphene oxide for high temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells in anhydrous atmosphere. J Appl Polym Sci 134(25)44986–44993. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.44986
Pan HY, Chen SX, Zhang YY et al (2015) Preparation and properties of the cross-linked sulfonated polyimide containing benzimidazole as electrolyte membranes in fuel cells. J Membr Sci 476:87–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2014.11.023
Mansoori Y, Atghia SV, Sanaei SS, Zamanloo MR, Imanzadeh G, Eskandari H et al (2012) New, organo-soluble, thermally stable aromatic polyimides and poly(amide-imide) based on 2- 5-(3,5-dinitrophenyl)-1,3, 4-oxadiazole-2-yl pyridine. Polym Int 61(7):1213–1220. https://doi.org/10.1002/pi.4234
Guo XX, Li W, Fang JH et al (2015) Synthesis and properties of novel multiblock copolyimides consisting of benzimidazole-groups-containing sulfonated polyimide hydrophilic blocks and non-sulfonated polyimide hydrophobic blocks as proton exchange membranes. Electrochim Acta 177:151–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2015.03.194
Chen JC, Wu JA, Lee CY, Tsai MC, Chen KH et al (2015) Novel polyimides containing benzimidazole for temperature proton exchange membrane fuel. J Membr Sci 483:144–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2015.02.035
Zhang GM, Guo XX, Fang JH et al (2009) Preparation and properties of covalently cross-linked sulfonated copolyimide membranes containing benzimidazole groups. J Membr Sci 326(2):708–713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2008.11.007
Smitha B, Sridhar S, Khan AA (2004) Polyelectrolyte complexes of chitosan and poly(acrylic acid) as proton exchange membranes for fuel cells. Macromolecules 37(6):2233–2239. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma0355913
Acknowledgments
The project is sponsored by National Science Foundation of China (51303134, 51173134).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Fig. S1
(PDF 69 kb).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, H., Chen, S., **, M. et al. Preparation and properties of sulfonated polybenzimidazole-polyimide block copolymers as electrolyte membranes. Ionics 24, 1629–1638 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-017-2341-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-017-2341-1