Abstract
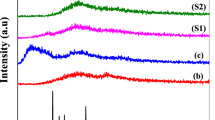
Factors affecting the softening temperature of polymer gel electrolytes (PGEs) made from poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) have been investigated. The melting temperature transition has been found to rise with increased polymer concentration and salt concentration but reduced by solvent dielectric constant. The solvent dielectric constant was reduced by mixing propylene carbonate (PC) with the non-solvent phenyl propanol (PhP). The use of lithium salt bis(oxalate)borate (LiBOB) in place of lithium tetrafluroborote (LiBF4) gives further enhancement to the softening temperature of PGEs. In all of those cases, there is an eventual trade-off between increased softening temperature and reduced ionic conductivity, in this fabricated gel electrolyte. Here, a variety of ways to tailor the properties of PGEs for different applications has been shown.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Song JY, Wang YY, Wan CC (1999) Review of gel-type polymer electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 77(2):183–197
Stephan AM (2006) Review on gel polymer electrolytes for lithium batteries. Eur Polym J 42(1):21–42
Gray F (1991) Solid polymer electrolytes: fundamentals and technological applications. VCH, New York
Zhu Y, Wang F, Liu L, **ao S, Chang Z, Wu Y (2013) Composite of a nonwoven fabric with poly(vinylidene fluoride) as a gel membrane of high safety for lithium ion battery. Energy Environ Sci 6:618–624
Zhu Y, Wang F, Liu L, **ao S, Yang Y, Wu Y (2013) Cheap glass fiber mats as a matrix of gel polymer electrolytes for lithium ion batteries. Sci Rep 3:3187
Bhute MV, Mahant YP, Kondawar SB (2017) Titanium dioxide/poly(vinylidene fluoride) hybrid polymer composite nanofibers as potential separator for lithium ion battery. J Mat Nano Sci 4(1):6–12
Sharma PK, Sharma AK, Sadiq M, Sharma AL (2017) Effect of nano filler on PEO based polymer electrolytes for energy storage devices applications. Int Res Adv 4(1):1–4
Ledwon P, Andrade JR, Lapkowski M, Pawlicka A (2015) Hydroxypropyl cellulose-based gel electrolyte for electrochromic devices. Electrochim Acta 159:227–233
Alamgir M, Abraham KM (1993) Li ion conductive electrolytes based on poly(vinyl chloride). J Electrochem Soc 140(6):L96–L97
Voice AM, Davies GR, Ward IM (1997) Structure of poly(vinylidene fluoride) gel electrolytes. Polym Gels Netw 5(2):123–144
Song S, Wang J, Tang J et al (2017) Preparation, properties, and Li-ion battery application of EC+PC-modified PVdF-HFP gel polymer electrolyte films. Ionics. doi:10.1007/s11581-017-2130-x
Periasamy P, Tatsumi K, Shikano M, Fujieda T, Saito Y, Sakai T, Mizuhata M, Ka**ami A, Deki S (2000) Studies on PVdF-based gel polymer electrolytes. J Power Sources 88(2:269–273
Takeru Y, Tomitaro H, Ken S, Kazuo H, Hiroyuki A (2007) 4.4 V lithium-ion polymer batteries with a chemical stable gel electrolyte. J Power Sources 174(2):1036–1040
Dikshit AK, Nandi AK (2000) Thermoreversible gelation of poly(vinylidene fluoride) in diesters: influence of intermittent length on morphology and thermodynamics of gelation. Macromolecules 33(7):2616–2625
Dikshit AK, Nandi AK (2001) Gelation mechanism of thermoreversible gels of poly(vinylidene fluoride) and its blends with poly(methyl acrylate) in diethyl Azelate. Langmuir 17(12):3607–3615
Egashira M, Todo H, Yoshimoto N, Morita M (2008) Lithium ion conduction in ionic liquid-based gel polymer electrolyte. J Power Sources 178(2):729–735
Sirisopanaporn C, Fernicola A, Scrosati B (2009) New, ionic liquid based membranes for lithium battery application. J Power Sources 186(2):490–495
Jan-Christoph P, Ulrich W, Mario W, Sandra S, Mehrens W (2006) Margret film formation in LiBOB-containing electrolytes. J Power Sources 153(2):396–401
Zhang SS, Xu K, Jow TR (2006) LiBOB-based gel electrolyte Li-ion battery for high temperature operation. J Power Sources 154(1):276–280
Gebbie MA, Smith AM, Dobbs HA, Lee AA, Warr GG, Banquy X, Valtiner M, Rutland MW, Israelachvili JN, Perkin S, Atkin R (2017) Long range electrostatic forces in ionic liquids. Chem Commun 53:1214–1224
Goren A, Costa CM, Machiavello MNT, Clintora-Juarez D, Nunes-Pereira J, Silva MM, Tirado JL, Gomez Ribeles JL, Lanceros-Mendez S (2015) Effect of the degree of porosity on the performance of poly(vinylidene fluoride-trifluoroethylene)/poly(ethylene oxide) blend membranes for lithium-ion battery separators. Solid State Ionics 280:1–9
Saito Y, Morimura W, Kuratani R, Nishikawa S (2016) Factors controlling the ionic mobility of lithium electrolyte solutions in separator membranes. J Phys Chem C120(7):3619–3624
Isa KBM, Osman Z, Arof AK, Othman L, Zainol NH, Samin SM, Chong WG, Kamarulzaman N (2014) Lithium ion conduction and ion–polymer interaction in PVdF-HFP based gel polymer electrolytes. Solid State Ionics 268:288–293
Reiter J, Dominko R, Nádherná M, Jakubec I (2009) Ion-conducting lithium bis(oxalato)borate-based polymer electrolytes. J Power Sources 189(1):133–138
Qin L, Ardebili H (2016) Flexible thin-film battery based on solid-like ionic liquid-polymer electrolyte. J Power Sources 303:17–21
Acknowledgements
The author wishes to thank Prof. I. M. Ward and Dr. A. M. Voice, Leeds University, UK, for their support of work and acknowledge the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC), UK, for the grant (EP/D056551/1). The author also wishes to thank CSIR-India, Govt. of India, for CSIR secondment leave to work at Leeds University, UK, and Dr. Toney M. Rajan for hel** in manuscript correction.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 71 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dikshit, A.K. Raising the softening temperature of poly(vinylidene fluoride) gel electrolytes. Ionics 24, 153–161 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-017-2195-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-017-2195-6