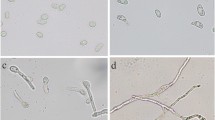
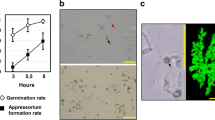
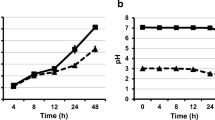
Abstract
The Basidiomycete Heterobasidion irregulare was recently sequenced and three cerato-platanin encoding genes were found in its genome (HiCPs). Cerato-platanin family proteins (CPPs) are produced by both plant pathogenic and non-pathogenic fungi, and can act both as virulence factors and elicitors of defence responses. In fungal life, these proteins seem to play a dual role, in the fungal cell wall and in the fungus–plant interaction, but most data available to date on CPPs derive from studies performed on Ascomycetes. In the present study, we investigated the expression of HiCPs in three homokaryotic isolates and two heterokaryotic isolates of the forest pathogen H. irregulare. Transcription of HiCPs was analysed both at the edge and at the centre of the fungal colony and compared between homokaryon and heterokaryon. The results showed that only HiCP1 and HiCP2 are likely to be translated in H. irregulare and that, under the tested conditions, HiCP1 is the gene with by far the highest transcript abundance among HiCPs. HiCP1 did not show any preferential expression in different sections of the fungal colony, while HiCP2 was significantly more expressed at the colony centre, thus suggesting a link with the production of conidia. The level of expression of HiCPs in heterokaryons was generally comparable to that of one or both the parental homokaryons, irrespective of the colony section, thus demonstrating that HiCPs are not transcriptionally influenced by the heterokaryotic stage.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baccelli I (2015) Cerato-platanin family proteins: one function for multiple biological roles? Front Plant Sci 5:769
Baccelli I, Comparini C, Bettini PP, Martellini F, Ruocco M, Pazzagli L, Bernardi R, Scala A (2012) The expression of the cerato-platanin gene is related to hyphal growth and chlamydospores formation in Ceratocystis platani. FEMS Microbiol Lett 327:155–163
Baccelli I, Lombardi L, Luti S, Bernardi R, Picciarelli P, Scala A, Pazzagli L (2014a) Cerato-platanin induces resistance in Arabidopsis leaves through stomatal perception, overexpression of salicylic acid- and ethylene-signalling genes and camalexin biosynthesis. PLoS ONE 9:e100959
Baccelli I, Luti S, Bernardi R, Scala A, Pazzagli L (2014b) Cerato-platanin shows expansin-like activity on cellulosic materials. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:175–184
Chen H, Kovalchuk A, Keriö S, Asiegbu FO (2013) Distribution and bioinformatic analysis of the cerato-platanin protein family in Dikarya. Mycologia 105:1479–1488
de Barsottini OMR, de Oliveira JF, Adamoski D, Teixeira PJ, do Prado PF, Tiezzi HO, Sforça ML, Cassago A, Portugal RV, de Oliveira PS, Zeri MAC, Dias SM, Pereira GA, Ambrosio AL (2013) Functional diversification of cerato-platanins in Moniliophthora perniciosa as seen by differential expression and protein function specialization. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 26:1281–1293
de Oliveira AL, Gallo M, Pazzagli L, Benedetti CE, Cappugi G, Scala A, Pantera B, Spisni A, Pertinhez TA, Cicero DO (2011) The structure of the elicitor Cerato-platanin (CP), the first member of the CP fungal protein family, reveals a double ψβ-barrel fold and carbohydrate binding. J Biol Chem 286:17560–17568
Djonović S, Pozo MJ, Dangott LJ, Howell CR, Kenerley CM (2006) Sm1, a proteinaceous elicitor secreted by the biocontrol fungus Trichoderma virens induces plant defense responses and systemic resistance. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 19:838–853
Dubey MK, Jensen DF, Karlsson M (2014) Hydrophobins are required for conidial hydrophobicity and plant root colonization in the fungal biocontrol agent Clonostachys rosea. BMC Microbiol 14:18
Frías M, González C, Brito N (2011) BcSpl1, a cerato-platanin family protein, contributes to Botrytis cinerea virulence and elicits the hypersensitive response in the host. New Phytol 192:483–495
Frías M, Brito N, González C (2013) The Botrytis cinerea cerato-platanin BcSpl1 is a potent inducer of systemic acquired resistance (SAR) in tobacco and generates a wave of salicylic acid expanding from the site of application. Mol Plant Pathol 14:191–196
Frischmann A, Neudl S, Gaderer R, Bonazza K, Zach S, Gruber S, Spadiut O, Friedbacher G, Grothe H, Seidl-Seiboth V (2013) Self-assembly at air/water interfaces and carbohydrate binding properties of the small secreted protein EPL1 from the fungus Trichoderma atroviride. J Biol Chem 288:4278–4287
Gaderer R, Bonazza K, Seidl-Seiboth V (2014) Cerato-platanins: a fungal protein family with intriguing properties and application potential. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:4795–4803
Garbelotto M, Gonthier P (2013) Biology, epidemiology, and control of Heterobasidion species worldwide. Annu Rev Phytopathol 51:39–59
Garbelotto M, Guglielmo F, Mascheretti S, Croucher PJ, Gonthier P (2013) Population genetic analyses provide insights on the introduction pathway and spread patterns of the North American forest pathogen Heterobasidion irregulare in Italy. Mol Ecol 22:4855–4869
Gonthier P, Garbelotto M (2011) Amplified fragment length polymorphism and sequence analyses reveal massive gene introgression from the European fungal pathogen Heterobasidion annosum into its introduced congener H. irregulare. Mol Ecol 20:2756–2770
Gonthier P, Nicolotti G, Linzer R, Guglielmo F, Garbelotto M (2007) Invasion of European pine stands by a North American forest pathogen and its hybridization with a native interfertile taxon. Mol Ecol 16:1389–1400
Gonthier P, Anselmi N, Capretti P, Bussotti F, Feducci M, Giordano L, Honorati T, Lione G, Luchi N, Michelozzi M, Paparatti B, Sillo F, Vettraino AM, Garbelotto M (2014) An integrated approach to control the introduced forest pathogen Heterobasidion irregulare in Europe. Forestry 87:471–481
Jeong JS, Mitchell TK, Dean RA (2007) The Magnaporthe grisea snodprot1 homolog, MSP1, is required for virulence. FEMS Microbiol Lett 273:157–165
Olson A, Aerts A, Asiegbu F, Belbahri L, Bouzid O, Broberg A, Canbäck B, Coutinho PM, Cullen D, Dalman K, Deflorio G, van Diepen LT, Dunand C, Duplessis S, Durling M, Gonthier P, Grimwood J, Fossdal CG, Hansson D, Henrissat B, Hietala A, Himmelstrand K, Hoffmeister D, Högberg N, James TY, Karlsson M, Kohler A, Kües U, Lee YH, Lin YC, Lind M, Lindquist E, Lombard V, Lucas S, Lundén K, Morin E, Murat C, Park J, Raffaello T, Rouzé P, Salamov A, Schmutz J, Solheim H, Ståhlberg J, Vélëz H, de Vries RP, Wiebenga A, Woodward S, Yakovlev I, Garbelotto M, Martin F, Grigoriev IV, Stenlid J (2012) Insight into trade-off between wood decay and parasitism from the genome of a fungal forest pathogen. New Phytol 194:1001–1013
Pazzagli L, Seidl-Seiboth V, Barsottini M, Vargas WA, Scala A, Mukherjee PK (2014) Cerato-platanins: elicitors and effectors. Plant Sci 228:79–87
Raffaello T, Chen H, Kohler A, Asiegbu FO (2013) Transcriptomic profiles of Heterobasidion annosum under abiotic stresses and during saprotrophic growth in bark, sapwood and heartwood. Environ Microbiol 16:1654–1667
Sampedro J, Cosgrove DJ (2005) The expansin superfamily. Genome Biol 6:242
Stenlid J, Rayner ADM (1991) Patterns of nuclear migration and heterokaryosis in pairings between sibling homokaryons of Heterobasidion annosum. Mycol Res 95:1275–1283
Yakovlev I, Vaaje-Kolstad G, Hietala AM, Stefańczyk E, Solheim H, Fossdal CG (2012) Substrate-specific transcription of the enigmatic GH61 family of the pathogenic white-rot fungus Heterobasidion irregulare during growth on lignocellulose. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 95:979–990
Yakovlev IA, Hietala AM, Courty PE, Lundell T, Solheim H, Fossdal CG (2013) Genes associated with lignin degradation in the polyphagous white-rot pathogen Heterobasidion irregulare show substrate-specific regulation. Fungal Genet Biol 56:17–24
Yang Y, Zhang H, Li G, Li W, Wang X, Song F (2009) Ectopic expression of MgSM1, a Cerato-platanin family protein from Magnaporthe grisea, confers broad-spectrum disease resistance in Arabidopsis. Plant Biotechnol J 7:763–777
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Fondi di Ateneo year 2012–2013, Università di Pisa, to R.B. Partial support was also obtained by the Italian Ministry of Education, University and Research, within the FIRB program (grant number RBFRI280NN) to P.G. I.B. was supported by a grant from Ente Cassa di Risparmio di Firenze (No. 2013/0444). The authors thank Dr. Luana Giordano for help with the laboratory work.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 24 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baccelli, I., Gonthier, P. & Bernardi, R. Gene expression analyses reveal a relationship between conidiation and cerato-platanin in homokaryotic and heterokaryotic strains of the fungal plant pathogen Heterobasidion irregulare . Mycol Progress 14, 40 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11557-015-1063-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11557-015-1063-x