Abstract
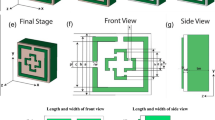
This research investigates the design of a nanostructured metamaterial absorber, featuring a core composition of nickel (Ni) metallic patch surrounded by an inductive grid. The proposed Ni-based nano-absorber exhibits a remarkable absorption bandwidth, spanning both visible and short-infrared wavelengths, with an impressive average absorption efficiency of 90% from 400 to 2000 nm. This study comprehensively examines the absorption characteristics of the nano-absorber across a range of incident angles and polarization states of optical light. Notably, the absorber demonstrates a polarization-insensitive response due to the inherent four-fold symmetry within its nanoresonator design and gives a sizeable absorption for various incident angles. Furthermore, the paper also investigates the surface electric field for a deeper understanding of its performance. Additionally, an equivalent circuit model has been developed for the proposed nanostructured absorber, and a comparison between the simulated and analytical absorption shows a close agreement between them. The simple and easily fabricable design of this absorber makes it a promising candidate for diverse applications, encompassing energy harvesting, solar cells, photodetectors, etc. Furthermore, the straightforward and versatile geometry of the proposed nano-absorber can be readily adapted for use in different operating frequency spectra, including microwave and terahertz ranges.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study
References
Engheta N, Ziolkowski RW (2006) Metamaterials: physics and engineering explorations. John Wiley & Sons
Yu N, Capasso F (2014) Flat optics with designer metasurfaces. Nat Mater 13(2):139–150
Alsulami QA, Wageh S, Al-Ghamdi AA, Bilal RMH, Saeed MA (2022) A tunable and wearable dual-band metamaterial absorber based on polyethylene terephthalate (PET) substrate for sensing applications. Polymers 14(21):4503
Bilal R, Baqir M, Choudhury P, Ali M, Rahim A (2020) Tunable and multiple plasmon-induced transparency in a metasurface comprised of silver s-shaped resonator and rectangular strip. IEEE Photonics J 12(3):1–13
Shalaev VM (2007) Optical negative-index metamaterials. Nat Photonics 1(1):41–48
Smith DR, Pendry JB, Wiltshire MC (2004) “Metamaterials and negative refractive index.” Science 305(5685):788–792
Groever B, Chen WT, Capasso F (2017) Meta-lens doublet in the visible region. Nano Lett 17(8):4902–4907
Grant J, Kenney M, Shah YD, Escorcia-Carranza I, Cumming DR (2018) CMOS compatible metamaterial absorbers for hyperspectral medium wave infrared imaging and sensing applications. Opt Express 26(8):10408–10420
Landy N, Smith DR (2013) A full-parameter unidirectional metamaterial cloak for microwaves. Nat Mater 12(1):25–28
Feuillet-Palma C, Todorov Y, Vasanelli A, Sirtori C (2013) Strong near field enhancement in THz nano-antenna arrays. Sci Rep 3(1):1361
Ahmad T et al (2022) Ultrawideband cross-polarization converter using anisotropic reflective metasurface. Electronics 11(3):487
Naveed MA, Bilal RMH, Rahim AA, Baqir MA, Ali MM (2021) Polarization-insensitive dual-wideband fractal meta-absorber for terahertz applications. Appl Opt 60(29):9160–9166
Zetterstrom O, Hamarneh R, Quevedo-Teruel O (2021) Experimental validation of a metasurface Luneburg lens antenna implemented with glide-symmetric substrate-integrated holes. IEEE Antennas Wirel Propag Lett 20(5):698–702
Zhu H, Cheung S, Chung KL, Yuk TI (2013) Linear-to-circular polarization conversion using metasurface. IEEE Trans Antennas Propag 61(9):4615–4623
Bilal RMH et al (2021) Wideband microwave absorber comprising metallic split-ring resonators surrounded with E-shaped fractal metamaterial. IEEE Access 9:5670–5677
Zheludev NI, Kivshar YS (2012) From metamaterials to metadevices. Nat Mater 11(11):917–924
Liu Y, Zhang X (2011) Metamaterials: a new frontier of science and technology. Chem Soc Rev 40(5):2494–2507
Landy NI, Sajuyigbe S, Mock JJ, Smith DR, Padilla WJ (2008) Perfect metamaterial absorber. Phys Rev Lett 100(20):207402
Feng H et al (2021) Ultrabroadband metamaterial absorbers from ultraviolet to near-infrared based on multiple resonances for harvesting solar energy. Opt Express 29(4):6000–6010
Staude I, Schilling J (2017) Metamaterial-inspired silicon nanophotonics. Nat Photonics 11(5):274–284
He Y, Gao Z, Jia D, Zhang W, Du B, Chen ZN (2017) Dielectric metamaterial-based impedance-matched elements for broadband reflectarray. IEEE Trans Antennas Propag 65(12):7019–7028
Iwaszczuk K, Strikwerda AC, Fan K, Zhang X, Averitt RD, Jepsen PU (2012) Flexible metamaterial absorbers for stealth applications at terahertz frequencies. Opt Express 20(1):635–643
Garg P, Jain P (2019) Isolation improvement of MIMO antenna using a novel flower shaped metamaterial absorber at 5.5 GHz WiMAX band. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst II Express Briefs 67(4):675–679
Wang BX, Zhai X, Wang G-Z, Huang WQ, Wang L-L (2015) “A novel dual-band terahertz metamaterial absorber for a sensor application.” J Appl Phys 117(1)
Liang JC et al (2021) An angle-insensitive 3-bit reconfigurable intelligent surface. IEEE Trans Antennas Propag 70(10):8798–8808
Bilal R, Baqir M, Choudhury PK, Ali MM, Rahim AA, Kamal W (2020) Polarization-insensitive multi-band metamaterial absorber operating in the 5G spectrum. Optik 216:164958
Bilal R, Naveed M, Baqir M, Ali M, Rahim A (2020) Design of a wideband terahertz metamaterial absorber based on Pythagorean-tree fractal geometry. Optical Materials Express 10(12):3007–3020
Deng G, Yang J, Yin Z (2017) Broadband terahertz metamaterial absorber based on tantalum nitride. Appl Opt 56(9):2449–2454. https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.56.002449
Yahiaoui R, Tan S, Cong L, Singh R, Yan F, Zhang W (2015) “Multispectral terahertz sensing with highly flexible ultrathin metamaterial absorber.” J Appl Phys 118(8)
Jiao S, Li Y, Yang H, Xu S (2021) Numerical study of ultra-broadband wide-angle absorber. Results in Physics 24:104146
Liu Y, Liu H, ** Y, Zhu L (2020) Ultra-broadband perfect absorber utilizing a multi-size rectangular structure in the UV-MIR range. Results in Physics 18:103336
Madni A, Bilal RMH, Khan WT (2022) “A compact metamaterial based high isolation MIMO antenna for 5.8 GHz WLAN applications,” in 2022. IEEE Int Symp Antennas Propag. USNC-URSI Radio Science Meeting (AP-S/URSI) IEEE 245–246
Yoo M, Kim HK, Lim S (2016) Electromagnetic-based ethanol chemical sensor using metamaterial absorber. Sens Actuators, B Chem 222:173–180
Zhang Y, Dong H, Mou N, Chen L, Li R, Zhang L (2020) High-performance broadband electromagnetic interference shielding optical window based on a metamaterial absorber. Opt Express 28(18):26836–26849
Liu Z, Liu G, Huang Z, Liu X, Fu G (2018) Ultra-broadband perfect solar absorber by an ultra-thin refractory titanium nitride meta-surface. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 179:346–352
Wang H, Sivan VP, Mitchell A, Rosengarten G, Phelan P, Wang L (2015) Highly efficient selective metamaterial absorber for high-temperature solar thermal energy harvesting. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 137:235–242
Tuan TS, Hoa NTQ (2019) Numerical study of an efficient broadband metamaterial absorber in visible light region. IEEE Photonics J 11(3):1–10
Naik GV, Shalaev VM, Boltasseva A (2013) Alternative plasmonic materials: beyond gold and silver. Adv Mater 25(24):3264–3294
Patel SK, Parmar J, Katrodiya D, Nguyen TK, Holdengreber E, Dhasarathan V (2020) Broadband metamaterial-based near-infrared absorber using an array of uniformly placed gold resonators. JOSA B 37(7):2163–2170
Liang C et al (2019) A broadband and polarization-independent metamaterial perfect absorber with monolayer Cr and Ti elliptical disks array. Results in Physics 15:102635
Bilal RMH, Baqir MA, Hameed M, Naqvi SA, Ali MM (2022) Triangular metallic ring-shaped broadband polarization-insensitive and wide-angle metamaterial absorber for visible regime. JOSA A 39(1):136–142
Bilal RMH, Zakir S, Naveed MA, Zubair M, Mehmood MQ, Massoud Y (2023) Nanoengineered nickel-based ultrathin metamaterial absorber for the visible and short-infrared spectrum. Optical Materials Express 13(1):28–40
Qian Q, Yan Y, Wang C (2018) Flexible metasurface black nickel with stepped nanopillars. Opt Lett 43(6):1231–1234
Zhou Y, Luo M, Shen S, Zhang H, Pu D, Chen L (2018) Cost-effective near-perfect absorber at visible frequency based on homogenous meta-surface nickel with two-dimension cylinder array. Opt Express 26(21):27482–27491
Naveed MA, Bilal RMH, Baqir MA, Bashir MM, Ali MM, Rahim AA (2021) Ultrawideband fractal metamaterial absorber made of nickel operating in the UV to IR spectrum. Opt Express 29(26):42911–42923
Hakim ML et al (2022) Ultrawideband polarization-independent nanoarchitectonics: a perfect metamaterial absorber for visible and infrared optical window applications. Nanomaterials 12(16):2849
Mehrabi S, Bilal RMH, Naveed MA, Ali MM (2022) Ultra-broadband nanostructured metamaterial absorber based on stacked square-layers of TiN/TiO 2. Optical Materials Express 12(6):2199–2211
Sheta E, Choudhury P, Ibrahim A-BM (2022) Polarization-insensitive ultra-wideband metamaterial absorber comprising different forms of ZrN structures at the metasurface. Opt Mater 133:112990
Costa F, Monorchio A, Manara G (2012) Efficient analysis of frequency-selective surfaces by a simple equivalent-circuit model. IEEE Antennas Propag Mag 54(4):35–48
Costa F, Genovesi S, Monorchio A, Manara G (2012) A circuit-based model for the interpretation of perfect metamaterial absorbers. IEEE Trans Antennas Propag 61(3):1201–1209
Lee CK, Langley R (1985) “Equivalent-circuit models for frequency-selective surfaces at oblique angles of incidence.” in IEEE Proceed H (Microwaves, Antennas and Propagation) 132(6):395–399
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zhipeng Gao is the single author of this article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, Z. Ultrabroadband Nanostructured Metamaterial Absorber for Visible and Short-Infrared Spectrum. Plasmonics (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-023-02132-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-023-02132-0