Abstract
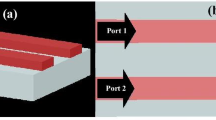
In this paper, we have proposed, analyzed, and verified the performance of an optimized plasmonic 10-dB directional coupler and a 3-dB directional coupler in 2-D plasmonic waveguides using the finite-difference-time-domain (FDTD) method. A plasmonic 10-dB directional coupler and a 3-dB directional coupler are based on the metal–insulator-metal (MIM) slab waveguide and analyzed at the telecommunication wavelength (λ) of 1550 nm. Here, coupling and transmission characteristics are analyzed with the optimized separation distance between the two parallel waveguides. The developed approach ensures the minimization of the crosstalk and overall directional coupler length via simultaneous adjustment of the separation distance between the parallel waveguide and the length of the linear waveguide. Then, an optimized structure is acquired by trading off between coupling length and separation distance. The proposed 10-dB directional coupler and 3-dB directional coupler feature good energy confinement, ultra-compact, and low propagation loss, which has potential applications in photonic integrated devices, optical signal processors, and other all-optical switching devices.





Similar content being viewed by others

Availability of Data and Material
We can provide the data as per request.
Code Availability
No source code is available for this manuscript.
References
Kumar S, Singh L (2016) Proposed new approach to design all optical and gate using plasmonic based Mach-Zehnder interferometer for high speed. Proc. SPIE 9884, Nanophoton. VI 98842D:1–7
Kumar A, Kumar S, Raghuwanshi SK (2014) Implementation of XOR/XNOR and AND logic gates by using Mach-Zehnder interferometers. Optik 125:5764–5767
Olyaee M, Tavakoli MB, Mokhtari A (2018) Analyze and calculation of coupling coefficient based on evanescence field for plasmonic directional coupler structure. Opt and Quant Electron 50:404–410
Thomaschewski M, Zenin VA, Wolff C, Bozhevolnyi SI (2020) Plasmonic monolithic lithium niobate directional coupler switches. Nat Commun 11:748–753
Nozhat N, Granpayeh N (2013) Controlling the coupling ratio of the plasmonic directional couplers by SPM and XPM nonlinear effects. 21stIranian. Conf Elect Engg (ICEE) IEEE Xplore. https://doi.org/10.1109/IranianCEE.2013.6599892
Kumar S, Singh L, Chen NK (2017) All-optical bit magnitude comparator device using metal-insulator-metal plasmonic waveguide. Opt Engg 56:1–5
Kumar S, Singh L, Swarnakar S (2016) Design of one-bit magnitude comparator using nonlinear plasmonic waveguide. Plasmon 12:369–375
Kumar S, Singh G, Bisht A, Amphawan A (2015) Design of D flip-flop and T flip-flop usingMach–Zehnder interferometers forhigh-speed communication. Appl Opt 54:6397–6405
Luo Y, Yu Y, Ye M, Sun C, Zhang X (2016) Integrated dual-mode 3 dB power coupler based on tapered directional coupler. Scient Rep 6(23516):1–7
Ando T, Kaji T, Yamaguchi K, Suzuki K, Kamada S, Okamoto T, Mori A, Haraguchi M (2018) MEMS plasmonic switch with stripe plasmonic waveguide. Jpn J Appl Phys 57(8S2):1–4
Allsop T, Neal R (2019) A review: evolution and diversity of optical fibre plasmonic sensors. Sens 19(22):1–19
Singh L, Kumar S, Kaushik BK (2019) All-optical switching device using plasmonic Mach-Zehnder interferometer structure. J Opt Commun. https://doi.org/10.1515/joc-2018-0215
Zeng D, Zhang L, **ong Q, Ma J (2018) Directional coupler based on an elliptic cylindrical nanowire hybrid plasmonic waveguide. Appl Opt 54:4701–4706
Pu M, Yao N, Hu C, **n X, Zhao Z, Wang C, Luo X (2010) Directional coupler and nonlinear Mach-Zehnder interferometer based on metal-insulator-metal plasmonic waveguide. Opt Exp 18:21030–21037
Chen CH, Liao KS (2013) 1xN plasmonic power splitters based on metal-insulator-metal waveguides. Opt Exp 21:4036–4043
Noghani TF, Samiei MHV (2013) Ultrashort hybrid metal–insulator plasmonic directional coupler. Appl Opt 52:7498–7503
Rao DGS, Swarnakar S, Kumar S (2020) Performance analysis of all-optical NAND, NOR, XNOR logic gates using photonic crystal waveguide for optical computing applications. Opt Engg 59(5):1–11
Kumar S, Singh L, Swarnakar S (2016) Design of one bit magnitude comparator using nonlinear plasmonic waveguide. Plasmon 12(2):369–375
Hosseini A, Nejati H, Massoud Y (2008) An analytical model for characteristic impedance in nanostrip plasmonic waveguides. IEEE Int Sym Cir Sys 2346–2349
Boltasseva A, Bozhevolnyi SI (2006) Directional couplers using long-range surface plasmon polariton waveguides. IEEE J Sel Top Quant Elect 12:1233–1241
Holmgaard T, Chen Z, Bozhevolnyi SI, Markey L, Dereux A (2009) Design and characterization of dielectric-loaded plasmonic directional couplers. J of Lightw Tech 27:5521–5528
Fu Y, Hu X, Lu C, Yue S, Yang H, Gong Q (2012) All-optical logic gates based on nanoscale plasmonic slot waveguides. Nano Lett 12:5784–5790
Manning RJ, Kelly AE, Poustie AJ, Blow KJ (1998) Wavelength dependence of switching contrast ratio of semiconductor optical amplifier-based nonlinear loop mirror. Electron Lett 34(9):1–2
Kumar S, Raghuwanshi SK, Rahman BMA (2015) Design of universal shift register based on electro-optic effect of LiNbO3 in Mach-Zehnder interferometer for high speed communication. Opt and Quant Electron 47:3509–3524
Pourali E, Baboli MA (2015) Design and analysis of an all optical OR gate using surface plasmon hop** along metallic nanorods. Phys Scr 90(4):1–6
Taraphdar C, Chattopadhyay T, Roy JN (2010) Mach-Zehnder interferometer-based all-optical reversible logic gate. Opt & Las Tech 42:249–259
Rao DGS, Palacharla V, Swarnakar S, Kumar S (2020) Design of all-optical D-flip flop using photonic crystal waveguides for optical computing and optical networking. Appl Opt 59(23):7139–7143
Rao DGS, Fathima MS, Manjula P, Swarnakar S (2020) Design and optimization of all-optical demultiplexer using photonic crystals for optical computing applications. J Opt Commun. https://doi.org/10.1515/joc-2020-0057
Swarnakar S, Kumar S, Sharma S (2018) Performance analysis of all-optical full-adder based on two-dimensional photonic crystals. J Comp Electron 17(3):1124–1134
Swarnakar S, Kumar S, Sharma S (2017) Design of all-optical half-subtractor circuit device using 2-D principle of photonic crystal waveguides. J Opt Commun 40(3):195–203
Swarnakar S, Kumar S, Sharma S (2016) All-optical half-adder circuit based on beam interference principle of photonic crystal. J Opt Commun 39(1):13–17
Swarnakar S, Rathi S, Kumar S (2017) Design of all-optical XOR gate based on photonic crystal ring resonator. J Opt Commun 41(1):51–56
Rathi S, Swarnakar S, Kumar S (2017) Design of one-bit magnitude comparator using photonic crystal waveguide. J Opt Commun 40(4):363–367
Swarnakar S, Kumar S, Sharma S, Singh L (2017) Design of XOR/AND gate using 2-D photonic crystal principle. SPIE Photon. West, San Francisco, USA 28
Dai D, Bowers JE (2011) Novel ultra-short and ultra-broadband polarization beam splitter based on a bent directional coupler. Opt Exp 19(19):18614–18620
Edelmann AG, Helfertand SF, Jahns J (2011) Transmission characteristics in plasmonic multimode waveguides. Opt and Quant Electron 42:531–540
Gramotnev DK, Vernon KC, Pile DFP (2008) Directional coupler using gap plasmon waveguides. Appl Phys B 93:99–106
Trinh PD, Yegnanarayanan S, Jalali B (1995) Integrated optical directional couplers in silicon-on-insulator. Electron Lett 31:2097–2098
Cheng HC, Ramaswamy RV (1990) Determination of the coupling length in directional couplers from spectral response. IFEE Photon Tech Lett 2:823–825
Gruszczynski S, Smolarz R, Wincza K (2019) Realization of high-performance broadbandquadrature directional couplers in UMSPH25 technology. Electron 8(12)
Dolatabady A, Granpayeh N (2013) Plasmonic waveguide directional coupler based on two dimensional two-hole coupler. 21stIranian Conf Elect Engg (ICEE) IEEE Xplore. https://doi.org/10.1109/IranianCEE.2013.6599794
Wen S, Wang Q, Tan TY (2012) Design of a compact 3dB Ka-band directional coupler. Int Works Microw Millimet. Wave Cir Sys Tech
**ng Y, Khan U, Riberio A, Bogaerts W (2017) Behavior model for directional coupler. Proc Sym IEEE Photon Soc Benelux 128–131
Suzuki K, Cong G, Tanizawa K, Kim SH, Ikeda K, Namiki S, Kawashima H (2015) Ultra-high-extinction-ratio 2×2 silicon optical switch with variable splitter. Opt Exp 23:9086–9092
Liang TK, Tsang HK (2005) Integrated polarization beam splitter in high index contrast silicon-on-insulator waveguides. IEEE Photon Tech Lett 17:393–395
Mehra R, Jaiswal S, Dixit HK (2012) SOA based all optical NAND gate and their comparison. IEEE 3rd Int Conf Compu Commun Tech (ICCCT) 175–177. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCCT.2012.42
Singh A, Pal A, Singh Y, Sharma S (2019) Design of optimized all-optical NAND gate using metal-insulator-metal waveguide. Opt Int J Light Elect Opt 182(7):524–528
Swarnakar S, Guddati A, Reddy SK, Harijan R, Kumar S (2021) Performance analysis of optimized plasmonic half-adder circuit using Mach-Zehnder interferometer for high-speed switching applications. Microelectron. J. 111:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mejo.2021.105040
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Rupalin Rath: investigation, formal analysis, and writing—original draft. Ramakrushna Rath: formal analysis and methodology. Sandip Swarnakar: conceptualization, investigation, formal analysis, writing—original draft, methodology, and supervision. Santosh Kumar: validation, writing—review, and editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Consent to Participate
For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nanda, R., Rath, R., Swarnakar, S. et al. Design of All-Optical Directional Coupler Using Plasmonic MIM Waveguide for Switching Applications. Plasmonics 17, 2153–2159 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-022-01695-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-022-01695-8