Abstract
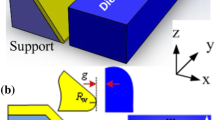
Exploring hybrid gap surface plasmon polariton waveguides (HGSPPWs) is an important milestone in develo** the next-generation, nanoscale integrated photonic circuit technology. To advance their potential applications, HGSPPWs are required to have tunable capability, highly reliable, simple fabrication process, and feasible integration. In this paper, we propose two tunable HGSPPWs fulfilling the requirements. The proposed HGSPPWs consist of a metallic wedge laterally coupled with a dielectric waveguide. The modal characteristics of HGSPPWs are investigated at the optical telecommunication wavelength, which shows the modal characteristics could be effectively controlled by tuning the key geometry parameters and structure of HGSPPWs. The propagation length could achieve the centimeter scale while maintaining the propagation mode size at the deep-subwavelength scale (~ λ2/105). The studies on fabrication tolerance and waveguide crosstalk show their robust property for practical implementations. The effective tunable mechanism is also proposed and studied, which shows remarkable feasibility to realize multifunctional plasmon-based photonic components. Compared with the conventional HGSPPWs, the proposed HGSPPWs exhibit superior features in ultralow loss deep-subwavelength light guiding, are highly reliable, and are easy to integrate.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maier SA (2007) Plasmonics: fundamentals and applications. Springer Science & Business Media
Wei H, Xu H (2012) Nanowire-based plasmonic waveguides and devices for integrated nanophotonic circuits. Nanophotonics 1(2):155–169
Gao Y, Gan Q, **n Z, Cheng X, Bartoli FJ (2011) Plasmonic Mach–Zehnder interferometer for ultrasensitive on-chip biosensing. ACS Nano 5(12):9836–9844
Fang Y, Sun M (2015) Nanoplasmonic waveguides: towards applications in integrated nanophotonic circuits. Light Sci Appl 4(6):e294
Kress SJ, Antolinez FV, Richner P, Jayanti SV, Kim DK, Prins F, Riedinger A, Fischer MP, Meyer S, McPeak KM (2015) Wedge waveguides and resonators for quantum plasmonics. Nano Lett 15(9):6267–6275
Moreno E, Rodrigo SG, Bozhevolnyi SI, Martín-Moreno L, García-Vidal F (2008) Guiding and focusing of electromagnetic fields with wedge plasmon polaritons. Phys Rev Lett 100(2):023901
Boltasseva A, Volkov VS, Nielsen RB, Moreno E, Rodrigo SG, Bozhevolnyi SI (2008) Triangular metal wedges for subwavelength plasmon-polariton guiding at telecom wavelengths. Opt Express 16(8):5252–5260
Lotan O, Smith CL, Bar-David J, Mortensen NA, Kristensen A, Levy U (2016) Propagation of channel plasmons at the visible regime in aluminum V-groove waveguides. Acs Photonics 3(11):2150–2157
Dionne J, Sweatlock L, Atwater H, Polman A (2006) Plasmon slot waveguides: towards chip-scale propagation with subwavelength-scale localization. Phys Rev B 73(3):035407
Sarid D (1981) Long-range surface-plasma waves on very thin metal films. Phys Rev Lett 47(26):1927–1930
Dintinger J, Martin OJ (2009) Channel and wedge plasmon modes of metallic V-grooves with finite metal thickness. Opt Express 17(4):2364–2374
Pile DF, Ogawa T, Gramotnev DK, Okamoto T, Haraguchi M, Fukui M, Matsuo S (2005) Theoretical and experimental investigation of strongly localized plasmons on triangular metal wedges for subwavelength waveguiding. Appl Phys Lett 87(6):061106
Oulton RF, Sorger VJ, Genov D, Pile D, Zhang X (2008) A hybrid plasmonic waveguide for subwavelength confinement and long-range propagation. Nat Photonics 2(8):496–500
Zhang Y, Zhang Z (2017) Ultra-subwavelength and low loss in v-shaped hybrid plasmonic waveguide. Plasmonics 12(1):59–63
Zhang B, Bian Y, Ren L, Guo F, Tang S-Y, Mao Z, Liu X, Sun J, Gong J, Guo X (2017) Hybrid dielectric-loaded nanoridge plasmonic waveguide for low-loss light transmission at the subwavelength scale. Sci Rep 7:40479
Gao L, Tang L, Hu F, Guo R, Wang X, Zhou Z (2012) Active metal strip hybrid plasmonic waveguide with low critical material gain. Opt Express 20(10):11487–11495
Bian Y, Ren Q, Kang L, Yue T, Werner PL, Werner DH (2018) Deep-subwavelength light transmission in hybrid nanowire-loaded silicon nano-rib waveguides. Photonics Res 6(1):37–45
Bian Y, Gong Q (2015) Metallic-nanowire-loaded silicon-on-insulator structures: a route to low-loss plasmon waveguiding on the nanoscale. Nanoscale 7(10):4415–4422
Dai D, Shi Y, He S, Wosinski L, Thylen L (2011) Gain enhancement in a hybrid plasmonic nano-waveguide with a low-index or high-index gain medium. Opt Express 19(14):12925–12936
Gui C, Wang J (2015) Wedge hybrid plasmonic THz waveguide with long propagation length and ultra-small deep-subwavelength mode area. Sci Rep 5:11457
Bian Y, Gong Q (2014) Deep-subwavelength light confinement and transport in hybrid dielectric-loaded metal wedges. Laser Photon Rev 8(4):549–561
Ding L, Qin J, Xu K, Wang L (2016) Long range hybrid tube-wedge plasmonic waveguide with extreme light confinement and good fabrication error tolerance. Opt Express 24(4):3432–3440
Ma Y, Farrell G, Semenova Y, Wu Q (2015) A hybrid wedge-to-wedge plasmonic waveguide with low loss propagation and ultra-deep-nanoscale mode confinement. J Lightwave Technol 33(18):3827–3835
Hao R, Cassan E, Xu Y, Qiu M, Wei X-C, Li E-P (2013) Reconfigurable parallel plasmonic transmission lines with nanometer light localization and long propagation distance. IEEE J Sel Top Quantum Electron 19(3):4601809–4601809
Gosciniak J, Bozhevolnyi SI, Andersen TB, Volkov VS, Kjelstrup-Hansen J, Markey L, Dereux A (2010) Thermo-optic control of dielectric-loaded plasmonic waveguide components. Opt Express 18(2):1207–1216
Pitilakis A, Kriezis EE (2011) Longitudinal 2 x 2 switching configurations based on thermo-optically addressed dielectric-loaded plasmonic waveguides. J Lightwave Technol 29(17):2636–2646
Weeber J-C, Bernardin T, Nielsen MG, Hassan K, Kaya S, Fatome J, Finot C, Dereux A, Pleros N (2013) Nanosecond thermo-optical dynamics of polymer loaded plasmonic waveguides. Opt Express 21(22):27291–27305
Rudé M, Simpson RE, Quidant R, Pruneri V, Renger J (2015) Active control of surface plasmon waveguides with a phase change material. ACS Photonics 2(6):669–674
Zografopoulos DC, Swillam MA, Shahada LA, Beccherelli R (2016) Hybrid electro-optic plasmonic modulators based on directional coupler switches. Appl Phys A 122(4):344
MacDonald KF, Sámson ZL, Stockman MI, Zheludev NI (2009) Ultrafast active plasmonics. Nat Photonics 3(1):55–58
Pacifici D, Lezec HJ, Atwater HA (2007) All-optical modulation by plasmonic excitation of CdSe quantum dots. Nat Photonics 1(7):402–406
Pala RA, Shimizu KT, Melosh NA, Brongersma ML (2008) A nonvolatile plasmonic switch employing photochromic molecules. Nano Lett 8(5):1506–1510
Sun X, Thylén L, Wosinski L (2017) MEMS tunable hybrid plasmonic-Si waveguide. In: Optical Fiber Communications Conference and Exhibition (OFC). IEEE, pp 1–3
Bozhevolnyi SI, Volkov VS, Devaux E, Laluet J-Y, Ebbesen TW (2006) Channel plasmon subwavelength waveguide components including interferometers and ring resonators. Nature 440(7083):508–511
Tobing LY, Tjahjana L, Hua Zhang D (2012) Demonstration of low-loss on-chip integrated plasmonic waveguide based on simple fabrication steps on silicon-on-insulator platform. Appl Phys Lett 101(4):041117
Zhu S, Lo G-Q, Kwong D-L (2012) Experimental demonstration of vertical Cu-SiO2-Si hybrid plasmonic waveguide components on an SOI platform. IEEE Photon Technol Lett 24(14):1224–1226
Xu Q, Schmidt B, Pradhan S, Lipson M (2005) Micrometre-scale silicon electro-optic modulator. nature 435(7040):325–327
Akihama Y, Hane K (2012) Single and multiple optical switches that use freestanding silicon nanowire waveguide couplers. Light Sci Appl 1(6):e16
Abe S, Chu MH, Sasaki T, Hane K (2014) Time response of a microelectromechanical silicon photonic waveguide coupler switch. IEEE Photon Technol Lett 26(15):1553–1556
Wang M, Zhao C, Miao X, Zhao Y, Rufo J, Liu YJ, Huang TJ, Zheng Y (2015) Plasmofluidics: merging light and fluids at the micro-/nanoscale. Small 11(35):4423–4444
Boales JA, Mateen F, Mohanty P (2017) Micromechanical resonator driven by radiation pressure force. Sci Rep 7(1):16056
Funding
This research is funded by Vietnam National Foundation for Science and Technology Development (NAFOSTED) under grant number “103.02-2015.86.”
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, H.T., Nguyen, S.N., Trinh, MT. et al. Tunable Hybrid Gap Surface Plasmon Polariton Waveguides with Ultralow Loss Deep-Subwavelength Propagation. Plasmonics 14, 1751–1763 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-019-00971-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-019-00971-4