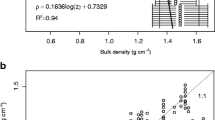
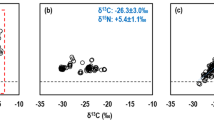
Abstract
Purpose
Vertical transfer of solid matter in soils (bioturbation and translocation) is responsible for changes in soil properties over time through the redistribution of most of the soil constituents with depth. Such transfers are, however, still poorly quantified.
Materials and methods
In this study, we examine matter transfer in four eutric Luvisols through an isotopic approach based on 137Cs, 210Pb(xs), and meteoric 10Be. These isotopes differ with respect to chemical behavior, input histories, and half-lives, which allows us to explore a large time range. Their vertical distributions were modeled by a diffusion-advection equation with depth-dependent parameters. We estimated a set of advection and diffusion coefficients able to simulate all isotope depth distributions and validated the resulting model by comparing the depth distribution of organic carbon (including 12/13C and 14C isotopes) and of the 0–2-μm particles with the data.
Results and discussion
We showed that (i) the model satisfactorily reproduces the organic carbon, 13C, and 14C depth distributions, indicating that organic carbon content and age can be explained by transport without invoking depth-dependent decay rates; (ii) translocation partly explains the 0–2-μm particle accumulation in the Bt horizon; and (iii) estimates of diffusion coefficients that quantify the soil mixing rate by bioturbation are significantly higher for the studied plots than those obtained by ecological studies.
Conclusions
This study presents a model capable of satisfactorily reproducing the isotopic profiles of several tracers and simulating the distribution of organic carbon and the translocation of 0–2-μm particles.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahrens B, Reichstein M, Borken W, Muhr J, Trumbore SE, Wortzler T (2014) Bayesian calibration of a soil organic carbon model using ∆14C measurements of soil organic carbon and heterotrophic respiration as joint constraints. Biogeosciences 11:2147–2168
Al-Masri MS (2006) Vertical distribution and inventories of Cs-137 in the Syrian soils of the eastern Mediterranean region. J Environ Radioactiv 86(2):187–198
Antoine P, Rousseau DD, Lautridou JP, Hatté C (1999) Last interglacial-glacial climatic cycle in loess-palaeosol successions of north-western France. Boreas 28:551–563
Antoine P, Catt J, Lautridou JP, Somm’e J (2003) The loess and coversands of northern France and southern England. J Quaternary Sci 18(3–4):309–318
Balesdent J, Balabane M (1992) Maize root-derived soil organic carbon estimated by natural 13C abundance. Soil Biol Biochem 24:97–101
Bettis EA, Muhs DR, Roberts HM, Wintle AG (2003) Last glacial loess in the conterminous USA. Quaternary Sci Rev 22(18–19):1907–1946
Bockheim J, Gennadiyev A (2000) The role of soil-forming processes in the definition of taxa in soil taxonomy and the world soil reference base. Geoderma 95(1–2):53–72
Bouché MB (1981) Contribution des lombriciens aux migrations d’éléments dans les sols tempérés. Colloques Internationaux du Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique 303:145–153
Bundt M, Albrecht A, Froidevaux P, Blaser P, Flühler H (2000) Impact of preferential flow on radionuclide distribution in soil. Environ Sci Technol 34(18):3895–3899
Cambray RS, Playford K, Lewis G, Carpenter R (1989) Radioactive fallout in air and rain: results to the end of 1988. Environmental and Medical Sciences Division, United Kingdom Atomic Energy Authority
Campforts B, Vanacker V, Vanderborght J, Baken S, Smolders E, Govers G (2016) Simulating the mobility of meteoric 10Be in the landscape through acoupled soil-hillslope model (Be2D). Earth plan. Sci Lett 439:143–157
Coleman K, Jenkinson D (1999) RothC-26.3. A model for the turnover of carbon in soils. Herts, Rothamsted Research, Harpenden, Hertfordshire, UK
Coplen T, Brand W, Gehre M, Gröning M, Meijer H, Toman B, Verkouteren R (2006) After two decades a second anchor for the VPDB δ13C scale. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry: RCM 20(21):3165
Cottereau E, Arnold M, Moreau C, Baqué D, Bavay D, Caffy I, Comby C, Dumoulin J, Hain S, Perron M, Salomon J, Setti V (2007) Artemis, the new 14C AMS at LMC14 in Saclay, France. Radiocarbon 49(2):291–299
Cremers A, Elsen A, Depreter P, Maes A (1988) Quantitative analysis of radiocesium retention in soils. Nature 335(6187):247–249
Davis BAS, Brewer S, Stenvenson AC, Guiot J, Contributors D (2003) The temperature of Europe during the Holocene reconstructed from pollen data. Quaternary Sci Rev 22:1701–1716
Dörr H, Münnich K (1989) Downward movement of soil organic-matter and its influence on trace-element transport (Pb-210, Cs-137) in the soil. Radiocarbon 31(3):655–663, 13th International Radiocarbon conf, Dubrovnik, Yugoslavia, June 20–25, 1988
Finke PA (2012) Modeling the genesis of Luvisols as a function of topographic position in loess parent material. Quaternary Int 265:3–17
Finke PA, Hutson JL (2008) Modelling soil genesis in calcareous loess. Geoderma 145(3):462–479
Francey R, Allison C, Etheridge D, Trudinger C, Enting I, Leuenberger M, Langenfelds R, Michel E, Steele L (1999) A 1000-year high precision record of δ13C in atmospheric CO2. Tellus B 51(2):170–193
Gobat JM, Aragno M, Matthey W (2004) The living soil: fundamentals of soil science and soil biology. Science Publishers
Graly JA, Bierman PR, Reusser LJ, Pavich MJ (2010) Meteoric Be-10 in soil profiles—a global meta-analysis. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 74(23):6814–6829
He Q, Walling D (1997) The distribution of fallout Cs-137 and Pb-210 in undisturbed and cultivated soils. Appl Radiat Isotopes 48(5):677–690
Hua Q, Barbetti M, Rakowski AZ (2013) Atmospheric radiocarbon for the period 1950–2010. Radiocarbon 55(4):2059–2072
Jacobsen OH, Moldrup P, Larsen C, Konnerup L, Petersen LW (1997) Particle transport in macropores of undisturbed soil columns. J Hydrol 196(1–4):185–203
Jagercikova M, Evrard O, Balesdent J, Lefèvre I, Cornu S (2014a) Modeling the migration of fallout radionuclides to quantify the contemporary transfer of fine particles in Luvisol profiles under different land uses and farming practices. Soil Till Res 140:82–97
Jagercikova M, Cornu S, Le Bas C, Evrard O (2014b) Vertical distributions of 137Cs in soils: a meta-analysis. J Soils Sediments 15(1):81–95
Jagercikova M, Cornu S, Bourlès D, Antoine P, Mayor M, Guillou V (2015) Understanding long-term soil processes using meteoric 10Be: a first attempt on loessic deposits. Quat Geochronol 27:11–21
Jamagne M (1973) Contribution à l’étude pédologique des formations loessiques du Nord de la France. Ph.D., Thèse d’état de la faculté des sciences agronomiques, Gembloux Belgique
Jamagne M, Pedro G (1981) Les phénomènes de migration et d’accumulation de particules au cours de la pédogenèse sur les formations limoneuses du Nord de la France. Essai de caractérisation du processus de “lessivage”. C R Acad Sci 292:1329–1332
Jarvis NJ, Taylor A, Larsbo M, Etana A, Rosen K (2010) Modelling the effects of bioturbation on the re-distribution of 137Cs in an undisturbed grassland soil. Eur J Soil Sci 61(1):24–34
Jenkinson D, Coleman K (2008) The turnover of organic carbon in subsoils. Part 2. Modelling carbon turnover. Eur J Soil Sci 59(2):400–413
Jenkinson DS, Rayner JH (1977) The turnover of soil organic matter in some of the Rothamsted classical experiments. Soil Sci 123(5):298–305
Joret G, Malterre H (1947) Les sols du Santerre et du Vermandois. In: Extrait Annales Agronomiques. Dunod, Paris
Kaste JM, Heimsath AM, Bostick BC (2007) Short-term soil mixing quantified with fallout radionuclides. Geology 35(3):243–246
Korschinek G, Bergmaier A, Faestermann T, Gerstmann UC, Knie K, Rugel G, Wallner A, Dillmann I, Dollinger G, Lierse Von Gostomski C, Kossert K, Maiti M, Poutivtsev M, Remmert A (2010) A new value for the half-life of 10Be by heavy-ion elastic recoil detection and liquid scintillation counting. Nucl Instrum 268:187–191
Koven CD, Riley WJ, Subin ZM, Tang JY, Torn MS, Collins WD, Bonan GB, Lawrence DM, Swenson SC (2013) The effect of vertically resolved soil biogeochemistry and alternate soil C and N models on C dynamics of CLM4. Biogeosciences 10:7109–7131
Lal D, Peters B (1967) Cosmic ray produced radioactivity on the Earth. In: Kosmische Strahlung II/Cosmic Rays II. Springer, pp 551e612
Loague K, Green RE (1991) Statistical and graphical methods for evaluating solute transport models: overview and application. Journal Contam Hydrol 7(1):51–73
Majdalani S, Michel E, Di Pietro L, Angulo-Jaramillo R, Rousseau M (2007) Mobilization and preferential transport of soil particles during infiltration: a corescale modeling approach. Water Resour Res 43(5). doi:10.1029/2006WR005057
Matisoff G, Ketterer ME, Rosen K, Mietelski JW, Vitko LF, Persson H, Lokas E (2011) Downward migration of chernobyl-derived radionuclides in soils in Poland and Sweden. Applied Geochem 26(1):105–115
Milton GM, Kramer SJ, Watson WL, Kotzer TG (2001) Qualitative estimates of soil disturbance in the vicinity of CANDUS stations, utilizing measurements of 137Cs and 210Pb in soil cores. J Environ Radioactiv 55(2):195–205
Pavich MJ, Brown L, Klein J, Middleton R (1984) Be-10 accumulation in a soil chronosequence. Earth Planet Sci Lett 68(2):198e204
Pavich MJ, Brown L, Harden J, Klein J, Middleton R (1986) Be-10 distribution in soils from Merced River terraces, California. Geochimica Cosmochimica Acta 50(8):1727e1735
Pécsi M (1990) Loess is not just the accumulation of dust. Quat Int 7:1–21
Persson T, Lenoir L, Taylor A (2007) Bioturbation in different ecosystems at Forsmark and Oskarhamn. SKB Rapport R-06-123. Stockholm Sweden
Quénard L, Samouëlian A, Laroche B, Cornu S (2011) Lessivage as a major process of soil formation: a revisitation of existing data. Geoderma 167-68:135–147
Reimer PJ, Baillie MG, Bard E, Bayliss A, Beck JW, Blackwell PG, Ramsey CB, Buck CE, Burr GS, Edwards RL, Friedrich M, Grootes PM, Guilderson TP, Hajdas I, Heaton TJ, Hogg AG, Hughen KA, Kaiser KF, Kromer B, McCormac FG, Manning SW, Reimer RW, Richards DA, Southon JR, Talamo S, Turney CSM, Van der Pflicht J, Weyhenmeyer CE (2009) Intcal09 and marine09 radiocarbon age calibration curves, 0-50,000 years cal BP. Radiocarbon 51:1111–1150
Roussel-Debel S, Renaud P, Metivier J-M (2007) 137Cs in French soils: deposition patterns and 15-year evolution. Science Total Environ 374(2):388–398
Salvador-Blanes S, Minasny B, McBratney A (2007) Modelling long-term in situ soil profile evolution: application to the genesis of soil profiles containing stone layers. Eur J Soil Sci 58(6):1535–1548
Sammartino S, Lissy AS, Bogner C, Van Den Bogaert R, Capowiez Y, Ruy S, Cornu S (2015) Identifying the functional macropore network related to preferential flow in structured soils. Vadose Zone J 14(10):2–16. doi:10.2136/vzj2015.05.0070
Samouelian A, Cornu S (2008) Modelling the formation and evolution of soils, a synthesis. Geoderma 145(3–4):401–409
Sawhney B (1972) Selective sorption and fixation of cations by clay minerals: a review. Clay Clay Miner 20:93–100
Schimmack W, Márquez FF (2006) Migration of fallout radiocaesium in a grassland soil from 1986 to 2001: part II: evaluation of the activity–depth profiles by transport models. Sci Total Environ 368(2):863–874
Schmitt J, Schneider R, Elsig J, Leuenberger D, Lourantou A, Chappellaz J, Köhler P, Joos F, Stocker TF, Leuenberger M, Lourantou A, Chappelaz J, Köhler P, Joos F, Stocker TF, Leuenberger M, Fischer H (2012) Carbon isotope constraints on the deglacial CO2 rise from ice cores. Science 336(6082):711–714
Schuller P, Ellies A, Kirchner G (1997) Vertical migration of fallout Cs-137 in agricultural soils from southern Chile. Sci Total Environ 193(3):197–205
Sterckeman T, Douay F, Baize D, Fourrier H, Proix N, Schvartz C, Carignan J (2006) Trace element distributions in soils developed in loess deposits from northern France. Eur J Soil Sci 57(3):392–410
Stuiver M, Polach HA (1977) Discussion; reporting of C-14 data. Radiocarbon 19(3):355–363
Swinnen J, Van Veen JA, Merckx R (1994) 14C pulse-labelling of field-frown spring wheat: an evaluation of its use in rhizosphere carbon budget estimation. Soil Biol Biochem 26:161–170
Takahashi Y, Minai Y, Ambe S, Makide Y, Ambe F (1999) Comparison of adsorption behavior of multiple inorganic ions on kaolinite and silica in the presence of humic acid using the multitracer technique. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 63(6):815–836
Tamura T, Jacobs D (1960) Structural implications in cesium sorption. Health Phys 2(4):391–398
Ullrich A, Volk M (2009) Application of the soil and water assessment tool (SWAT) to predict the impact of alternative management practices on water quality and quantity. Agric Water Manag 96(8):1207–1217
Verbruggen C, Denys L, Kiden P (1996) Belgium. In: Berglund BE, Birks HJB, Ralska-Jasiewiczowa M, Wright HE (eds) Palaeoecological events during the last 15000 years. Regional Syntheses of Palaeoecological Studies of Lakes and Mires in Europe. Wiley, Chistester
Warembourg FR, Paul EA (1977) Seasonal transfers of assimilated 14C in grassland: plant production and turnover, soil and plant respiration. Soil Biol Biochem 9:295–301
White J, Vaughn B (2011) University of Colorado, Institute of Arctic and Alpine Research (INSTAAR), Stable Isotopic Composition of Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide (13C and 18O) from the NOAA ESRL Carbon Cycle Cooperative Global Air Sampling Network, 1990–2012, Version: 2013–04-05. URL ftp://ftp.cmdl.noaa.gov/ccg/co2c13/flask/event/
Wilkinson MT, Richards PJ, Humphreys GS (2009) Breaking ground: pedological, geological, and ecological implications of soil bioturbation. Earth-Sci Rev 97(1–4):257–272
Willenbring JK, von Blanckenburg F (2010) Meteoric cosmogenic beryllium-10 adsorbed to river sediment and soil: applications for earth-surface dynamics. Earth-Sci Rev 98(1e2):105e122
You CF, Lee T, Li YH (1989) The partition of Be between soil and water. Chem Geol 77(2):105–118
Acknowledgments
This research was conducted in the framework of the Agriped project (ANR-10-BLANC-605) supported by the French National Research Agency (ANR). M. Jagercikova received a PhD grant from the French National Institute for Agricultural Research (INRA). The authors are grateful to Dr. Frédéric Golay, Dr. Cédric Galusinski, and Dr. Gloria Faccanoni for their suggestions regarding numerical modeling; to Patrick Signoret for the carbon stable isotope analyses; to Dr. Bruno Mary, Dr. David Montagne, and Nicolas Brunet for providing the soil bulk density data; to the Agriped team for its contribution to sampling; and to the INRA of Mons-en-Chaussée, Grignon, and Arvalis for providing access to their long-term experimental sites and the associated data. M. Arnold, G. Aumaître, and K. Keddadouche are thanked for their valuable assistance during 10Be measurement at the ASTER AMS national facility (CEREGE, Aix-en-Provence), which is supported by the INSU/CNRS, the ANR through the “Projets thématiques d’excellence” program for the “Equipements d’excellence” ASTER-CEREGE action (ANR-10-EQPX-24-1), IRD, and the CEA. This is an LSCE contribution no. 2016-5885.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Maxine J. Levin
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jagercikova, M., Cornu, S., Bourlès, D. et al. Quantification of vertical solid matter transfers in soils during pedogenesis by a multi-tracer approach. J Soils Sediments 17, 408–422 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-016-1560-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-016-1560-9