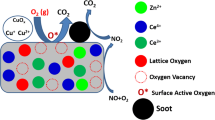
Abstract
Diesel soot is a significant contributor to air pollution. Soot particles present in diesel engine exhaust have a negative impact on the environment and human health. Diesel oxidation catalysts (DOCs) and diesel particulate filters (DPFs) currently use noble metal-based catalysts for soot oxidation. Due to the use of noble metals in the catalyst, the cost of diesel after-treatment systems is steadily rising. As a result, diesel vehicles have become commercially less viable than gasoline vehicles and electronic vehicles. The study focuses on an alternative diesel oxidation catalyst with efficiency similar to that of a noble metal catalyst but with a much lower cost. CeO2-Al2O3 catalysts are known for their oxygen storage capacity and high redox activity, making them suitable for soot oxidation. Adding Zr to these catalysts has been shown to influence their structural and chemical properties, significantly affecting their catalytic behavior. Therefore, the current study is focused on using Zr/CeO2-Al2O3 as a substitute for noble metal-based catalysts to enhance its performance for diesel soot oxidation in automotive exhaust. Evaporation-induced self-assembly (EISA) was used to prepare 1, 3, and 5 weight (wt) % Zr supported mesoporous CeO2-Al2O3 catalysts. Morphological, structural, and physicochemical properties of the synthesized catalysts were examined using Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) absolute isotherm, Scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), Temperature programmed reduction (TPR), and Temperature-programmed desorption of ammonia (NH3-TPD). XRD, BET, and SEM data confirmed that the catalysts were mesoporous and low-crystalline with a high surface area. The soot oxidation activity of the catalysts was evaluated using a thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) technique. The loose contacts soot oxidation activity test suggested that 50% oxidation of soot occurred at 390 °C in the absence of a catalyst. T50 of CeO2-Al2O3 catalyzed soot oxidation was 296 °C. Adding Zr to the catalyst significantly improved catalytic activity for diesel soot oxidation. We observed a further drastic change in T50 of soot over 1, 3, and 5% Zr/CeO2-Al2O3, which were 220 °C, 210 °C, and 193 °C, respectively. According to these results, incorporating Zr into the CeO2-Al2O3 catalyst significantly improved the oxidation process of soot.
Graphical Abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The data supporting the findings of the study are available within the manuscript. Raw data supporting this study's findings are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Abdollahzadeh-Ghom S, Zamani C, Andreu T, Epifani M, Morante JR (2011) Improvement of oxygen storage capacity using mesoporous ceria-zirconia solid solutions. Appl Catal B Environ 108–109:32–38
Ai C, Zhang Y, Wang P, Wang W (2019) Catalytic combustion of diesel soot on Ce/Zr series catalysts prepared by sol-gel method. Catalysts 9(8):646
Alinezhadchamazketi A, Khodadadi AA, Mortazavi Y, Nemati A (2013) Catalytic evaluation of promoted CeO2 -ZrO2 by transition, alkali, and alkaline-earth metal oxides for diesel soot oxidation. J Environ Sci 25(12):2498–2506
Andana T, Piumetti M, Bensaid S, Russo N, Fino D, Pirone R (2016) CO and soot oxidation over Ce-Zr-Pr oxide catalysts. Nanoscale Res Lett 11:1–9
Atribak I, A. Bueno-López, Garcı A (2008) Thermally stable ceria – zirconia catalysts for soot oxidation by O 2. Catal Commun 9:250–255
Bendieb Aberkane A, Yeste MP, Fayçal D, Goma D, Cauqui MÁ (2019) Catalytic soot oxidation activity of NiO–CeO2 catalysts prepared by a coprecipitation method: influence of the preparation ph on the catalytic performance. Materials 12(20):3436
Beisl S, Herrera Díaz R, Maroušek J, Maroušková A, Periakaruppan R, Gokul GM, Anbukumaran A, Bohatá A, Kříž P, Bárta J, Pavelčerný PP, Olšan P (2022) Silica nanoparticles from coir pith synthesized by acidic sol-gel method improve germination economics. Polymers 14(2):266
Bhardawaj A, Habib G, Kumar A, Singh S, Nema AK (2017) A review of ultrafine particle-related pollution during vehicular motion, health effects and control. Environ Sci Public Health 1(4):268–288
Bosch H, Janssen F (1988) Catalytic reduction of nitrogen oxides-a review on the fundamentals and technology. Catalysis Today;(Netherlands) 2(4)
Bueno-López A, Krishna K, Makkee M, Moulijn JA (2005) Active oxygen from CeO2 and its role in catalysed soot oxidation. Catal Lett 99(3–4):203–205
Calafat A (1998) The influence of preparation conditions on the surface area and phase formation of zirconia. In Studies in surface science and catalysis, vol. 118. Elsevier, pp 837–843
Chanerika R, Shozi ML, Friedrich HB (2022) Synthesis and characterization of Ag/Al2O3 catalysts for the hydrogenation of 1-octyne and the preferential hydrogenation of 1-octyne vs 1-octene. ACS Omega 7(5):4026–4040
Chang LH, Sasirekha N, Chen YW, Wang WJ (2006) Preferential oxidation of CO in H2 stream over Au/MnO2-CeO2 catalysts. Ind Eng Chem Res 45(14):4927–4935
Davies C, Thompson K, Cooper A, Golunski S, Taylor SH, Bogarra M, Doustdar O, Tsolakis A (2018) Simultaneous removal of NO x and soot particulate from diesel exhaust by in- situ catalytic generation and utilisation of N 2 O. Appl Catal B: Environ 239(x):10–15
Dhakad M, Rayalu SS, Kumar R, Doggali P, Bakardjieva S, Subrt J, Mitsuhashi T, Haneda H, Labhsetwar N (2008) Low cost, ceria promoted perovskite type catalysts for diesel soot oxidation. Catal Lett 121(1–2):137–143
Förster F, Crua C, Davy M, Ewart P (2019) Temperature measurements under diesel engine conditions using laser induced grating spectroscopy. Combust Flame 199:249–257
Fulan Z, Yujiao Z, Yihong X, Guohui CAI, Yong Z, Kemei WEI (2011) Sulfur resistance and activity of Pt / CeO2 -ZrO2 -La2O3 diesel oxidation catalysts. Chin J Catal 32(9):1469–1476
Glorius M, Markovits MA, Breitkopf C (2018) Design of specific acid-base-properties in CeO2-ZrO2-mixed oxides via templating and Au modification. Catalysts 8(9):358
Guillén-Hurtado N, García-García A, Bueno-López A (2015) Active oxygen by Ce-Pr mixed oxide nanoparticles outperform diesel soot combustion Pt catalysts. Appl Catal B 174–175(2):60–66
Han D, E J, Feng C, Han C, Kou C, Tan Y, Peng Y, Wei L (2024) Experimental and simulation investigation on the different iron content beta zeolite for controlling the cold-start hydrocarbon emission from a gasoline vehicle. Energy 294(March):130954
Heywood JB (2018) Internal combustion engine fundamentals. 2nd edn. New York: McGraw-Hill Education
Jeong DW, Na HS, Shim JO, Jang WJ, Roh HS (2015) A crucial role for the CeO 2–ZrO 2 support for the low temperature water gas shift reaction over Cu–CeO 2–ZrO 2 catalysts. Catal Sci Technol 5(7):3706–3713
Johnson TV, Transactions SSAE, Journal S, Fuels OF, Johnson TV (2007) Diesel emission control in review. J Fuels Lubricants 116:76–87
Khalil KMS (2007) Synthesis and characterization of mesoporous ceria/alumina nanocomposite materials via mixing of the corresponding ceria and alumina gel precursors. J Colloid Interface Sci 307(1):172–180
Koltsov I, Smalc-Koziorowska J, Prześniak-Welenc M, Małysa M, Kimmel G, McGlynn J, Stelmakh S (2018) Mechanism of reduced sintering temperature of Al2O3–ZrO2 nanocomposites obtained by microwave hydrothermal synthesis. Materials 11(5):829
Kumar K, Kumar N, Singh H (2017) Comprehensive review of three way catalytic converter. Ijariie-Issn 3(3):1197–1202
Machida M, Murata Y, Kishikawa K, Zhang D, Ikeue K (2008) On the reasons for high activity of CeO2 catalyst for soot oxidation. Chem Mater 20(13):4489–4494
Madier Y, Descorme C, Le Govic AM, Duprez D (1999) Oxygen mobility in CeO2 and CexZr (1–x) O2 compounds: study by CO transient oxidation and 18 O / 16 O isotopic exchange. J Phys Chem B 103:10999–11006
Maroušek J (2022a) Aluminum nanoparticles from liquid packaging board improve the competitiveness of (bio) diesel. Clean Technol Environ Policy 25(3):1–9
Maroušek J (2022b) Nanoparticles can change (bio) hydrogen competitiveness. Fuel 328:125318
Maroušek J, Gavurová B, Strunecký O, Maroušková A, Sekar M, Marek V (2023) Techno-economic identification of production factors threatening the competitiveness of algae biodiesel. Fuel 344:128056
Mierczynski P, Mierczynska A, Ciesielski R, Mosinska M, Nowosielska M, Czylkowska A, Maniukiewicz W, Szynkowska MI, Vasilev K (2018) High active and selective Ni/Ceo2 –Al2O3 and Pd–Ni/Ceo2 –Al2O3 catalysts for oxy-steam reforming of methanol. Catalysts 8(9):13–16
Modabberian A, Storm X, Shamekhi A-M, Vasudev A, Zenger K, Hyvönen J, Mikulski M (2024) Low temperature combustion modeling and predictive control of marine engines. Appl Sci 14(5):2033
Naeem M, Yan Z, Subhan F, Ullah A, Aslam S, Ibrahim M, Khan A (2020) Effective performance of CeO 2 based silica for preparation of octanal. J Porous Mater 27:1101–1108
Onn TM, Zhang S, Arroyo-Ramirez L, **a Y, Wang C, Pan X, Graham GW, Gorte RJ (2016) High-surface-area ceria prepared by ALD on Al2O3 support. Appl Catal B Environ 201:430–437
Piumetti M, Andana T, Bensaid S, Fino D, Russo N, Pirone R (2016) Ceria-based nanomaterials as catalysts for CO oxidation and soot combustion: effect of Zr-Pr do** and structural properties on the catalytic activity. AIChE J 63:216–225
Pukale KS, Digvijay M, Solage RD, Jadhav CC (2021) Investigation of three-way catalytic converter on stationary diesel engine. Russian Social Science Review 5:34–44
Reddy BM, Rao KN, Bharali P (2009) Copper promoted cobalt and nickel catalysts supported on ceria− alumina mixed oxide: structural characterization and CO oxidation activity. Ind Eng Chem Res 48(18):8478–8486
Sandaka BP, Kumar J (2023) Alternative vehicular fuels for environmental decarbonization: a critical review of challenges in using electricity, hydrogen, and biofuels as a sustainable vehicular fuel. Chem Eng J Adv 14(January):100442
Setiabudi A, Jiuling C (2004) CeO2 catalysed soot oxidation: the role of active oxygen to accelerate the oxidation conversion. Appl Catal B Environ Energy 51:9–19
Shukla MK, Dumaga K, Balyan Y, Bhaskar T, Dhar A (2021) Performance of Zr/CeO2-Al2O3 catalyst towards oxidation of diesel soot (No. 2021-28-0013). SAE Technical Paper
Shukla MK, Balyan Y, Kumar A, Bhaskar T, Dhar A (2022) Catalytic oxidation of soot by CeO2–ZrO2 catalysts: Role of Zr. Mater Chem Phys 286:126161
Sing K (2001) The use of nitrogen adsorption for the characterisation of porous materials. Colloids Surf, A: Physicochem Eng Aspects 187–188:3–9
Sun H, Liu Y, Li N, Tan J (2022) Study on characteristics and control strategy of diesel particulate filters based on engine bench. Processes 10(7):1–20
Tan W, **e S, Wang X, Wang C, Li Y, Shaw TE (2021) Highly efficient Pt catalyst on newly designed CeO2-ZrO2-Al2O3 support for catalytic removal of pollutants from vehicle exhaust. Chem Eng J 426:1–47
Tan Y, Kou C, E J, Feng C, Han D (2024) Effect of different exhaust parameters on conversion efficiency enhancement of a Pd–Rh three-way catalytic converter for heavy-duty natural gas engines. Energy 292(x):130483
Trueba M, Trasatti SP (2005) γ-alumina as a support for catalysts: a review of fundamental aspects. Eur J Inorg Chem 17:3393–3403
Uppara HP, Feroz A, John NS, Singh SK, Labhsetwar NK, Dasari H (2019) Soot oxidation studies on SrMn0.98B0.02O3 (B - Fe, Ni) Perovskites. IOP Conf Ser: Mater Sci Eng 654(0):1–6
Vochozka M, Horák J, Krulický T, Pardal P (2020a) Predicting future brent oil price on global markets. Acta Montanist Slovaca 25(3):375–392
Vochozka M, Rowland Z, Suler P, Marousek J (2020b) The influence of the international price of oil on the value of the EUR/USD exchange rate. J Compet 12(2):167–190
Wang X, Wang H, Maeda N, Baiker A (2019) Structure and catalytic behavior of alumina supported bimetallic au-rh nanoparticles in the reduction of NO by CO. Catalysts 9(11):937
Wei K, Cao X, Gu W, Liang P, Huang X, Zhang X (2019) Ni-induced C-Al2O3-framework (NiCAF) supported core-multi shell catalysts for efficient catalytic ozonation: a structure-to-performance study. Environ Sci Technol 53(12):6917–6926
Xu W, Kou C, E J, Feng C, Tan Y (2024) Effect analysis on the flow uniformity and pressure drop characteristics of the rotary diesel particulate filter for heavy-duty truck. Energy 288(September 2023):129820
Yang Z, Hu W, Zhang N, Li Y, Liao Y (2019) Facile synthesis of ceria–zirconia solid solutions with cubic–tetragonal interfaces and their enhanced catalytic performance in diesel soot oxidation. J Catal 377:98–109
Yu J, Kou C, Ma Y, E J, Feng C (2024) Effect analysis on hydrocarbon adsorption enhancement of different zeolites in cold start of gasoline engine based on Monte Carlo method. Energy 294(February):130738
Zhang Z, Liu H, Li Y, Ye Y, Tian J, Li J, Xu Y, Lv J (2024) Research and optimization of hydrogen addition and EGR on the combustion, performance, and emission of the biodiesel-hydrogen dual-fuel engine with different loads based on the RSM. Heliyon 10(1):e23389
Zhao X, Zuo H, Jia G (2022) Effect analysis on pressure sensitivity performance of diesel particulate filter for heavy-duty truck diesel engine by the nonlinear soot regeneration combustion pressure model. Energy 257:124766
Zhao X, Jiang J, Zuo H, Mao Z (2023) Performance analysis of diesel particulate filter thermoelectric conversion mobile energy storage system under engine conditions of low-speed and light-load. Energy 282(May):128411
Zuo H, Jiang J, Zhao X, Jia G (2023) Soot combustion characteristics of oxygen concentration and regeneration temperature effect on continuous pulsation regeneration in diesel particulate filter for heavy-duty truck. Energy 264(November 2022):126265
Funding
The authors declare that no external funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript. We thank CSIR-IIP for hel** us complete the research paper to its final stage.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Dr. Mritunjay Kumar Shukla: The author was responsible for Conceptualization, Methodology, and experimental analysis.
Ms. Vibhuti Bangwal: The author conducted data analysis, draft preparation, writing, and editing.
Dr. Atul Dhar: Experimental analysis and data curation for the experimental results.
Dr. Thallada Bhaskar: Concept and Design of Experiments
Mr. Adarsh Kumar: Synthesizing the catalyst required for the study and editing of the final draft prepared.
Later on, the conclusions were thoroughly discussed among all the authors, and hence, they are mentioned according to the views of all the authors. This is the total contribution and combined effort of all the above-mentioned authors to take this research paper to the final stage.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The manuscript entitled “Catalytic activity of Zr/CeO2-Al2O3 catalyst for diesel soot oxidation: synthesis, characterization, and performance evaluation” is submitted for consideration for publication in the Environmental Science and Pollution Research. This is to confirm that the research described in this manuscript did not involve human or animal participants and, therefore, did not require ethical approval from an ethics committee or institutional review board (IRB).
Consent to participate
All authors have agreed to the journal’s terms and conditions, which may cover aspects such as originality of the work, ethical considerations, copyright, and permissions for the publication. We confirm that all the authors voluntarily participated, had the opportunity to ask questions, and received satisfactory answers.
Consent for publication
We, the researchers of CSIR-IIP, agree on the submission and publication of the paper. The submitted work is original and has not been published before. We confirm that the content of the paper and all information provided in the manuscript are accurate to the best of our knowledge.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: George Z. Kyzas
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shukla, M.K., Bangwal, V., Dhar, A. et al. Catalytic activity of Zr/CeO2-Al2O3 catalyst for diesel soot oxidation: synthesis, characterization, and performance evaluation. Environ Sci Pollut Res (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-34052-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-34052-9