Abstract
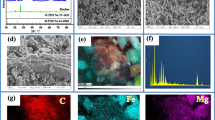
Development of carbon materials with high activity was important for rapid degradation of emerging pollutants. In this paper, a novel nanoscale zero-valent iron-copper bimetallic biochar (nZVIC-BC) was synthesized by carbothermal reduction of waste pine wood and copper-iron layered double hydroxides (LDHs). Characterization and analysis of its structural, elemental, crystalline, and compositional aspects using XRD, FT-IR, SEM, and TEM confirmed the successful preparation of nZVIC-BC and the high dispersion of Fe-Cu nanoparticles in an ordered carbon matrix. The experimental results showed that the catalytic activity of nZVIC-BC (Kobs of 0.0219 min−1) in the degradation of tetracycline (TC) in anoxic water environment was much higher than that of Fe-BC and Cu-BC; the effective degradation rate reached 85%. It was worth noting that the negative effects of Ca2+, Mg2+, and H2PO4− on TC degradation at ionic strengths greater than 15 mg/L were due to competition for active sites. Good stability and reusability were demonstrated in five consecutive cycle tests for low leaching of iron and copper. Combined with free radical quenching experiments and XPS analyses, the degradation of TC under air conditions was only 62%, with hydroxyl radicals (·OH) playing a dominant role. The synergistic interaction between Fe2+/Fe3+ and Cu0/Cu+/Cu2+ under nitrogen atmosphere enhances the redox cycling process; π-π adsorption, electron transfer processes, and active [H] were crucial for the degradation of TC; and possible degradation pathways of TC were deduced by LC-MS, which identified seven major aromatic degradation by-products. This study will provide new ideas and materials for the treatment of TC.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Burke V, Richter D, Greskowiak J (2016) Occurrence of antibiotics in surface and groundwater of a drinking water catchment area in Germany. Water Environ Res 88:652–659
Che MD, Chen ZG, Qiu S (2021) High chloroform removal using tannic acid to promote the activation of persulfate with Fe/Ni nanoparticles. Environ Chem Lett 19:4015–4020
Che MD, **ao JZ, Shan CC (2023) Efficient removal of chloroform from groundwater using activated percarbonate by cellulose nanofiber-supported Fe/Cu nanocomposites. Water Res 243:120420
Exall K, Balakrishnan VK, Toito J (2013) Impact of selected wastewater constituents on the removal of sulfonamide antibiotics via ultrafiltration and micellar enhanced ultrafiltration. Sci Total Environ 461-462:371–376
Fang G, Zhu C, Dionysiou DD (2015) Mechanism of hydroxyl radical generation from biochar suspensions: implications to diethyl phthalate degradation. Bioresour Technol 176:210–217
Gao FZ, Zou HY, Wu DL (2016) Swine farming elevated the proliferation of Acinetobacter with the prevalence of antibiotic resistance genes in the groundwater. Environ Int, 136, 105484.
Hua C, Ren, Dong (2011) Preparation of modified nanoscale zero-valent iron particles and its application in removal of tetracycline from wastewater. CJEE 5(4):767–771
Kandel R, Jang SR, Shrestha S (2021) A bimetallic load-bearing bioceramics of TiO2 @ ZrO2 integrated polycaprolactone fibrous tissue construct exhibits anti bactericidal effect and induces osteogenesis in MC3T3-E1 cells. Mater Sci Eng C 131:112501
Kaur M, Umar A, Mehta SK (2018) Reduced graphene oxide-CdS heterostructure: an efficient fluorescent probe for the sensing of Ag(I) and sunset yellow and a visible-light responsive photocatalyst for the degradation of levofloxacin drug in aqueous phase. Appl Catal B-Environ 245:143–158
Kim S, Eichhorn P, Jensen JN (2005) Removal of antibiotics in wastewater: effect of hydraulic and solid retention times on the fate of tetracycline in the activated sludge process. Environ Sci Technol 39:5816–5823
Kong L, Zhu Y, Liu M (2016) Conversion of Fe-rich waste sludge into nano-flake Fe-SC hybrid Fenton-like catalyst for degradation of AOII. Environ Pollut 216:568–574
Lee H, Lee HJ, Jeong J (2015) Activation of persulfates by carbon nanotubes: oxidation of organic compounds by nonradical mechanism. Chem Engi J 266:28–33
Lengliz S, Cheriet S, Raddaoui A (2022) Species distribution and genes encoding antimicrobial resistance in enterococcus spp. isolates from rabbits residing in diverse ecosystems: a new reservoir of linezolid and vancomycin resistance. J. Appl Microbiol 132(4):2760–2772
Li C, Wu J, Peng W (2019) Peroxymonosulfate activation for efficient sulfamethoxazole degradation by Fe3O4/β-FeOOH nanocomposites: coexistence of radical and non-radical reactions. Chem Eng J 356:904–914
Li L, Zhang Q, She Y (2021) High-efficiency degradation of bisphenol A by heterogeneous Mn–Fe layered double oxides through peroxymonosulfate activation: performance and synergetic mechanism. Separ Purif Technol 270:118770
Liu B, Liu Z, Yu P (2020) Enhanced removal of tris(2-chloroethyl) phosphate using a resin-based nanocomposite hydrated iron oxide through a Fenton-like process: capacity evaluation and pathways. Water Res 175:115655
Makowska N, Koczura R, Mokracka J (2016) Class 1 integrase, sulfonamide and tetracycline resistance genes in wastewater treatment plant and surface water. Chemosphere 144:1665–1673
Martins VV, Zanetti MOB, Pitondo-Silva A (2014) Aquatic environments polluted with antibiotics and heavy metals: a human health hazard. Sci Pollut Res 21:5873–5878
Meng X, Zhang C, Zhuang J (2020) Assessment of schwertmannite, jarosite and goethite as adsorbents for efficient adsorption of phenanthrene in water and the regeneration of spent adsorbents by heterogeneous fenton-like reaction. Chemosphere 244:125523
Peng XX, Wang ZN, Huang JF (2017) Efficient degradation of tetrabromobisphenol A by synergistic integration of Fe/Ni bimetallic catalysis and microbial acclimation. Water Res 122:471–480
Si Q, Guo W, Wang H (2021) Difunctional carbon quantum dots/g-C3N4 with in-plane electron buffer for intense tetracycline degradation under visible light: tight adsorption and smooth electron transfer. Appl Catal B-Environ 299:120694
Sunkara B, Zhan J, He J (2010) Nanoscale zerovalent iron supported on uniform carbon microspheres for the in situ remediation of chlorinated hydrocarbons. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2(10):2854–2862
Tian X, ** H, Nie Y (2017) Heterogeneous Fenton-like degradation of ofloxacin over a wide pH range of 3.6 to 10.0 over modified mesoporous iron oxide. Chem Eng J 328:397–405
Wang A, Jiang Y, Yan Y (2023) Mechanistic and quantitative profiling of electro-Fenton process for wastewater treatment. Water Res 235:119838
Watkinson AJ, Murby EJ, Costanzo SD (2007) Removal of antibiotics in conventional and advanced wastewater treatment: implications for environmental discharge and wastewater recycling. Water Res 41(18):4164–4176
Wen Z, Zhang Y, Dai C (2015) Nanocasted synthesis of magnetic mesoporous iron cerium bimetal oxides (MMIC) as an efficient heterogeneous Fenton-like catalyst for oxidation of arsenite. J Hazard Mater 287:225–233
Weng X, Lin S, Zhong Y (2013) Chitosan stabilized bimetallic Fe/Ni nanoparticles used to remove mixed contaminants-amoxicillin and Cd (II) from aqueous solutions. Chem Eng J 229(22):27–34
Xu K, Ben W, Ling W (2017) Impact of humic acid on the degradation of levofloxacin by aqueous permanganate: kinetics and mechanism. Water Res 123:67–74
Xu X, Huang H, Zhang Y (2018) Biochar as both electron donor and electron shuttle for the reduction transformation of Cr(VI) during its sorption. Environ Pollut 244:423–430
Yang J, Jiangdongwang L, Wennaxie A, **songyan Y (2019) Ultrahigh adsorption of tetracycline on willow branche-derived porous carbons with tunable pore structure: isotherm, kinetics, thermodynamic and new mechanism study. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 96:473–482
Yang Z, Lin Q, Zeng G (2023) Ternary hetero-structured BiOBr/Bi2MoO6@MXene composite membrane: construction and enhanced removal of antibiotics and dyes from water. J Membrane Sci 669:121329
Zhang L, Zeng G, Dong H, Chen Y, Zhang J, Yan M, Zhu Y, Yuan Y, **e Y, Huang Z (2017) The impact of silver nanoparticles on the co-composting of sewage sludge and agricultural waste: evolutions of organic matter and nitrogen. Bioresour Technol 230:132–139
Zhang Z, Huang X, Ma J (2021) NEfficient removal of bisphenol S by non-radical activation of peroxydisulfate in the presence of nano-graphite. Water Res 201(8):117288
Zhao LX, Li MH, Jiang HL (2022) Activation of peroxymono sulfate by a stable Co-Mg-Al LDO heterogeneous catalyst for the efficient degradation of ofloxacin. Separ Purif Technol 294:121231
Zhao Z, Zhang G, Zhang Y (2020) Fe3O4 accelerates tetracycline degradation during anaerobic digestion: synergistic role of adsorption and microbial metabolism. Water Res 185(1):116225
Zhuang Y, ** L, Luthy RG (2012) Kinetics and pathways for the debromination of polybrominated diphenyl ethers by bimetallic and nanoscale zerovalent iron: effects of particle properties and catalyst. Chemosphere 89(4):426–432
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52270079), Hunan Province Science and Technology Talents (2020TJ-N09), Chenzhou National Sustainable Development Agenda Innovation Demonstration Zone Innovation (2019sfq37), and Key Project of Hunan Provincial Education Department (21A0112).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Lingling Zhang (**angtan, Hunan 411105, P. R. China): investigation, data curation, formal analysis, writing — original draft. Yujiao Wang (**angtan, Hunan 411105, P. R. China): formal analysis; writing — original draft; writing — review and editing; validation. Yin Xu (**angtan, Hunan 411105, P. R. China): conceptualization; methodology; writing — review and editing; funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Weiming Zhang
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, ., Wang, Y. & Xu, Y. Highly efficient degradation of tetracycline in groundwater by nanoscale zero-valent iron-copper bimetallic biochar: active [H] attack and direct electron transfer mechanism. Environ Sci Pollut Res (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-33976-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-33976-6