Abstract
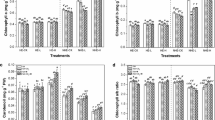
Phytoremediation using fast-growing woody plants assisted by plant growth-promoting bacteria (PGPB) on cadmium (Cd)–contaminated sites is considered a promising technique; however, its remediation efficiency is still affected by multiple factors. In this study, the mining areas’ soil conditions were simulated with different Cd addition levels (0, 3, 6, 9 mg kg−1) in order to investigate the response strategy to Cd stress of fast-growing economic tree species, slash pine (Pinus elliottii), and the effects of inoculation with the PGPB strain Herbaspirillum sp. YTG72 on the physiological activity and Cd accumulation of plants. The main results showed that there were significant (p < 0.05) increases in contents of chlorophyll and nutrient elements (P, K, Ca, and Mg) at low Cd addition level (3 mg kg−1) compared to non-Cd addition treatment. When the additive amount of Cd increased, the growth of plants was severely inhibited and the content of proline was increased, as well as Cd in plants. Besides, the ratios of K:P, Ca:P, and Mg:P in plants were negatively correlated with the contents of Cd in plants and soils. Inoculation of P. elliottii with the PGPB strain Herbaspirillum sp. YTG72 improved the physiological functions of the plants under Cd stress and activated the antioxidant system, reduced the accumulation of proline, and decreased the ratios of K:P, Ca:P, and Mg:P in plant. More importantly, planting P. elliottii in Cd-contaminated soil could significantly (p < 0.05) reduce the Cd content in the rhizosphere soil, and furthermore, inoculation treatment could promote the reduction of soil Cd content and increased the accumulation of Cd by root. The results of the present study emphasized the Cd response mechanism of P. elliottii based on multifaceted regulation, as well as the feasibility of strain Herbaspirillum sp. YTG72 assisted P. elliottii for the remediation on Cd-contaminated sites.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abbas S, Javed MT, Ali Q, Akram MS, Tanwir K, Ali S, Chaudhary HJ, Iqbal N (2021) Elucidating Cd-mediated distinct rhizospheric and in planta ionomic and physio-biochemical responses of two contrasting Zea mays L. cultivars. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 27:297–312. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-021-00936-0
Aebi H (1984) [13] Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126
Ali H, Khan E, Sajad MA (2013) Phytoremediation of heavy metals-concepts and applications. Chemosphere 91:869–881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.01.075
Ali J, Ali F, Ahmad I, Rafique M, Munis MFH, Hassan SW, Sultan T, Iftikhar M, Chaudhary HJ (2021) Mechanistic elucidation of germination potential and growth of Sesbania sesban seedlings with Bacillus anthracis PM21 under heavy metals stress: An in vitro study. Ecotox Environ Safe 208:111769. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111769
Baker AJM, Brooks RR (1989) Terrestrial higher plants which hyperaccumulate metallic elements. A review of their distribution, ecology and phytochemistry. Biorecovery 1:81–126
Bali AS, Sidhu GPS, Kumar V (2020) Root exudates ameliorate cadmium tolerance in plants: a review. Environ Chem Lett 18:1243–1275. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-020-01012-x
Bates LS, Waldren RP, Teare ID (1973) Rapid determination of proline for water stress studies. Plant Soil 39:305–307. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00018060
Begum N, Afzal S, Zhao HH, Lou LQ, Cai QS (2018) Shoot endophytic plant growth-promoting bacteria reduce cadmium toxicity and enhance switchgrass (Panicum virgatum L.) biomass. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 40:170. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-018-2737-1
Bruno LB, Anbuganesan V, Karthik C, Tripti Kumar A, Banu JR, Freitas H, Rajkumar M (2021) Enhanced phytoextraction of multi-metal contaminated soils under increased atmospheric temperature by bioaugmentation with plant growth promoting Bacillus cereus. J Environ Manag 289:112553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112553
Buysse J, Merckx R (1993) An improved colorimetric method to quantify sugar content of plant-tissue. J Exp Bot 44:1627–1629. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/44.10.1627
Carvalho MEA, Castro PRC, Kozak M, Azevedo RA (2020) The sweet side of misbalanced nutrients in cadmium-stressed plants. Ann Appl Biol 176:275–284. https://doi.org/10.1111/aab.12569
Chojnacka K, Chojnacki A, Gorecka H, Gorecki H (2005) Bloavailability of heavy metals from polluted soils to plants. Sci Total Environ 337:175–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2004.06.009
de la Luz Buendia-Valverde M, Gomez-Merino FC, Corona-Torres T, Cruz-Izquierdo S, Mateos-Nava RA, Trejo-Tellez LI (2022) Thallium differentially affects macronutrients concentration and stoichiometric ratios with nitrogen in the leaves of chili pepper varieties. Water Air Soil Pollut 233:201. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05671-0
Doerge DR, Divi RL, Churchwell MI (1997) Identification of the colored guaiacol oxidation product produced by peroxidases. Anal Biochem 250:10–17. https://doi.org/10.1006/abio.1997.2191
El Aafi N, Brhada F, Dary M, Maltouf AF, Pajuelo E (2012) Rhizostabilization of metals in soils using Lupinus luteus inoculated with the metal resistant rhizobacterium Serratia sp. MSMC541. Int J Phytoremediat 14:261–274. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2011.604693
El-Esawi MA, Elkelish A, Soliman M, Elansary HO, Zaid A, Wani SH (2020) Serratia marcescens BM1 enhances cadmium stress tolerance and phytoremediation potential of soybean through modulation of osmolytes, leaf gas exchange, antioxidant machinery, and stress-responsive genes expression. Antioxidants 9:43. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9010043
Eltahawy A, Awad EAM, Ibrahim AH, Merwad A, Desoky EM (2022) Integrative application of heavy metal-resistant bacteria, moringa extracts, and nano-silicon improves spinach yield and declines its contaminant contents on a heavy metal-contaminated soil. Front Plant Sci 13:1019014. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.1019014
Etesami H (2018) Bacterial mediated alleviation of heavy metal stress and decreased accumulation of metals in plant tissues: mechanisms and future prospects. Ecotox Environ Safe 147:175–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.08.032
Fu ZY, Wu FC, Mo CL, Deng QJ, Meng W, Giesy JP (2016) Comparison of arsenic and antimony biogeochemical behavior in water, soil and tailings from **kuangshan, China. Sci Total Environ 539:97–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.08.146
Guo Z, Yuan M, Ao Y (2009) Effect of cadmium on photosynthesis and nutrient elements uptake of Solanum nigrum L. seedlings. Ecol Environ Sci 18:824–829. https://doi.org/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2009.03.004. ((In Chinese))
Guo JK, Tang SR, Ju XH, Ding YZ, Liao SQ, Song NN (2011) Effects of inoculation of a plant growth promoting rhizobacterium Burkholderia sp D54 on plant growth and metal uptake by a hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii Hance grown on multiple metal contaminated soil. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 27:2835–2844. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-011-0762-y
Haider FU, Cai LQ, Coulter JA, Cheema SA, Wu J, Zhang RZ, Ma WJ, Farooq M (2021) Cadmium toxicity in plants: impacts and remediation strategies. Ecotox Environ Safe 211:111887. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111887
Hakeem KR, Alharby HF, Pirzadah TB (2022) Exogenously applied calcium regulates antioxidative system and reduces cadmium-uptake in Fagopyrum esculentum. Plant Physiol Biochem 180:17–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2022.03.011
Handa N, Kohli SK, Thukral AK, Bhardwaj R, Alyemeni MN, Wijaya L, Ahmad P (2018) Protective role of selenium against chromium stress involving metabolites and essential elements in Brassica juncea L. seedlings. 3 Biotech 8:66. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-018-1087-4
Hassan Z, Aarts MGM (2011) Opportunities and feasibilities for biotechnological improvement of Zn, Cd or Ni tolerance and accumulation in plants. Environ Exp Bot 72:53–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2010.04.003
Hossain MA, Piyatida P, Silva JATD, Fujita M (2012) Molecular mechanism of heavy metal toxicity and tolerance in plants: central role of glutathione in detoxification of reactive oxygen species and methylglyoxal and in heavy metal chelation. J Appl Microbiol 2012:872875. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/872875
Huang XC, Ho SH, Zhu SS, Ma F, Wu JT, Yang JX, Wang L (2017) Adaptive response of arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis to accumulation of elements and translocation in Phragmites australis affected by cadmium stress. J Environ Manag 197:448–455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.04.014
Huang Y, Wang LY, Wang WJ, Li TQ, He ZL, Yang XE (2019) Current status of agricultural soil pollution by heavy metals in China: a meta-analysis. Sci Total Environ 651:3034–3042. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.185
Ismael MA, Elyamine AM, Moussa MG, Cai MM, Zhao XH, Hu CX (2019) Cadmium in plants: uptake, toxicity, and its interactions with selenium fertilizers. Metallomics 11:255–277. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8mt00247a
Kan XQ, Dong YQ, Feng L, Zhou M, Hou HB (2021) Contamination and health risk assessment of heavy metals in China’s lead-zinc mine tailings: a meta-analysis. Chemosphere 267:128909. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128909
Konkolewska A, Piechalak A, Ciszewska L, Antos-Krzeminska N, Skrzypczak T, Hanc A, Sitko K, Malkowski E, Baralkiewicz D, Malecka A (2020) Combined use of companion planting and PGPR for the assisted phytoextraction of trace metals (Zn, Pb, Cd). Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:13809–13825. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-07885-3
Kumar H, Ishtiyaq S, Favas PJC, Varun M, Paul MS (2023) Effect of metal-resistant PGPB on the metal uptake, antioxidative defense, physiology, and growth of Atriplex lentiformis (Torr.) S.Wats. in soil contaminated with cadmium and nickel. J Plant Growth Regul 42:3868–3887. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-022-10853-5
Laureysens I, Blust R, De Temmerman L, Lemmens C, Ceulemans R (2004) Clonal variation in heavy metal accumulation and biomass production in a poplar coppice culture: I. Seasonal variation in leaf, wood and bark concentrations. Environ Pollut 131:485–494. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2004.02.009
Li XH, Zhou QX, Sun XY, Ren WJ (2016) Effects of cadmium on uptake and translocation of nutrient elements in different welsh onion (Allium fistulosum L.) cultivars. Food Chem 194:101–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.07.114
Li Y, Wang C, Yan C, Liu S, Chen X, Zeng M, Dong Y, Jiao R (2023a) Heavy metal concentrations and accumulation characteristics of dominant woody plants in iron and lead-zinc tailing areas in Jiangxi, Southeast China. Forests 14:846. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14040846
Li Y, Wei S, Chen X, Dong Y, Zeng M, Yan C, Hou L, Jiao R (2023b) Isolation of cadmium-resistance and siderophore-producing endophytic bacteria and their potential use for soil cadmium remediation. Heliyon 9:e17661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e17661
Liu ZL, He XY, Chen W (2011) Effects of cadmium hyperaccumulation on the concentrations of four trace elements in Lonicera japonica Thunb. Ecotoxicology 20:698–705. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-011-0609-1
Marmiroli M, Pietrini F, Maestri E, Zacchini M, Marmiroli N, Massacci A (2011) Growth, physiological and molecular traits in Salicaceae trees investigated for phytoremediation of heavy metals and organics. Tree Physiol 31:1319–1334. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/tpr090
Mir AR, Alam P, Hayat S (2022) Auxin regulates growth, photosynthetic efficiency and mitigates copper induced toxicity via modulation of nutrient status, sugar metabolism and antioxidant potential in Brassica juncea. Plant Physiol Biochem 185:244–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2022.06.006
Nawaz F, Ashraf MY, Ahmad R, Waraich EA, Shabbir RN, Bukhari MA (2015) Supplemental selenium improves wheat grain yield and quality through alterations in biochemical processes under normal and water deficit conditions. Food Chem 175:350–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.11.147
Ou C, Cheng WH, Wang ZL, Yao XM, Yang SM (2023) Exogenous melatonin enhances Cd stress tolerance in Platycladus orientalis seedlings by improving mineral nutrient uptake and oxidative stress. Ecotox Environ Safe 252:114619. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2023.114619
Pajevi S, Boriev M, Nikoli N, Arsenov DD, Upunski M (2016) Phytoextraction of heavy metals by fast-growing trees: a review. Phytoremediation 29–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-40148-5_2
Patra J, Lenka M, Panda BB (1994) Tolerance and CO-tolerance of the grass Chloris barbata Sw. to mercury, cadmium and zinc. New Phytol 128:165–171. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.1994.tb03999.x
Rengel Z, Bose J, Chen Q, Tripathi BN (2015) Magnesium alleviates plant toxicity of aluminium and heavy metals. Crop Pasture Sci 66:1298–1307. https://doi.org/10.1071/cp15284
Rochayati S, Du Laing G, Rinklebe J, Meissner R, Verloo M (2011) Use of reactive phosphate rocks as fertilizer on acid upland soils in Indonesia: accumulation of cadmium and zinc in soils and shoots of maize plants. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 174:186–194. https://doi.org/10.1002/jpln.200800309
Sabir A, Naveed M, Bashir MA, Hussain A, Mustafa A, Zahir ZA, Kamran M, Ditta A, Nunez-Delgado A, Saeed Q, Qadeer A (2020) Cadmium mediated phytotoxic impacts in Brassica napus: managing growth, physiological and oxidative disturbances through combined use of biochar and Enterobacter sp. MN17. J Environ Manag 265:110522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110522
Sangsuwan P, Prapagdee B (2021) Cadmium phytoremediation performance of two species of Chlorophytum and enhancing their potentials by cadmium-resistant bacteria. Environ Technol Innov 21:101311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2020.101311
Sardar R, Ahmed S, Shah AA, Yasin NA (2022) Selenium nanoparticles reduced cadmium uptake, regulated nutritional homeostasis and antioxidative system in Coriandrum sativum grown in cadmium toxic conditions. Chemosphere 287:132332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132332
Shah AA, Bibi F, Hussain I, Yasin NA, Akram W, Tahir MS, Ali HM, Salem MZM, Siddiqui MH, Danish S, Fahad S, Datta R (2020) Synergistic effect of Bacillus thuringiensis IAGS 199 and putrescine on alleviating cadmium-Induced phytotoxicity in Capsicum annum. Plants-Basel 9:1512. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9111512
Shahid M, Javed MT, Masood S, Akram MS, Azeem M, Ali Q, Gilani R, Basit F, Abid A, Lindberg S (2019) Serratia sp. CP-13 augments the growth of cadmium (Cd)-stressed Linum usitatissimum L. by limited Cd uptake, enhanced nutrient acquisition and antioxidative potential. J Appl Microbiol 126:1708–1721. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.14252
Shahid M, Javed MT, Tanwir K, Akram MS, Tazeen SK, Saleem MH, Masood S, Mujtaba S, Chaudhary HJ (2020) Plant growth-promoting Bacillus sp. strain SDA-4 confers Cd tolerance by physio-biochemical improvements, better nutrient acquisition and diminished Cd uptake in Spinacia oleracea L. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 26:2417–2433. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-020-00900-4
Smith PK, Krohn RI, Hermanson GT, Mallia AK, Gartner FH, Provenzano MD, Fujimoto EK, Goeke NM, Olson BJ, Klenk DC (1985) Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Biochem 150:76–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7
Sterckeman T, Redjala T, Morel JL (2011) Influence of exposure solution composition and of plant cadmium content on root cadmium short-term uptake. Environ Exp Bot 74:131–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2011.05.010
Tanveer Y, Jahangir S, Shah ZA, Yasmin H, Nosheen A, Hassan MN, Illyas N, Bajguz A, El-Sheikh MA, Ahmad P (2023) Zinc oxide nanoparticles mediated biostimulant impact on cadmium detoxification and in silico analysis of zinc oxide-cadmium networks in Zea mays L. regulome. Environ Pollut 316:120641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.120641
Wang Y, Liu C, Zhou D, Chen H (2014) A critical view on the status quo of the farmland soil environmental quality in China: Discussion and suggestion of relevant issues on report on the national general survey of soil contamination. J Agro-Environ Sci 33:1465–1473. https://doi.org/10.11654/jaes.2014.08.001. ((In Chinese))
Wang M, Sheng G, Wang R (2021a) Progress in disposal technologies for plants polluted with heavy metals after phytoextraction. J Agric Resour Environ 38:151–159. https://doi.org/10.13254/j.jare.2020.0756. ((In Chinese))
Wang SF, Volk TA, Xu J (2021b) Variability in growth and cadmium accumulation capacity among willow hybrids and their parents: implications for yield-based selection of Cd-efficient cultivars. J Environ Manag 299:113643. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113643
Wellburn AR (1994) The spectral determination of chlorophylls a and b, as well as total carotenoids, using various solvents with spectrophotometers of different resolution. J Plant Physiol 144:307–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0176-1617(11)81192-2
Wu G (2008) Effects of cadmium on the growth, physiological and ecological characteristics of peanut seedling. J Biol 25:31–33 ((In Chinese))
**n JP, Ma SS, Li Y, Zhao C, Tian RN (2020) Pontederia cordata, an ornamental aquatic macrophyte with great potential in phytoremediation of heavy-metal-contaminated wetlands. Ecotox Environ Safe 203:111024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111024
Yang LP, Zhu J, Wang P, Zeng J, Tan R, Yang YZ, Liu ZM (2018) Effect of Cd on growth, physiological response, Cd subcellular distribution and chemical forms of Koelreuteria paniculata. Ecotox Environ Safe 160:10–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.05.026
Zeng P, Guo ZH, **ao XY, Cao X, Peng C (2018) Response to cadmium and phytostabilization potential of Platycladus orientalis in contaminated soil. Int J Phytoremediat 20:1337–1345. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2018.1501338
Zeng P, Guo ZH, **ao XY, Peng C, Liu LQ, Yan DM, He YL (2020) Physiological stress responses, mineral element uptake and phytoremediation potential of Morus alba L. in cadmium-contaminated soil. Ecotox Environ Safe 189:109973. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109973
Zhang J, Cui W, Jiao X, Zhang Q (2011) Effect of low concentration cadmium on the growth and accumulation of nutrient elements in pakchoi. Acta Agric. Univ. Jiangxiensis 33:22–28. https://doi.org/10.13836/j.jjau.2011005. ((In Chinese))
Zhang M, ** ZH, Zhang X, Wang GL, Li R, Qu JN, ** Y (2020) Alleviation of Cd phytotoxicity and enhancement of rape seedling growth by plant growth-promoting bacterium Enterobacter sp. Zm-123. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:33192–33203. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09558-7
Zhang GY, Zhang X, Yu SJ, Sun HG (2022) Novel insights on genes and pathways involved in Pinus elliottii response to resinosis. Tree Physiol. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/tpac118
Zhou JH, Cheng K, Zheng JY, Liu ZQ, Shen WB, Fan HB, ** ZN (2019) Physiological and biochemical characteristics of Cinnamomum camphora in response to Cu- and Cd-contaminated soil. Water Air Soil Pollut 230:15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-4048-y
Zhou JY, Li P, Meng DL, Gu YB, Zheng ZY, Yin HQ, Zhou QM, Li J (2020) Isolation, characterization and inoculation of Cd tolerant rice endophytes and their impacts on rice under Cd contaminated environment. Environ Pollut 260:113990. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.113990
Acknowledgements
Thanks for the technical support provided by the Chinese Academy of Forestry.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yanglong Li: investigation, data curation, formal analysis, methodology, writing—original draft. **angteng Chen: investigation, formal analysis. Yuhong Dong: methodology, writing—review and editing. Shumeng Wei: formal analysis. Mansheng Zeng: resources. Ruzhen Jiao: conceptualization, supervision, writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors read and approved the final manuscript. The work described has not been published. It is not under consideration for publication elsewhere. Its publication has been approved by all coauthors. If the manuscript is accepted for publication, the authors agree to automatic transfer of the copyright to the publisher.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Gangrong Shi
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Chen, X., Dong, Y. et al. Response strategies of slash pine (Pinus elliottii) to cadmium stress and the gain effects of inoculation with Herbaspirillum sp. YTG72 in alleviating phytotoxicity and enhancing accumulation of cadmium. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 31590–31604 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-33353-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-33353-3